Tools & Platforms
With dawn of AI, talk of tech and religion merge for some
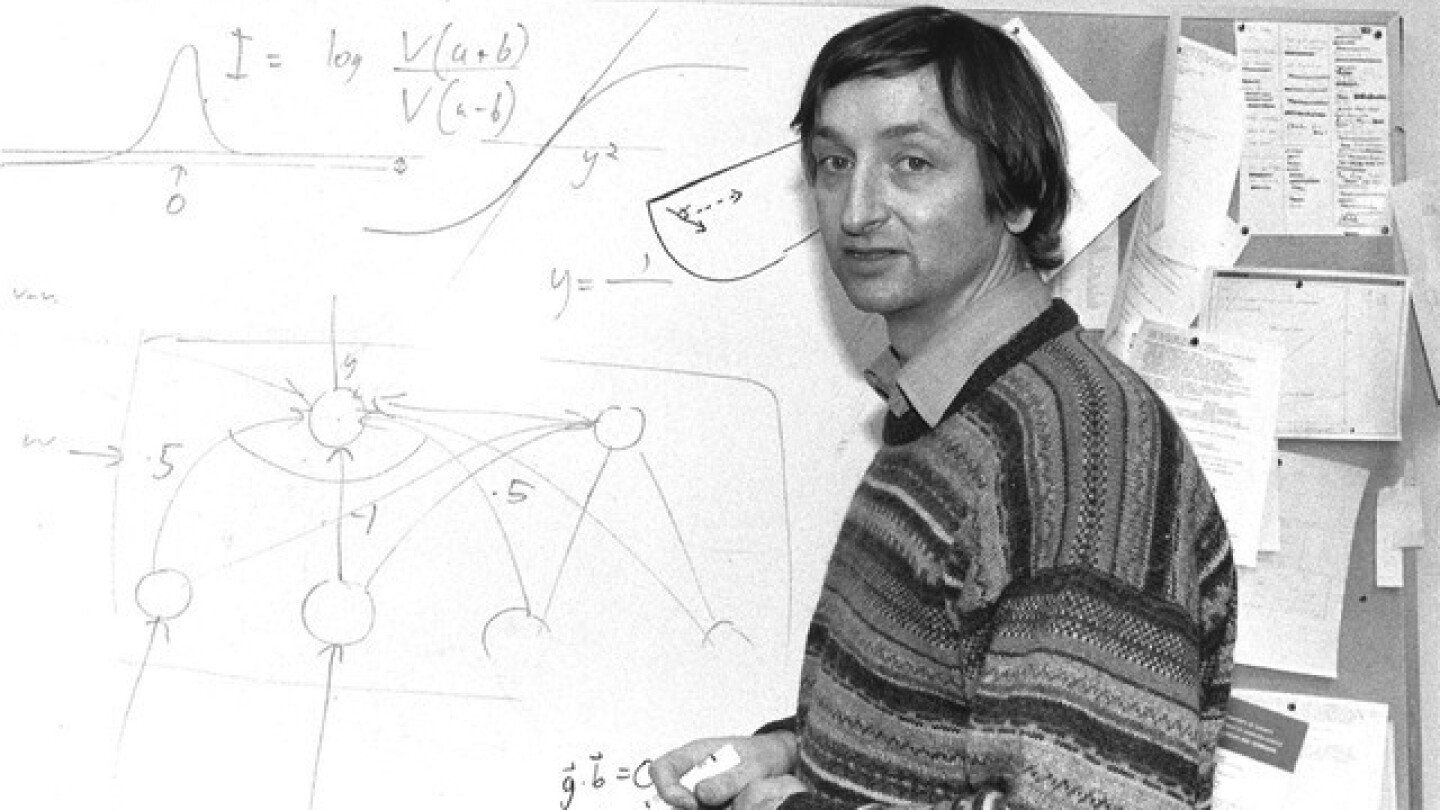
TORONTO (AP) — At 77 years old, Geoffrey Hinton has a new calling in life. Like a modern-day prophet, the Nobel Prize winner is raising alarms about the dangers of uncontrolled and unregulated artificial intelligence.
Frequently dubbed the “Godfather of AI,” Hinton is known for his pioneering work on deep learning and neural networks which helped lay the foundation for the AI technology often used today. Feeling “somewhat responsible,” he began speaking publicly about his concerns in 2023 after he left his job at Google, where he worked for more than a decade.
As the technology — and investment dollars — powering AI have advanced in recent years, so too have the stakes behind it.
“It really is godlike,” Hinton said.
Hinton is among a growing number of prominent tech figures who speak of AI using language once reserved for the divine. OpenAI CEO Sam Altman has referred to his company’s technology as a “magic intelligence in the sky,” while Peter Thiel, the co-founder of PayPal and Palantir, has even argued that AI could help bring about the Antichrist.
Will AI bring condemnation or salvation?
There are plenty of skeptics who doubt the technology merits this kind of fear, including Dylan Baker, a former Google employee and lead research engineer at the Distributed AI Research Institute, which studies the harmful impacts of AI.
“I think oftentimes they’re operating from magical fantastical thinking informed by a lot of sci-fi that presumably they got in their formative years,” Baker said. “They’re really detached from reality.”
Although chatbots like ChatGPT only recently penetrated the zeitgeist, certain Silicon Valley circles have prophesied of AI’s power for decades.
“We’re trying to wake people up,” Hinton said. “To get the public to understand the risks so that the public pressures politicians to do something about it.”
While researchers like Hinton are warning about the existential threat they believe AI poses to humanity, there are CEOs and theorists on the other side of the spectrum who argue we are approaching a kind of technological apocalypse that will usher in a new age of human evolution.
In an essay published last year titled “Machines of Loving Grace: How AI Could Transform the World for the Better,” Anthropic CEO Dario Amodei lays out his vision for a future “if everything goes right with AI.”
The AI entrepreneur predicts “the defeat of most diseases, the growth in biological and cognitive freedom, the lifting of billions of people out of poverty to share in the new technologies, a renaissance of liberal democracy and human rights.”
While Amodei opts for the phrase “powerful AI,” others use terms like “the singularity” or “artificial general intelligence (AGI).” Though proponents of these concepts don’t often agree on how to define them, they refer broadly to a hypothetical future point at which AI will surpass human-level intelligence, potentially triggering rapid, irreversible changes to society.
Computer scientist and author Ray Kurzweil has been predicting since the 1990s that humans will one day merge with technology, a concept often called transhumanism.
“We’re not going to actually tell what comes from our own brain versus what comes from AI. It’s all going to be embedded within ourselves. And it’s going to make ourselves more intelligent,” Kurzweil said.
In his latest book, “The Singularity Is Nearer: When We Merge with AI,” Kurzweil doubles down on his earlier predictions. He believes that by 2045 we will have “multiplied our own intelligence a millionfold.”
“Yes,” he eventually conceded when asked if he considers AI to be his religion. It informs his sense of purpose.
“My thoughts about the future and the future of technology and how quickly it’s coming definitely affects my attitudes towards being here and what I’m doing and how I can influence other people,” he said.
Visions of the apocalypse bubble up
Despite Thiel’s explicit invocation of language from the Book of Revelation, the positive visions of an AI future are more “apocalyptic” in the historical sense of the word.
“In the ancient world, apocalyptic is not negative,” explains Domenico Agostini, a professor at the University of Naples L’Orientale who studies ancient apocalyptic literature. “We’ve completely changed the semantics of this word.”
The term “apocalypse” comes from the Greek word “apokalypsis,” meaning “revelation.” Although often associated today with the end of the world, apocalypses in ancient Jewish and Christian thought were a source of encouragement in times of hardship or persecution.
“God is promising a new world,” said Professor Robert Geraci, who studies religion and technology at Knox College. “In order to occupy that new world, you have to have a glorious new body that triumphs over the evil we all experience.”
Geraci first noticed apocalyptic language being used to describe AI’s potential in the early 2000s. Kurzweil and other theorists eventually inspired him to write his 2010 book, “Apocalyptic AI: Visions of Heaven in Robotics, Artificial Intelligence, and Virtual Reality.”
The language reminded him of early Christianity. “Only we’re gonna slide out God and slide in … your pick of cosmic science laws that supposedly do this and then we were going to have the same kind of glorious future to come,” he said.
Geraci argues this kind of language hasn’t changed much since he began studying it. What surprises him is how pervasive it has become.
“What was once very weird is kind of everywhere,” he said.
Has Silicon Valley finally found its God?
One factor in the growing cult of AI is profitability.
“Twenty years ago, that fantasy, true or not, wasn’t really generating a lot of money,” Geraci said. Now, though, “there’s a financial incentive to Sam Altman saying AGI is right around the corner.”
But Geraci, who argues ChatGPT “isn’t even remotely, vaguely, plausibly conscious,” believes there may be more driving this phenomenon.
Historically, the tech world has been notoriously devoid of religion. Its secular reputation had so preceded it that one episode of the satirical HBO comedy series, “Silicon Valley,” revolves around “outing” a co-worker as Christian.
Rather than viewing the skeptical tech world’s veneration of AI as ironic, Geraci believes they’re causally linked.
“We human beings are deeply, profoundly, inherently religious,” he said, adding that the impressive technologies behind AI might appeal to people in Silicon Valley who have already pushed aside “ordinary approaches to transcendence and meaning.”
No religion is without skeptics
Not every Silicon Valley CEO has been converted — even if they want in on the tech.
“When people in the tech industry talk about building this one true AI, it’s almost as if they think they’re creating God or something,” Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg said on a podcast last year as he promoted his company’s own venture into AI.
Although transhumanist theories like Kurzweil’s have become more widespread, they are still not ubiquitous within Silicon Valley.
“The scientific case for that is in no way stronger than the case for a religious afterlife,” argues Max Tegmark, a physicist and machine learning researcher at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Like Hinton, Tegmark has been outspoken about the potential risks of unregulated AI. In 2023, as president of the Future of Life Institute, Tegmark helped spearhead an open letter calling for powerful AI labs to “immediately pause” the training of their systems.
The letter collected more than 33,000 signatures, including from Elon Musk and Apple co-founder Steve Wozniak. Tegmark considers the letter to have been successful because it helped “mainstream the conversation” about AI safety, but believes his work is far from over.
With regulations and safeguards, Tegmark thinks AI can be used as a tool to do things like cure diseases and increase human productivity. But it is imperative, he argues, to stay away from the “quite fringe” race that some companies are running — “the pseudoreligious pursuit to try to build an alternative God.”
“There are a lot of stories, both in religious texts and in, for example, ancient Greek mythology, about how when we humans start playing gods, it ends badly,” he said. “And I feel there’s a lot of hubris in San Francisco right now.”
___
Associated Press religion coverage receives support through the AP’s collaboration with The Conversation US, with funding from Lilly Endowment Inc. The AP is solely responsible for this content.
Tools & Platforms
Understanding Ghanaian STEM Students’ AI Learning Intentions

In recent years, the field of education has undergone a remarkable transformation, particularly with the rise of technology and artificial intelligence (AI). Amidst this evolution, a pressing question emerges: how do we foster an environment conducive for students to embrace AI technology, particularly in the context of Ghana? The research conducted by Abreh, Arthur, Akwetey, and their colleagues aims to unravel this very question, delving deep into STEM students’ intentions to learn about AI through a comprehensive modeling approach utilizing Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) and fuzzy set Qualitative Comparative Analysis (fsQCA).
The study focuses primarily on Ghana’s educational landscape, where the integration of AI into the curriculum presents new opportunities as well as challenges. The authors argue that understanding the factors influencing students’ intention to learn AI is crucial for policymakers and educators aiming to enhance the educational experience and job readiness of future generations. In an era defined by digital progression, an examination of student motivations and aspirations is not only relevant but essential in shaping the future of education in Ghana and beyond.
By employing the PLS-SEM approach, the researchers parsed through various dimensions, including individual characteristics, social influences, and perceived educational effectiveness, to determine how these factors impact students’ willingness to engage with AI. The data generated by this method offers a robust mechanism to visualize complex interrelations that traditional research methods might overlook. Importantly, PLS-SEM serves as a powerful tool to facilitate an understanding of both direct and indirect influences on students’ learning intentions.
In conjunction with PLS-SEM, the application of fsQCA provided an innovative lens through which to evaluate the heterogeneous nature of student populations. This method recognizes that varying combinations of factors can lead to the same outcome—in this case, the intention to learn AI. The researchers found that while certain commonalities existed among students, unique pathways also emerged depending on individual backgrounds, learning environments, and available resources. This nuanced understanding allows educators to craft tailored interventions that meet diverse learner needs.
Ghana’s demographic landscape presents both advantages and hurdles in increasing students’ interest in AI. The nation is youthful, with a significant percentage of the population being students. Capitalizing on this demographic dividend requires systematic educational reforms that align with the global demand for AI competency. By showcasing the vast potentials of AI, classrooms can become incubators for innovation where students are not only passive recipients of knowledge but active creators of technology.
The research highlights that students often struggle with understanding what AI entails and its relevance to their future careers. There is a gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application. To address this divide, educational institutions must incorporate hands-on learning experiences that engage students with real-world AI applications. Workshops, internships, and collaborative projects could serve as catalysts for interest and excitement in AI studies.
Moreover, the role of peer influence cannot be understated. The study underscores the importance of social interactions in shaping attitudes toward learning AI. Mentorship programs and peer-led initiatives can provide a supportive atmosphere wherein students encourage one another to delve deeper into AI topics. Creating a collaborative rather than competitive learning environment enhances motivation and retention of knowledge.
Further, the researchers found that exposure to technology and AI-related content significantly boosts students’ intentions to learn. Integrating AI concepts across various disciplines—be it economics, healthcare, or environmental science—can broaden students’ perspectives and demonstrate the interdisciplinary applications of AI. Students should be able to see AI not just as a tool but as a transformative force that can solve complex problems in diverse fields.
The findings of this study also resonate beyond Ghana, highlighting the global need to assess students’ readiness to embrace emerging technologies. Countries grappling with similar educational challenges can adopt and adapt the models presented in this research. As we move into a future increasingly dominated by AI, educational methodologies must evolve to prepare students not only to consume technology but to innovate and lead in this field.
To ensure these educational reforms are sustainable, government support and investment are imperative. Stakeholders must collaborate to provide the necessary funding, infrastructure, and resources for educational institutions to thrive in the AI domain. Encouraging partnerships between academia, industry, and government can lead to synergies that enhance learning outcomes and pave the way for a skilled workforce equipped for the challenges of the 21st century.
Importantly, the study’s implications extend to teacher training programs as well. Educators themselves must be well-versed in AI technologies and methodologies to effectively teach their students. Professional development opportunities focused on AI can empower teachers, enabling them to inspire and guide students as they explore new territories in technology.
In essence, this research encapsulates a vital exploration of factors influencing students’ intentions to engage with AI in Ghana’s educational space. By employing advanced modeling techniques and reflecting on the complexities of various student experiences, the authors provide valuable insights that can inform effective teaching practices and policies. As AI continues to reshape the world, the educational approaches guided by this research may well serve as stepping stones toward a future where students are not only consumers of technology but innovative contributors to an AI-driven world.
Subject of Research: Intention of STEM Students to Learn Artificial Intelligence in Ghana
Article Title: Modelling STEM students’ intention to learn artificial intelligence (AI) in Ghana: a PLS-SEM and fsQCA approach
Article References:
Abreh, M.K., Arthur, F., Akwetey, F.A. et al. Modelling STEM students’ intention to learn artificial intelligence (AI) in Ghana: a PLS-SEM and fsQCA approach.
Discov Artif Intell 5, 223 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44163-025-00466-8
Image Credits: AI Generated
DOI: 10.1007/s44163-025-00466-8
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence, Education, STEM, Learning Intentions, Ghana, PLS-SEM, fsQCA, Student Engagement, Educational Reform, Technology Integration, Teacher Training, Peer Influence, Interdisciplinary Learning.
Tags: AI integration in curriculumAI learning intentionsdigital progression in educationeducational transformation in Ghanaenhancing job readinessfactors influencing AI learningfuture of education in Ghanafuzzy set qualitative analysisGhanaian STEM educationPLS-SEM methodologystudent motivation for AItechnology in education
Tools & Platforms
Globevisa CEO Unveils its AI Strategy, Transforming Traditional Services Into a Tech-Driven Powerhouse
— In a decisive move set to redefine the future of service industries, Globevisa Group CEO and co-founder Henry Fan has launched a groundbreaking artificial intelligence (AI) transformation strategy that embeds AI at the core of the company’s operations. This bold initiative is not only improving efficiency and customer service but also positioning Globevisa as a global innovator in tech-driven business leadership.
Rather than relegating AI to a standalone IT function, Henry established an in-house AI Empowerment Center—a “special forces” unit that reports directly to him. This reflects his belief that AI is a business-wide opportunity, not a departmental add-on. As the architect of this transformation, Henry serves as strategist, change agent, and internal evangelist, overseeing a company-wide shift in how AI is deployed, adopted, and embraced.
The Strategist: Defining a Clear Vision for AI
Henry’s leadership begins with a clear vision for an “AI-driven Globevisa,” which he positions as the company’s North Star. This vision guides every decision, from budget allocation to the selection of core technologies. Henry ensures that AI efforts are tightly aligned with Globevisa’s business objectives, such as revenue growth, operational efficiency, and brand enhancement.
His approach is pragmatic and phased, focusing on high-value pilot projects before scaling up. He champions a “showcase to full coverage” strategy, quickly demonstrating tangible results in areas like marketing, customer service, and human resources. By tying AI initiatives directly to measurable business outcomes, such as reducing document processing times, increasing content production efficiency, or improving sales conversion rates, Henry ensures that Globevisa’s AI efforts are not just theoretical but practical and impactful.
Tackling Operational Inefficiencies with AI
Henry’s journey into AI began with a recognition of inefficiencies in the company’s internal processes, which were bogged down by repetitive, manual tasks. He saw AI not as a buzzword but as a tool to address these core operational challenges.
1.Document Processing
Globevisa’s success involves processing countless client documents, such as bank statements and passports, a task prone to human error and delays. To combat this, Henry spearheaded the development of an AI document extraction and auditing tool. This technology scans documents, extracts key information, and cross-checks it against system requirements, significantly reducing manual review time and errors. The result is faster, more accurate processing, enabling the team to handle a higher volume of clients.
2.Customer Service
Globevisa’s customer service team was overwhelmed by repetitive inquiries, leaving little time for complex, high-value interactions. Henry’s team introduced a 24/7 AI-powered chatbot capable of handling up to 80% of standard queries. This freed human staff to focus on nuanced, emotional, and complex client concerns, enhancing overall customer satisfaction.
3.Marketing Content Creation
The process of generating marketing content was slow and often lacked variety. Henry addressed this by deploying an “AI Content Factory” that generates blog posts, social media updates, and ad copy from simple keywords. This tool dramatically increased content production efficiency while reducing costs, ensuring Globevisa remains competitive in its digital marketing efforts.
The Breaker of Barriers: Overcoming Organizational Challenges
While implementing AI solutions, Henry quickly realized that the biggest obstacles were not technological but organizational and cultural. Resistance to change, data silos, and fears of job displacement were among the challenges he faced.
1.Breaking Data Silos
With 110,000 successful cases in hand, Globevisa sits on a treasury of data. However, many departments at Globevisa operated in isolation, hoarding data and refusing to share it. For instance, the AI team often needed years of sales data to train models, but obtaining access required navigating internal politics. Henry personally stepped in as a “Breaker of Barriers,” reframing data-sharing as an investment in the company’s future rather than a threat. He emphasized that AI would provide departments with sharper tools to achieve their goals, fostering a spirit of collaboration.
2.Addressing Job Displacement Fears
Employees, particularly senior staff such as copywriters, were initially hostile toward AI, viewing it as a potential replacement for their roles. Henry tackled this by redefining their positions and elevating their value. He assured employees that AI would handle 80% of mundane tasks, allowing them to focus on the remaining 20% of creative, high-value work. Copywriters, for example, were rebranded as “AI Creative Strategists” and “Final Quality Controllers,” responsible for refining and overseeing AI-generated drafts. This reframing not only eased fears but also inspired employees to embrace AI as a tool for professional growth.
3.Adjusting KPIs to Reward Adoption
In traditional service industries, departments often cling to outdated KPIs, which can hinder the adoption of new technologies. Henry addressed this head-on by personally revising performance metrics for teams involved in AI pilots. For example, customer service teams previously measured on “calls handled per hour” were now evaluated on metrics like “complex problem-solving rates” and “customer satisfaction scores.” This ensured that employees were rewarded for adopting new behaviors, not for sticking to inefficient practices.
The Chief Evangelist: Fostering a Culture of Innovation
Henry understands that technology alone cannot drive change; it requires a cultural shift. As Globevisa’s “Chief Evangelist,” he regularly communicates the importance of AI initiatives through all-hands meetings, internal newsletters, and personal demonstrations. By openly using AI tools, such as leveraging AI for meeting summaries, he leads by example, fostering a company-wide culture of innovation.
His leadership style is characterized by inclusivity and transparency. Instead of imposing top-down mandates, he actively involves employees in the transformation process, ensuring that AI is seen not as a threat but as an enabler. This human-centric approach has been instrumental in building trust and enthusiasm for AI across the organization.
A Model for the Future of Services
Henry’s approach provides a replicable roadmap for other service-based companies navigating digital transformation. His model centers on measurable value, cultural readiness, and human-AI collaboration, proving that even traditional industries can lead in a tech-first economy.
About Globevisa
Globevisa Group is a global leader in immigration and relocation services, with over 110,000 successful cases worldwide. Committed to service excellence and innovation, the company helps individuals and families navigate complex immigration processes with confidence.
Contact Info:
Name: Lena Huang
Email: Send Email
Organization: GLOBEVISA GROUP (HONG KONG) LIMITED
Website: https://www.globevisa.com/
Release ID: 89168612
In case of identifying any errors, concerns, or inconsistencies within the content shared in this press release that necessitate action or if you require assistance with a press release takedown, we strongly urge you to notify us promptly by contacting error@releasecontact.com (it is important to note that this email is the authorized channel for such matters, sending multiple emails to multiple addresses does not necessarily help expedite your request). Our expert team is committed to addressing your concerns within 8 hours by taking necessary actions diligently to rectify any identified issues or supporting you with the removal process. Delivering accurate and reliable information remains our top priority.
Tools & Platforms
Oak Lawn Community High School to implement AI gun detection tech – NBC Chicago

A high school in suburban Chicago was awarded a grant to implement AI-powered gun detection technology.
Oak Lawn Community High School District 229 was one of 50 recipients selected nationwide for the Omnilert Secure Schools Grant Program, the school said in a recent announcement.
The district was awarded a three-year license for Omnilert Gun Detect, an “advanced AI-powered gun detection technology” — at no cost.
The AI system identifies firearms “in real-time through existing security camera infrastructure,” the announcement said.
Once a potential threat is identified, the AI system activates a rapid response process by alerting school officials and law enforcement, ultimately ensuring that threats can be addressed “as quickly and effectively as possible,” the announcement said.
The implementation of the AI system aligns with District 229’s security strategy, that includes a combination of physical safety measures, emergency preparedness and mental health resources, the announcement said.
The school said staff training and safety drills will be done to ensure the technology is used effectively and responsibly.
-
Tools & Platforms3 weeks ago
Building Trust in Military AI Starts with Opening the Black Box – War on the Rocks
-

 Ethics & Policy1 month ago
Ethics & Policy1 month agoSDAIA Supports Saudi Arabia’s Leadership in Shaping Global AI Ethics, Policy, and Research – وكالة الأنباء السعودية
-

 Events & Conferences3 months ago
Events & Conferences3 months agoJourney to 1000 models: Scaling Instagram’s recommendation system
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoThe Guardian view on Trump and the Fed: independence is no substitute for accountability | Editorial
-

 Jobs & Careers2 months ago
Jobs & Careers2 months agoMumbai-based Perplexity Alternative Has 60k+ Users Without Funding
-

 Funding & Business2 months ago
Funding & Business2 months agoKayak and Expedia race to build AI travel agents that turn social posts into itineraries
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoVEX Robotics launches AI-powered classroom robotics system
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoHappy 4th of July! 🎆 Made with Veo 3 in Gemini
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoOpenAI 🤝 @teamganassi
-

 Jobs & Careers2 months ago
Jobs & Careers2 months agoAstrophel Aerospace Raises ₹6.84 Crore to Build Reusable Launch Vehicle



















