AI Insights
What Is Swarm Intelligence? | Built In

Swarm intelligence is the collective behavior of multiple individuals — like drones, bits of code or even animals — that work together as one coordinated group without a central leader. Each unit, or “agent,” follows basic rules, gathering information of its surroundings and sharing these responses to nearby members of the swarm. These constant local interactions create a feedback loop of data that helps the group make decisions and solve complex problems no single agent could handle alone.
Swarm Intelligence Definition
Swarm intelligence is when many units collaborate without a leader, continuously communicating and following evolving rules based on shared local information. This dynamic interaction allows the group to adapt in real time and tackle complex problems together more effectively than any individual could alone.
The concept is inspired by nature: ants building tunnels, birds flying in formation, bees working together in hives. First coined by Gerado Beni and Jing Wang in 1989 while studying cellular robotic systems, swarm intelligence has become a growing area of research in robotics, logistics and data analysis as an extension of artificial intelligence.
These hive-minded systems are highly adaptable and resilient. If one agent fails, the other keeps going, making them useful in unpredictable or large-scale operations. While challenges like communication and coordination remain, swarm intelligence shows how decentralized systems can tap into the power of many.
What Is Swarm Intelligence?
Swarm intelligence is a form of collective problem-solving where many simple agents — like robots, drones or software programs — work together without a central leader. Each agent follows basic rules and communicates locally with nearby peers, creating a constant flow of information and feedback that allows the group to adapt and make decisions in real time. Inspired by natural systems like ant colonies and bird flocks, swarm intelligence enables groups to tackle complex tasks more efficiently and with more resilience than any single agent could do alone.
How Does Swarm Intelligence Work?
Swarm intelligence works through the decentralized coordination of multiple agents that follow simple, predefined rules. It begins with each agent acting independently, often making random guesses based on whatever information they have in front of them. The agents then gauge the success of their actions in real time using a “fitness score,” which is a numerical measure of how well it’s performing on a given task.
Agents continuously share this performance data with other nearby agents, forming a sort of local communication network. Using this shared feedback, each agent adjusts its behavior slightly, learning both from its own experience and the success of its neighbors. Over time, this constant loop of exploring, scoring, sharing and adjusting causes the entire swarm to gradually align toward better and better solutions.
Over time, this constant loop of exploring, scoring, sharing and adjusting causes the entire swarm to gradually align toward better and better solutions. The process doesn’t require a central leader — rather, the intelligence emerges organically from collective behavior and small, localized interactions.
Examples of Swarm Intelligence
Swarm Robotics
Swarm robotics involves groups of simple, autonomous robots working together without centralized control. These organized machines — in the form of airborne drones or ground robots — use an array of sensors, distributed algorithms and mesh networking protocols to coordinate in real time as they move and solve complex tasks as a unit. Some of the most impressive proofs-of-concept to date include the U.S. Department of Defense’s Perdix drones, which demonstrated self-healing flight formations, and Zhejiang University’s forest-navigating swarm, primarily designed for use in search-and-rescue missions.
Computational Algorithms
Computational algorithms like Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) and Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) mimic the collective behaviors of animals such as birds and ants to solve complex problems. PSO is commonly used in engineering design and neural network training, figuring out the most efficient way to move through high-dimensional search spaces where anything can happen. On the other hand, ACO also takes inspiration from how ants use pheromone trails to discover shortcuts, speeding up areas like computer network routing and vehicle scheduling.
Telecommunications
In telecommunications, swarm intelligence helps networks manage themselves by letting devices figure out the best paths for data on the fly, without needing a central controller. Ant-based algorithms that use ACO protocols (as discussed above) have been implemented into wireless mobile ad hoc networks, which are used in field operations like military missions and disaster response to enable decentralized, fault-tolerant communication paths that temporarily sync mobile devices.
Finance
Swarm intelligence is increasingly being explored in finance to sharpen forecasts and decision-making. Instead of relying on isolated inputs or simple averages, human swarms — closed-loop networks where participants interact, continuously adjusting their contributions based on collective dynamics — function as a single-thinking system to converge on shared predictions. In a 19-week study, swarming increased the accuracy of financial traders’ predictions from 57 percent to 77 percent, outperforming both individuals and majority-vote crowds in forecasting indices like SPX, GLD, GDX and Crude Oil.
Logistics
Route optimization, warehouse management and delivery scheduling all benefit from self-organizing algorithms. Equipped with swarm intelligence, delivery fleets and autonomous robots can reroute around traffic or redistribute workloads on the spot without relying on a control center. Following a few successful pilot runs, global logistics leader DHL deployed a 5,000 fleet of swarm-programmed LocusBots across more than 35 warehouses.
Smart Farming
When swarms are applied in farming, they can coordinate multiple autonomous agricultural machines to monitor fields, apply treatments, manage irrigation, collect data and even pollinate crops. In a simulated scenario, one 2023 study showed that increasing the number of drones from one to eight reduced the scanning time spent during field monitoring from 19 minutes to less than three minutes. These lightweight, efficient machines also show promise in reducing soil damage, conserving resources and cutting down on pesticide use.
Military
Drones are becoming modern warfare’s weapon of choice, and tapping into swarm intelligence is an inevitable next step. Today, swarms are being deployed in defense scenarios to carry out high-risk missions like surveillance, electronic warfare, target acquisition and even coordinated strikes without endangering pilots or ground troops. In June, Ukraine used a swarm of 117 small, semi-autonomous drones to identify enemy targets and destroy 34 percent of Russia’s strategic cruise missile-carrying bomber fleet. The U.S. military is developing its own swarm intelligence with programs like DARPA’s OFFSET, which trains tactical urban combat swarms, and the Air Force’s Perdix drones, a large-scale micro-drone swarm that’s capable of adaptive formation flying and self-healing behavior.
Wildlife Tracking
Swarm intelligence is helping scientists monitor wildlife like zebras, elephants and dolphins more effectively by using multiple drones to capture high-quality data from different angles. Rather than one single overhead drone, swarms combine vertical and horizontal views to track movement patterns, social behavior and identify individual animals without disturbing them. Researchers are now testing out centralized swarm control systems, like one developed for the WildDrone Project, to feed the swarm real-time data and develop best practices.
Benefits of Swarm Intelligence
Swarm intelligence turns groups of simple machines into powerful, coordinated teams. Here are some key benefits to this collective approach:
- Live Coordination: Drone swarms work together and adapt in real time, tackling complex missions in sync that no single drone could handle alone.
- Decentralized Resilience: Even if some drones get taken out, the swarm is able to carry on thanks to its distributed control and self-healing mechanisms.
- Risk Mitigation: Autonomous swarms take on dangerous jobs so soldiers and pilots don’t have to risk their lives on the job.
- Strength in Numbers: Sending out large numbers of low-cost drones en masse at once is one way to overwhelm an enemy’s defenses and regain the high ground.
- Enhanced Situational Awareness: A swarm’s integrated sensors provide a clear, up-to-the-minute picture of what’s happening on the ground and in the air across miles of operational areas.
Challenges of Swarm Intelligence
Still, swarm intelligence still comes with some significant challenges that researchers and developers are still working to overcome. These include:
- Unreliable Communication: Drones need to stay connected to work together, but signals can get jammed, interrupted or lost — which can throw the whole swarm off.
- Autonomous Decision-Making: Without a leader drone calling the shots, each drone has to adapt as the swarm travels through dynamic environments. This level of synchronicity requires sophisticated AI systems — all of which are still in development — to pull off.
- Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities: The larger the drone swarm, the higher the more susceptible it is to hacking or spoofing attacks due to its expanded attack surface and an increase in points of entry. Cyberattacks could compromise a swarm’s targeted mission, or turn them against friendly forces.
- Regulatory and Ethical Constraints: Deploying swarms raises tough questions about things like privacy, accountability when something goes wrong and the rules around letting machines make lethal decisions. All of which still need clear, standardized answers. Right now, the U.S. military’s guidelines require a human operator to approve any lethal action, keeping them “in the loop” to make sure accountability stays clear.
What is the difference between artificial intelligence and swarm intelligence?
Artificial intelligence is about teaching one machine to think and make decisions, while swarm intelligence is all about how a bunch of simple machines come together as a team to tackle tasks.
Is swarm intelligence being used?
Yes; swarm intelligence is actively being used in military drone operations. Beyond that, it’s applied in agriculture for crop monitoring, in disaster response for search-and-rescue missions and in environmental science for wildlife tracking.
AI Insights
California Wraps Up Legislative Session With AI, Chatbot Measures Under Consideration

Washington – California legislators wrap up their session this week and will consider measures aimed at online safety that could also have an impact on various companies innovating in artificial intelligence located in their state and around the country.
Two priorities under discussion involve chatbots with the goal of protecting younger users online. AB 1064 would effectively create a prohibition on any chatbot that could potentially be accessed by children. SB 243, meanwhile, is more targeted, proposing mandatory reporting requirements when people discuss self-harm with chatbots, plus a ban on addictive reward structures sometimes used to increase user engagement with the bots.
The Computer & Communications Industry Association understands that younger internet users warrant more protections online and supports media literacy programs and online tools that empower parents to make decisions on what is appropriate for their teenager.
The following can be attributed to Aodhan Downey, West Regional State Policy Manager at CCIA:
“California legislators are considering multiple pieces of landmark legislation aimed at regulating novel technologies like artificial intelligence and chatbots. Some measures, like AB 1064, would have drastic consequences that would stifle the innovation and educational opportunities for the children in California. SB 243 creates standards that chatbot service operators must follow in order to provide a safer environment for children, while also not creating an overbroad ban on AI products.”
About CCIA:
CCIA is an international, not-for-profit trade association representing a broad cross section of communications and technology firms. For more than 50 years, CCIA has promoted open markets, open systems, and open networks. CCIA members employ more than 1.6 million workers, invest more than $100 billion in research and development, and contribute trillions of dollars in productivity to the global economy.
AI Insights
New life for the mainframe: AI cost savings materialize, modernization efforts pay off

Another significant survey finding is that mainframe modernization plans are more dynamic than they’ve been in the past due to changing market conditions: 80% of organizations reported that their modernization strategy has shifted in the past year, “indicating widespread re-evaluation and a degree of agility not commonly associated with technology projects of such significant size, scope and complexity,” Kyndryl stated.
Mainframe modernization can take a few forms; enterprise customers can keep data on the mainframe, migrate workloads off, or create a hybrid environment.
Among organizations that said they’ve shifted their modernization approach, 43% are more focused on modernizing directly on the mainframe, and 50% are moving more towards a hybrid strategy, Kyndryl found. Among those that are moving towards a hybrid IT approach, 34% are prioritizing integration with cloud platforms, and 16% are increasing the pace of moving applications off the mainframe. Only one out of 500 respondents reported plans to move entirely off the mainframe.
The reasons for changing their migration strategies vary widely among respondents and include factors such as the success of previous projects, budget shifting to new technologies, and external factors such as geopolitical, macroeconomic and regulatory concerns, Kyndryl stated.
Cost is another motivator: The average cost of modernizing on the mainframe dropped from $9.1 million in 2024 to $7.2 million in 2025, and the ROI on such a move more than doubled, Kyndryl stated.
Other trends noted in the mainframe modernization report include:
AI Insights
AI Goes Mission Critical as Palantir Powers Essential Systems

Artificial intelligence is no longer confined to experiments or pilot projects. From airlines optimizing flight schedules to hospitals reducing patient deaths, and from oil rigs in the Gulf of Mexico to emergency crews in flooded Texas towns, AI has entered the realm of the mission critical. It now runs the systems that keep people alive, economies powered and industries moving.
That reality was on display at Palantir’s eighth AIPCon, where executives, engineers and public officials described how they’re using the company’s platforms to manage operations that cannot fail.
Aviation: Keeping Flights on Time
At American Airlines, Anne Moroni, the company’s vice president of operations, described a planning process that, until recently, was drowning in spreadsheets.
“Our planning is incredibly manual, incredibly sequential, and unfortunately, as a result, quite siloed,” she said. “From outdated UIs…Excel spreadsheets, attachments being sent via emails between teams, we spend an inordinate amount of time trying to actually build the best schedule we can.”
Palantir
Amit Shinde, American’s director of operations, schedule and block planning, explained how a planning tool the company calls Vector, built on Palantir’s Foundry platform, now helps.
“Over the last year or so, we’ve been on a journey with Palantir to try and reimagine our workflows,” he said. “These are recommendations that the models are scanning the network on, and they’re saying there’s something that I’ve found you probably want to take a look at.”
The result, he said, has been tens of millions of dollars in value unlocked within a single year.
Health and Pharma: Saving Lives and Speeding Discoveries
The promise of data-driven transformation isn’t limited to aviation. In pharmaceuticals, Novartis described an even more daunting problem: drug discovery.
“Currently, it takes us about 12 years on average, and $3 billion to develop a novel medicine,” Birgit Schoeberi, head of Data 42 at Novartis, said. “This is largely driven by a low probability of success. It’s an odds ratio of one in 10,000 for one of our discovery station molecules synthesized by chemists early on to ever reach regulatory approval.”
Along with Palantir, the company built Data 42, integrating “700 million patient lives from real-world data, as well as from our 3,000 clinical trials encompassing about a million patients.” The platform, Schoeberi said, is more than a database; it is an engine that allows scientists to query information across silos instantly.
“We’ve been able to reduce the time one of our translational modelers usually spends on the human dose prediction per compound by approximately 90 or 98 percent, from one week down to two hours today,” Schoeberi said.
Hospitals are seeing similar results. “Insurance denials are a significant financial burden for hospitals in our state,” said Dr. Ed Kimlin, Maine Health’s medical director, payer operations. “With Palantir’s AIP, we analyze insurance coverage criteria against patient medical records to create compelling appeal letters and streamline authorization processes.”
He described the journey of fictional patient “Mr. Baggins,” whose treatment was nearly derailed by bureaucracy. “His care journey involved AI-assisted authorization for a procedure, an unplanned hospital admission, and a post-discharge coding denial appeal,” he said. “At every stage, Palantir’s technology helped ensure he received the care he needed.”
Ashis Barad, chief digital and technology officer at Hospital for Special Surgery, highlighted the clinical impact. “The first appeal that we sent out with Palantir…The AI did it in five minutes, and the human did it in 45 minutes. And the [five] and the 45 minutes doesn’t include all the wrap-around, trying to get the data back and everything else. This was like, completely sealed…Our appeals have gone from 68 percent to 99 percent,” he told Newsweek.
For Tampa General Hospital, Palantir helped reduce the length of stay for sepsis patients by 30 percent, said Drew Goldstein, who helps lead the company’s health care business. “That’s focused on recognizing at-risk patients and giving care teams the action plan to intervene quickly.”
Energy and Infrastructure: Safety at Scale
AI is also becoming inseparable from the energy infrastructure that powers economies.
Thunder Horse, BP’s largest production and drilling platform in the Gulf of Mexico, is “capable of producing 250,000 barrels of oil daily,” said Sanjay Pandey, BP’s chief product and technology officer. “It’s massive. Operating a platform like this is highly complex, and we have to balance maximizing efficiency with the safety of our teams.”
Pandey emphasized the impact of Palantir on operations: “We ran over 1.4 million digital twin simulations in the last year alone…This has reduced the time to get to operational insights on maintenance data by 75 percent…This is all about operational excellence. For us, safety is at the core.”
Jonathan Webb, co-founder of The Nuclear Company, argued that nuclear power is not unsafe, just inefficient. “The most reliable source of power on planet Earth is nuclear power,” he told Newsweek. “I think, to me, the shocking thing is, this town created a narrative… that nuclear is not safe. It has nothing to do with reality.”
His company is applying Palantir’s technology to nuclear construction, which has historically been plagued by overruns. “We’re still running construction sites like 1982,” Webb said.
“If the weld’s off, you could have a foreman with glasses and an earpiece, a drone with LiDAR, and it’s off by a millimeter. Hey, go check that weld. Versus you figured it out three weeks later. You spent thousands of man-hours building a bunch of things, then you have to spend tens of millions of dollars ripping it all up. That’s demoralizing. Why are we not doing this?”
AI is also helping manufacturers adapt to workforce challenges. Yoshinami Takahashi, Fujitsu’s chief operating officer (in charge of solution service), explained that Japan faces a demographic crisis, with its labor force projected to shrink by 40 percent by 2045. “So that’s a massive need…So that’s where, like Palantir, let’s work together to resolve that.”
Using AI, Takahashi said, Panasonic’s factory operators gained full visibility into inventory, allowing them to optimize workflows and reduce manual labor. “Using Palantir Foundry, we built the system in two weeks…They were able to minimize inventory workload by 50 percent…in one year’s time, they can reduce inventory costs of maybe more than $10 million,” he told Newsweek.
Disaster Response and Public Safety: When Seconds Count
For Captain John Miller of the Texas Department of Public Safety, AI technology became indispensable during a tragedy.
Palantir
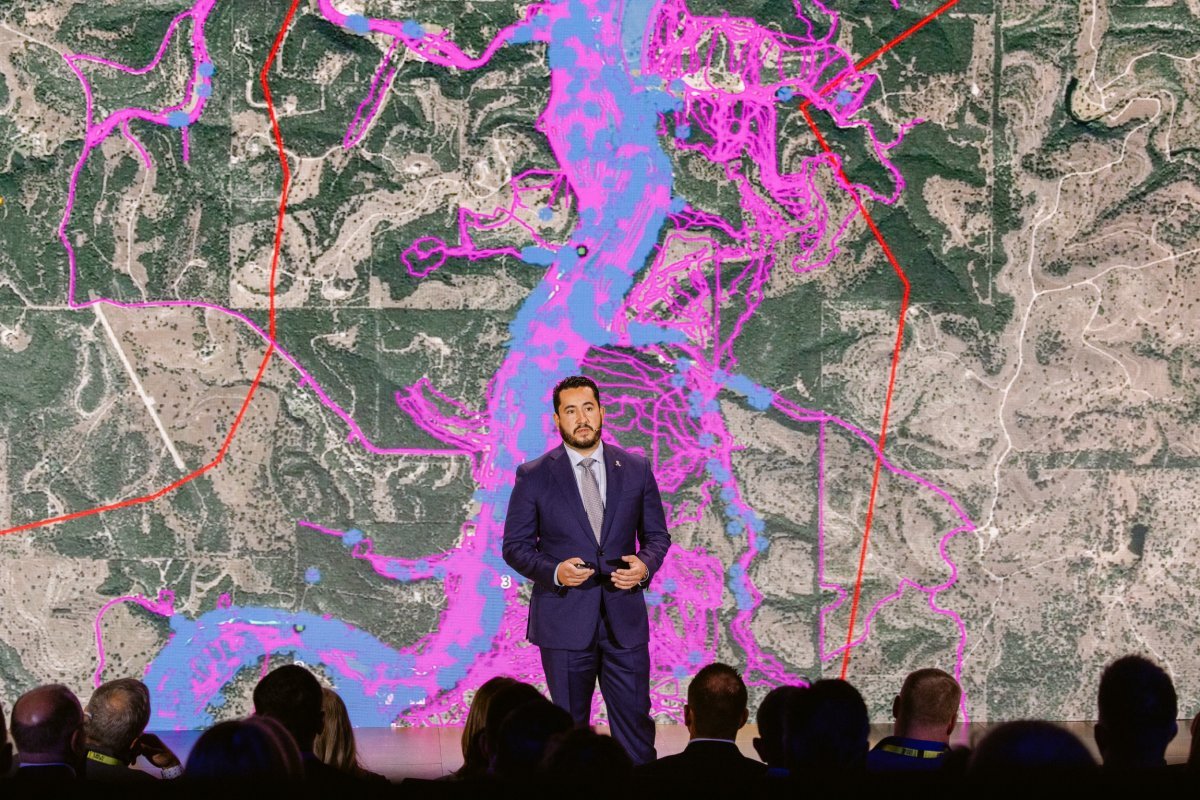
Recalling the catastrophic July 4th flooding in Kerr County, Miller said, “The storm system caused record rainfall, increasing stream velocity from 50 to 900,000 gallons per second. Thirty-nine children and 80 adults died, primarily at campgrounds.”
Palantir’s support allowed responders to build a “common operating picture” from dozens of data sources. “This aided in search efforts, locating 117 victims in 3.5 days,” Miller explained.
“The mission continues to find the last two victims, Jeff Ramsey and Cile Steward, with Palantir’s technology providing an unfair advantage.”
AI systems are also enabling rapid response to manufacturing disruptions caused by natural disasters. Fujitsu’s Yoshinami Takahashi described to Newsweek how, during a 2024 earthquake, Panasonic was able to assess supply chain impacts in a single day and reroute suppliers immediately, a process that previously would have taken five days.
“When an earthquake happened in 2024…Panasonic was able to assess impact in one day, and then within one day they could change from supplier A to supplier B,” he said.
In addition to enabling rapid response to rural emergencies, AI today is also reshaping emergency response in cities.
Skydio CEO Adam Bry told Newsweek that drones are “used by what we really think of as like the critical industries that our civilization runs on…energy, construction, law enforcement, public safety, defense, and they’re basically the ultimate flying sensor platforms.”
Highlighting AI’s role, he said, “One of the subtle but key things there is it enables us to fly with confidence in very challenging environments, because the drone can see everything around it…it knows the 3D structure of the world around it.”
He added, “This is fully autonomous flight…This is a feature we call Pathfinder, where the operator says, here’s where I want to go, and then it uses its knowledge of the buildings and terrain and everything else to autonomously find its way there.”
Bry showed camera footage of a rescue and explained the impact: “The paramedics got there super quickly, and they saved this guy’s life, like he was probably going to bleed out on the train tracks there, and survived.”
On city deployments, he added, “Most of the major cities in the U.S. will be using our drones to respond to 911 calls and emergencies, and get there first and fastest and get…useful information for first responders.”
Human Judgment in Mission-Critical AI
Palantir Deployment Strategist Hind Kraytem, while reflecting on building Palantir across Europe and Asia, cautioned against blind trust.
“We are building Palantir across Europe and Asia. We’re in Japan, we’re in Korea, we’re in Singapore, we’re in Germany.” She emphasized that adoption is as much cultural as technical. “It’s really more of a cultural thing, the way that we’re talking about, like, you know, what is the right way to build these tools?”
Kraytem explained that the focus is on augmenting, not replacing, human expertise. “You have to be critical. We can’t just trust it,” she told Newsweek, encouraging users to test AI on domains they know well before relying on it for unfamiliar tasks.
Goldstein echoed the point. “It’s way less about the model and more about what happens before and after,” he told Newsweek. “Focusing on the model alone misses how much value comes from understanding the human processes around it.”
Software as Survival Infrastructure
Closing his keynote, Palantir CEO Alex Karp tied these examples together.

Palantir
“An LLM is a raw material that has to be processed, and the processing of the LLM will change America and change the world,” he said. “You can actually transform your business by being open to different ways of doing business…It means extending the human mind. It means being able to use a large language model to change margins, to increase safety, to increase revenue.”
Karp emphasized the transformative potential of AI. “You’re able to radically increase growth, radically decrease margins and increase the happiness of the people in your business at all levels of business, including workers,” he said.
“And that is actually the real promise of the AI revolution.”
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoThe Guardian view on Trump and the Fed: independence is no substitute for accountability | Editorial
-
Tools & Platforms4 weeks ago
Building Trust in Military AI Starts with Opening the Black Box – War on the Rocks
-

 Ethics & Policy1 month ago
Ethics & Policy1 month agoSDAIA Supports Saudi Arabia’s Leadership in Shaping Global AI Ethics, Policy, and Research – وكالة الأنباء السعودية
-

 Events & Conferences4 months ago
Events & Conferences4 months agoJourney to 1000 models: Scaling Instagram’s recommendation system
-

 Jobs & Careers2 months ago
Jobs & Careers2 months agoMumbai-based Perplexity Alternative Has 60k+ Users Without Funding
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoVEX Robotics launches AI-powered classroom robotics system
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoMacron says UK and France have duty to tackle illegal migration ‘with humanity, solidarity and firmness’ – UK politics live | Politics
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoHappy 4th of July! 🎆 Made with Veo 3 in Gemini
-

 Funding & Business2 months ago
Funding & Business2 months agoKayak and Expedia race to build AI travel agents that turn social posts into itineraries
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoOpenAI 🤝 @teamganassi

