AI Insights
WMO supports Artificial Intelligence forecasting pilot in Africa
Use of AI in meteorological modelling has recently demonstrated the ability to produce state-of-the-art predictions with relatively small computational power. Thus, there is growing interest in leveraging AI technology to help countries without sophisticated super-computers to “leapfrog” to the latest most advanced prediction systems.
WMO’s Executive Council recently set up a new Joint Advisory Council on Artificial Intelligence to inform WMO activities and to balance opportunities and challenges.
WMO is therefore excited about a new pilot project in Malawi, with funding from the Climate Risk and Early Warning Systems (CREWS) initiative. It will test the ground in leveraging a state-of-the-art AI-based Weather Prediction (AI-WP) system to improve the accuracy, timeliness, and accessibility of weather predictions in Malawi.
It aims to empower Malawi’s Department of Climate Change and Meteorological Services (DCCMS) to build operational capacity in AI-WP and early warning provision, and to evaluate how an AI-WP system can help in closing critical capacity gaps in Malawi and more generally in Least Developed Countries and Small Island Developing States.
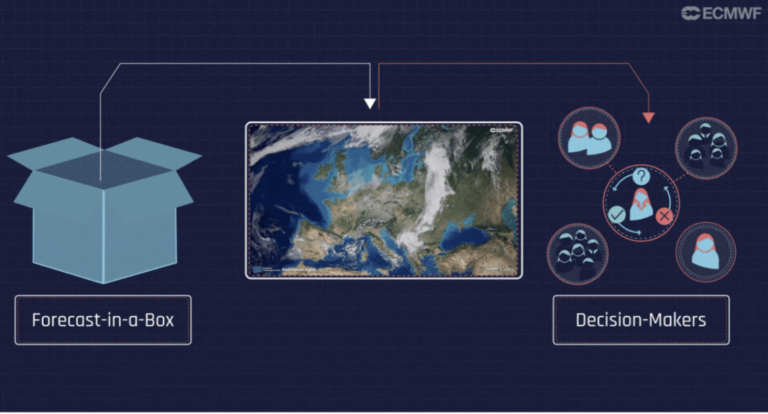
The project builds on a high-resolution data-driven weather forecasting model named Bris developed by MET-Norway and the “forecast-in-a-box” concept developed by the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF).
Through this pilot, meteorologists in Malawi will gain hands-on experience running AI-enabled forecasts locally, assessing their operational feasibility, forecast skill, and potential to support timely early warnings for high-impact weather events.
Malawi – like many African Least Developed countries – is highly vulnerable to climate-related hazards. Its early warning systems face significant gaps due to limited observational infrastructure, constrained human resources, and outdated forecasting systems.
“We firmly believe this initiative represents a strategic opportunity to strengthen Malawi’s early warning infrastructure, deliver actionable insights, and support long-term capacity development for our forecasting staff,” said Lucy Mtilatila, director for Climate Change and Meteorological Services and permanent representative of Malawi to WMO.
The project – which combines Norway’s AI expertise with Malawi’s local knowledge and data – was presented by Roar Skålin, permanent representative of Norway to WMO at the High-Level Open Consultative Platform on AI during the week of the WMO Executive Council.
Forecast-in-a-Box
It is being launched in collaboration with the European Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasing (ECMWF) which is developing early prototypes of Artificial Intelligence/Integrated Forecasting System (AIFS) packaged as a Forecast-in-a-Box as part of the AI-driven solutions of the Digital Twin Engine and the Destination Earth initiative of the European Commission.
Data-driven models such as ECMWF’s AIFS and MET Norway’s Bris are fundamentally different from traditional numerical weather prediction systems. They are lighter, faster, and more portable, making them well suited to run outside large high-performance computing (HPC) infrastructures.
This set-up enables to run forecasts closer to where the data is needed, offering key benefits:
- Users can tailor the forecasting pipeline to their specific needs.
- Improved responsiveness and timeliness.
- Deployment across a range of environments.
- No deep expertise in system setup or infrastructure is needed.
WMO Integrated Processing and Prediction System
Despite the huge possibilities, there question marks about the capability of AI to support forecasts and warnings of local high-impact weather and water hazards. The WMO’s Executive Council therefore requested the development of technical guidelines on the use of AI-based technologies and how incorporate AI into the WMO Integrated Processing and Prediction System (WIPPS). This is the worldwide network of operational centres of WMO’s Members and is the backbone of all forecasting.
The planned Joint Advisory Group will be a coordination mechanism among WMO’s Infrastructure and Services Commissions, Research Board and other relevant WMO bodies. It will include experts from the public, private and academic sectors and will steer joint efforts to explore the opportunities and challenges of AI/ML technology.
AI Insights
Pittsburgh’s AI summit: five key takeaways

The push for artificial intelligence-related investments in Western Pennsylvania continued Thursday with a second conference that brought together business leaders and elected officials.
Not in attendance this time was President Donald Trump, who headlined a July 15 celebration of AI opportunity at Carnegie Mellon University.
This time Gov. Josh Shapiro, U.S. Sen. David McCormick and others converged in Bakery Square in Larimer to emphasize emerging public-private initiatives in anticipation of growing data center development and other artificial intelligence-related infrastructure including power plants.
Here’s what speakers and attendees at the summit were saying.
AI is not a fad
As regional leaders and business investors consider their options, BNY Mellon’s CEO Robin Vince cautioned against not taking AI seriously.
“The way to get left behind in the next 10 years is to not care about AI,” Vince said
“AI is transforming everything,” said Selin Song during Thursday’s event. As president of Google Customer Solutions, Song said that the company’s recent investment of $25 million across the Pennsylvania-Jersey-Maryland grid will help give AI training access to the more than 1 million small businesses in the state.
Google isn’t the only game in town
Shapiro noted that Amazon recently announced plans to spend at least $20 billion to establish multiple high-tech cloud computing and AI innovation campuses across the state.
“This is a generational change,” Shapiro said, calling it the largest private sector investment in Pennsylvania’s history. “This is our next chapter in innovative growth. It all fits together. This new investment is beyond data center 1.0 that we saw in Virginia.”
Fracking concerns elevated
With all of the plans for new power-hungry data centers, some are concerned that the AI push will create more environmental destruction. Outside the summit, Food & Water Watch Pennsylvania cautioned that the interest in AI development is a “Trojan horse” for more natural gas fracking. Amid President Donald Trump’s attempts to dismantle wind and solar power, alternatives to natural gas appear limited.
Nuclear ready for its moment
But one possible alternative was raised at the AI conference by Westinghouse Electric Company’s interim CEO Dan Summer.
The Pittsburgh-headquartered organization is leading a renewed interest in nuclear energy with plans to build a number of its AP 1000 reactors to help match energy needs and capabilities.
Summer said that the company is partnering with Google, allowing them to leverage Google’s AI capabilities “with our nuclear operations to construct new nuclear here.”
China vs. ‘heroes’
Underlying much of the AI activity: concerns with China’s work in this field
“With its vast resources, enormous capital, energy, workforce, the Chinese government is leveraging its resources to beat the United States in AI development,” said Nazak Nikakhtar, a national security and international trade attorney who chaired one of the panels Thursday.

Speaking to EQT’s CEO Toby Rice and Groq executive Ian Andrews, Nikakhtar outlined some of the challenges she saw in U.S. development of AI technology compared to China.
“We are attempting to leverage, now, our own resources, albeit in some respects much more limited vis-a-vis what China has, to accelerate AI leadership here in the United States and beat China,” she said. “But we’re somewhat constrained by the resources we have, by our population, by workforce, capital.”
Rice said in response that the natural resources his company is extracting will help power the country’s ability to compete with China.
Rice drew a link between the 9/11 terror attacks 24 years earlier and the “urgency” of competing with China in AI.
“People are looking to take down American economies,” Rice said. “And we have heroes. Never forget. And I do believe that us winning this race against China in AI is going to be one of the most heroic things we’re going to do.”
Eric Jankiewicz is PublicSource’s economic development reporter and can be reached at ericj@publicsource.org or on Twitter @ericjankiewicz.
AI Insights
Commanders vs. Packers props, SportsLine Machine Learning Model AI picks, bets: Jordan Love Over 223.5 yards

The NFL Week 2 schedule gets underway with a Thursday Night Football matchup between NFC playoff teams from a year ago. The Washington Commanders battle the Green Bay Packers beginning at 8:15 p.m. ET from Lambeau Field. Second-year quarterback Jayden Daniels led the Commanders to a 21-6 opening-day win over the New York Giants, completing 19 of 30 passes for 233 yards and one touchdown. Jordan Love, meanwhile, helped propel the Packers to a dominating 27-13 win over the Detroit Lions in Week 1. He completed 16 of 22 passes for 188 yards and two touchdowns.
NFL prop bettors will likely target the two young quarterbacks with NFL prop picks, in addition to proven playmakers like Deebo Samuel, Romeo Doubs and Zach Ertz. Green Bay’s Jayden Reed has been dealing with a foot injury, but still managed to haul in a touchdown pass in the opener, while Austin Ekeler (shoulder) does not carry an injury designation for TNF. The Packers enter as a 3-point favorite with Green Bay at -172 on the money line, while the over/under is 49 points. Before betting any Commanders vs. Packers props for Thursday Night Football, you need to see the Commanders vs. Packers prop predictions powered by SportsLine’s Machine Learning Model AI.
Built using cutting-edge artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques by SportsLine’s Data Science team, AI Predictions and AI Ratings are generated for each player prop.
For Packers vs. Commanders NFL betting on Monday Night Football, the Machine Learning Model has evaluated the NFL player prop odds and provided Commanders vs. Packers prop picks. You can only see the Machine Learning Model player prop predictions for Washington vs. Green Bay here.
Top NFL player prop bets for Commanders vs. Packers
After analyzing the Commanders vs. Packers props and examining the dozens of NFL player prop markets, the SportsLine’s Machine Learning Model says Packers quarterback Love goes Over 223.5 passing yards (-112 at FanDuel). Love passed for 224 or more yards in eight games a year ago, despite an injury-filled season. In 15 regular-season games in 2024, he completed 63.1% of his passes for 3,389 yards and 25 touchdowns with 11 interceptions. Additionally, Washington allowed an average of 240.3 passing yards per game on the road last season.
In a 30-13 win over the Seattle Seahawks on Dec. 15, he completed 20 of 27 passes for 229 yards and two touchdowns. Love completed 21 of 28 passes for 274 yards and two scores in a 30-17 victory over the Miami Dolphins on Nov. 28. The model projects Love to pass for 259.5 yards, giving this prop bet a 4.5 rating out of 5. See more NFL props here, and new users can also target the FanDuel promo code, which offers new users $300 in bonus bets if their first $5 bet wins:
How to make NFL player prop bets for Washington vs. Green Bay
In addition, the SportsLine Machine Learning Model says another star sails past his total and has nine additional NFL props that are rated four stars or better. You need to see the Machine Learning Model analysis before making any Commanders vs. Packers prop bets for Thursday Night Football.
Which Commanders vs. Packers prop bets should you target for Thursday Night Football? Visit SportsLine now to see the top Commanders vs. Packers props, all from the SportsLine Machine Learning Model.
AI Insights
Adobe Says Its AI Sales Are Coming in Strong. But Will It Lift the Stock?

Adobe (ADBE) just reported record quarterly revenue driven by artificial intelligence gains. Will it revive confidence in the stock?
The creative software giant late Thursday posted adjusted earnings per share of $5.31 on revenue that jumped 11% year-over-year to a record $5.99 billion in the fiscal third quarter, above analysts’ estimates compiled by Visible Alpha, as AI revenues topped company targets.
CEO Shantanu Narayen said that with the third-quarter’s revenue driven by AI, Adobe has already surpassed its “AI-first” revenue goals for the year, leading the company to boost its outlook. The company said it now anticipates full-year adjusted earnings of $20.80 to $20.85 per share and revenue of $23.65 billion to $23.7 billion, up from adjusted earnings of $20.50 to $20.70 on revenue of $23.50 billion to $23.6 billion previously.
Shares of Adobe were recently rising in late trading. But they’ve had a tough year so far, with the stock down more than 20% for 2025 through Thursday’s close amid worries about the company’s AI progress and growing competition.
Wall Street is optimistic. The shares finished Thursday a bit below $351, and the mean price target as tracked by Visible Alpha, above $461, represents a more than 30% premium. Most of the analysts tracking the stock have “buy” ratings.
But even that target represents a degree of caution in the context of recent highs. The shares were above $600 in February 2024.
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoThe Guardian view on Trump and the Fed: independence is no substitute for accountability | Editorial
-
Tools & Platforms1 month ago
Building Trust in Military AI Starts with Opening the Black Box – War on the Rocks
-

 Ethics & Policy2 months ago
Ethics & Policy2 months agoSDAIA Supports Saudi Arabia’s Leadership in Shaping Global AI Ethics, Policy, and Research – وكالة الأنباء السعودية
-

 Events & Conferences4 months ago
Events & Conferences4 months agoJourney to 1000 models: Scaling Instagram’s recommendation system
-

 Jobs & Careers2 months ago
Jobs & Careers2 months agoMumbai-based Perplexity Alternative Has 60k+ Users Without Funding
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoHappy 4th of July! 🎆 Made with Veo 3 in Gemini
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoMacron says UK and France have duty to tackle illegal migration ‘with humanity, solidarity and firmness’ – UK politics live | Politics
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoVEX Robotics launches AI-powered classroom robotics system
-

 Funding & Business2 months ago
Funding & Business2 months agoKayak and Expedia race to build AI travel agents that turn social posts into itineraries
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoOpenAI 🤝 @teamganassi





















