Education
We’re losing STEM teachers–here are 5 ways to keep them and grow the ones we need

Key points:
The critical shortage of qualified STEM teachers continues to challenge schools and districts across the country. This is especially true in high-need schools where early-career or uncertified teachers are more common.
With almost half of all new educators leaving the profession within their first five years, and teacher satisfaction at its lowest in two decades, school and district leaders have a big task at hand. They not only need to fill open positions, but they need to put the structures into place to build a sustainable pipeline of STEM teachers. This is essential for providing students with engaging, hands-on, and equitable learning experiences.
If you ask engineers, technicians, or other professionals what led them to their careers, you will almost always hear the same thing: “A teacher inspired me.” We all understand how essential STEM educators are in shaping future innovators. However, too often, we overlook what it takes to support and sustain the very teachers who spark that journey.
In a recent webinar, I facilitated a panel conversation with Dr. Josh Stewart, founder of Rocky Mountain Research & Strategy, and Jess Holman, STEM specialist at NSTA, who shared in-depth insights on this topic as well as practical strategies to support school and district leaders in this undertaking.
Here are takeaways from this conversation and five ways to effectively attract, retain, and support STEM teachers this school year and beyond.
1. Have a clear vision
When recruiting for open roles, remember that teachers are drawn to strong leadership, a clear school vision, and a culture that emphasizes innovation and respect. When leaders showcase their commitment to equity, professional growth, and student-centered learning, teachers are typically interested in joining–and staying at–that school.
During the recruitment period, highlight your school’s unique culture, use of technology, mentorship programs, and commitment to STEM innovation. With candidates, ask meaningful interview questions about their real-world teaching experience, instructional approach, and vision for their own classroom to ensure it is a mutual fit, but don’t overlook their soft skills. Relationship building, resilience, and adaptability are all qualities of an exemplary teacher.
Above all, it is important that any candidate is passionate about teaching and eager to make a difference in the classroom. These are the individuals who are worth investing in and the ones who are most likely to continue to show up and grow into the profession.
2. Leverage grow-your-own and apprenticeship programs
To meet immediate staffing needs, many districts are turning to teacher apprenticeship or “grow-your-own” (GYO) models. States like Tennessee, South Dakota, and Colorado, for example, have seen success with this structured pathway approach, especially when stipends and microcredential opportunities are offered to educators.
Developing strong and collaborative partnerships with post-secondary institutions is an important aspect of a successful GYO model. When school and district leaders clearly communicate the core competencies and skills they are looking for in their teachers, post-secondary institutions can make sure these areas are covered both in the coursework and the coaching and feedback these aspiring teachers receive. Alignment and dialog among districts and post-secondary institutions is key.
By launching or expanding local apprenticeship programs, schools and districts can also help paraprofessionals and community members earn STEM teaching credentials. This contributes to a more diverse, community-rooted workforce and reduces reliance on out-of-area hires.
3. Embrace hands-on technology
Passionate STEM teachers are often drawn to schools where they can engage students with real-world tools like 3D printers, robotics kits, coding platforms, simulations, probeware, and data analysis software.
Access to modern, hands-on technology can drive student engagement, while helping teachers feel confident, current, and creatively fulfilled. As such, equipping STEM classrooms with tools that support inquiry-based, student-centered learning is important. Equally important is providing teachers with training on these technologies and allotting them planning time to incorporate these tools into their lessons.
4. Support NGSS-aligned instruction and real-world learning
From learning about local weather patterns and nearby waterways to understanding how food impacts the human body, authentic STEM learning involves engaging students with real-world phenomena.
However, making the instructional shift to teach the Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) can be hard. It requires strong instructional leadership–school and district leaders need to truly understand what three-dimensional, NGSS-aligned instruction looks like in action so they can support teachers with the implementation of it in a way that’s meaningful, not just evaluative.
School and district leaders can further support teachers with the shift to NGSS-aligned instruction by offering time to successfully implement new lessons, encouraging innovation and getting outside of their comfort zone, setting realistic goals together, and celebrating shared progress.
5. Cultivate a culture of belonging, mentorship, and purpose
STEM teachers, especially those early in their careers, can feel isolated or burned out if the right supports are not in place. This is why providing robust professional learning aligned to teachers’ interests and goals is so important, particularly when it comes to helping teachers build their professional identity early on in their careers.
Creating STEM-focused professional learning communities (PLCs), having teachers share the best practices they learn at conferences, encouraging participation in industry or regional associations, suggesting virtual networks to join, matching new teachers with subject-specific mentors, and giving time for cross-discipline collaboration with fellow teachers to take place can all help create community and a culture of belonging, which is a gamechanger for teacher retention.
This culture is especially important for recruiting and retaining STEM teachers from diverse backgrounds. Today, more than 50 percent of students enrolled in public schools are students of color—however, 80 percent of teachers are white. Setting educators up to stay and grow in the profession helps ensure students have access to teachers who reflect their identities.
The power of effective STEM teachers
Recruiting and retaining STEM teachers isn’t just about filling vacancies–it’s about giving every student a steady opportunity to be seen, challenged, and inspired by educators who believe in their potential, whether or not they choose a career in science.
When students have access to consistent, purpose-driven teachers–especially those who bring a variety of life experiences to the classroom–they not only perform better academically, they begin to see themselves as future scientists, engineers, and change makers. In fact, when students have effective teachers for even three years in a row, their performance can jump as much as 50 percent. That’s the power of teacher stability and support.
At a time when schools face growing complexity and competing demands, it is essential to focus on what matters: building classrooms where all students feel connected, curious, and capable. That starts with supporting the people who guide them every day.
Let’s make sure those teachers have every reason to stay–and every opportunity to thrive.
Education
A largely invisible role of international students: Fueling the innovation economy
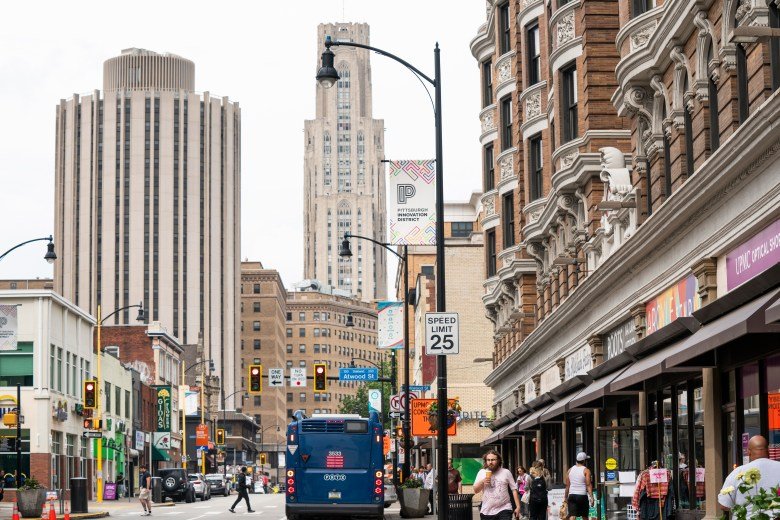

PITTSBURGH — Saisri Akondi had already started a company in her native India when she came to Carnegie Mellon University to get a master’s degree in biomedical engineering, business and design.
Before she graduated, she had co-founded another: D.Sole, for which Akondi, who is 28, used the skills she’d learned to create a high-tech insole that can help detect foot complications from diabetes, which results in 6.8 million amputations a year.
D.Sole is among technology companies in Pittsburgh that collectively employ a quarter of the local workforce at wages much higher than those in the city’s traditional steel and other metals industries. That’s according to the business development nonprofit the Pittsburgh Technology Council, which says these companies pay out an annual $27.5 billion in salaries alone.
A “significant portion” of Pittsburgh’s transformation into a tech hub has been driven by international students like Akondi, said Sean Luther, head of InnovatePGH, a coalition of civic groups and government agencies promoting innovation businesses.
“Next Happens Here,” reads the sign above the entrance to the co-working space where Luther works and technology companies are incubated, in an area near Carnegie Mellon and the University of Pittsburgh dubbed the Pittsburgh Innovation District. The neighborhood is filled with people of various ethnicities speaking a variety of languages over lunch and coffee.
What might happen next to the international students and graduates who have helped fuel this tech economy has become an anxiety-inducing subject of those conversations, as the second presidential administration of Donald Trump brings visa crackdowns, funding cuts and other attacks on higher education — including here, in a state that voted for Trump.
Related: Interested in innovations in higher education? Subscribe to our free biweekly higher education newsletter.
Inside the bubble of the universities and the tech sector, “there’s so much support you get,” Akondi observed, in a gleaming conference room at Carnegie Mellon. “But there still is a part of the population that asks, ‘What are you doing here?’ ”
Much of the ongoing conversation about international students has focused on undergraduates and their importance to university revenues and enrollment. Many of these students — especially in graduate schools — fill a less visible role in the economy, however. They conduct research that can lead to commercial applications, have skills employers need and start a surprising number of their own companies in the United States.
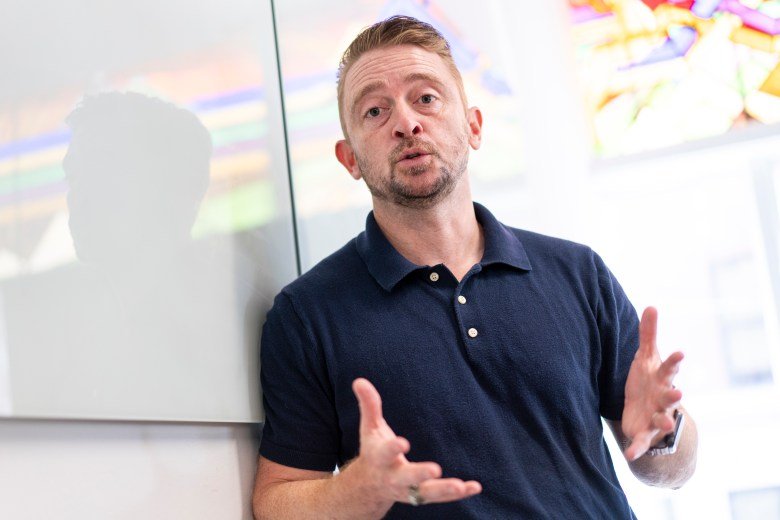

“The high-tech engineering and computer science activities that are central to regional economic development today are hugely dependent on these students,” said Mark Muro, a senior fellow at the Brookings Institution who studies technology and innovation. “If you go into a lab, it will be full of non-American people doing the crucial research work that leads to intellectual property, technology partnerships and startups.”
Some 143 U.S. companies valued at $1 billion or more were started by people who came to the country as international students, according to the National Foundation for American Policy, a nonprofit that conducts research on immigration and trade. These companies have an average of 860 employees each and include SpaceX, founded by Elon Musk, who was born in South Africa and graduated from the University of Pennsylvania.
Whether or not they invent new products or found businesses of their own, international graduates are “a vital source” of workers for U.S.-based tech companies, the National Science Foundation reported last year in an annual survey on the state of American science and engineering.
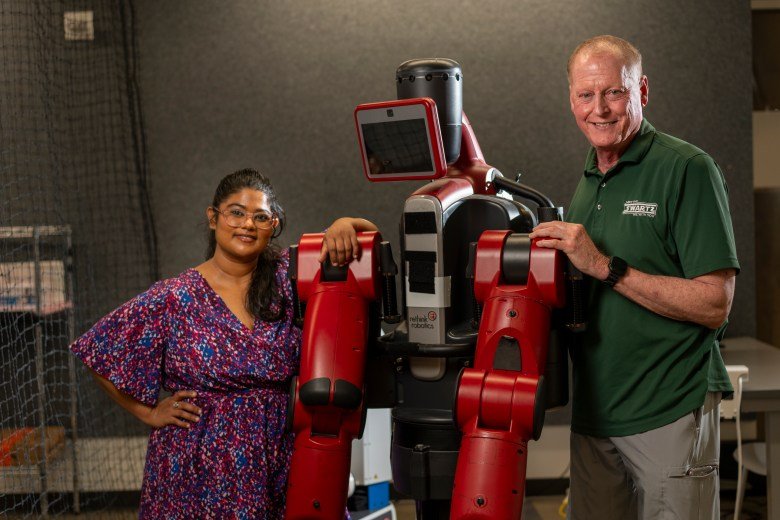

It’s supply and demand, said Dave Mawhinney, a professor of entrepreneurship at Carnegie Mellon and founding executive director of its Swartz Center for Entrepreneurship, which helps many of that school’s students do research that can lead to products and startups. “And the demand for people with those skills exceeds the supply.”
States with the most international students
California: 140,858
New York: 135,813
Texas: 89,546
Massachusetts: 82,306
Illinois: 62,299
Pennsylvania: 50,514
Florida: 44,767
Source: NAFSA: Association of International Educators. Figures are from the 2023-24 academic year, the most recent available.
Related: So much for saving the planet. Climate careers, and many others, evaporate for class of 2025
That’s in part because comparatively few Americans are going into fields including science, technology, engineering and math. Even before the pandemic disrupted their educations, only 20 percent of college-bound American high school students were prepared for college-level courses in these subjects. U.S. students scored lower in math than their counterparts in 21 of the 37 participating nations of the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development on an international assessment test in 2022, the most recent year for which the outcomes are available.
One result is that international students make up more than a third of master’s and doctoral degree recipients in science and engineering at American universities. Two-thirds of U.S. university graduate students and more than half of workers in AI and AI-related fields are foreign born, according to Georgetown University’s Center for Security and Emerging Technology.
“A real point of strength, and a reason our robotics companies especially have been able to grow their head counts, is because of those non-native-born workers,” said Luther, in Pittsburgh. “Those companies are here specifically because of that talent.”
International students are more than just contributors to this city’s success in tech. “They have been drivers” of it, Mawhinney said, in his workspace overlooking the studio where the iconic children’s television program “Mister Rogers’ Neighborhood” was taped.
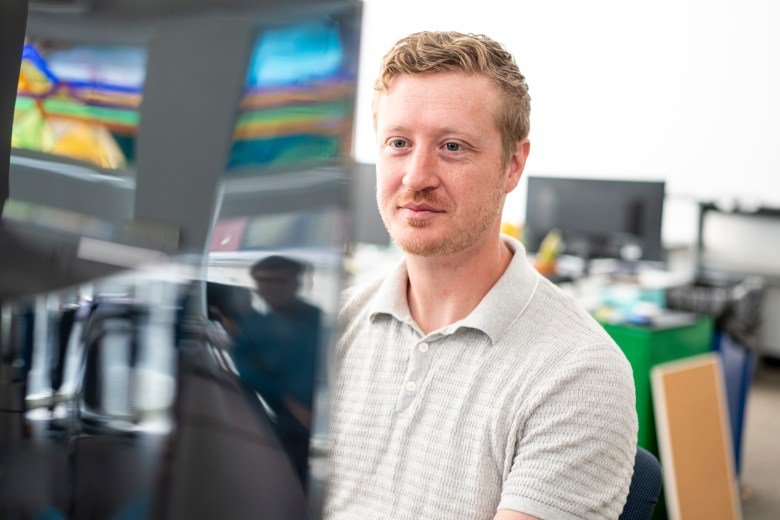

“Every year, 3,000 of the smartest people in the world come here, and a large proportion of those are international,” he said of Carnegie Mellon’s graduate students. “Some of them go into the research laboratories and work on new ideas, and some come having ideas already. You have fantastic students who are here to help you build your company or to be entrepreneurs themselves.”
Boosters of the city’s tech-driven turnaround say what’s been happening in Pittsburgh is largely unappreciated elsewhere. It followed the effective collapse of the steel industry in the 1980s, when unemployment hit 18 percent.
In 2006, Google opened a small office at Carnegie Mellon to take advantage of the faculty and student expertise in computer science and other fields there and at neighboring higher education institutions; the company later moved to a nearby former Nabisco factory and expanded its Pittsburgh workforce to 800 employees. Apple, software and AI giant SAP and other tech firms followed.
“It was the talent that brought them here, and so much of that talent is international,” said Audrey Russo, CEO of the Pittsburgh Technology Council.
Sixty-one percent of the master’s and doctoral students at Carnegie Mellon come from abroad, according to the university. So do 23 percent of those at Pitt, an analysis of federal data shows.
Related: International students are rethinking coming to the US. That’s a problem for colleges
The city has become a world center for self-driving car technology. Uber opened an advanced research center here. The autonomous vehicle company Motional — a joint venture between Hyundai and the auto parts supplier Aptiv — moved in. So did the Ford- and Volkswagen-backed Argo AI, which eventually dissolved, but whose founders went on to create the Pittsburgh-based self-driving truck developer Stack AV. The Ford subsidiary Latitude AI and the autonomous flight company Near Earth Autonomy also are headquartered in Pittsburgh.
Among other tech firms with homes here: Duolingo, which has 830 employees and is worth an estimated $22 billion. It was co-founded by a professor at Carnegie Mellon and a graduate of the university who both came to the United States as international students, from Guatemala and Switzerland, respectively.
InnovatePGH tracks 654 startups that are smaller than those big conglomerates but together employ an estimated 25,000 workers. Unemployment in Pittsburgh (3.5 percent in April) is below the national average (3.9 percent). Now Pitt and others are developing Hazelwood Green, which includes a former steel mill that closed in 1999, into a new district housing life sciences, robotics and other technology companies.
In a series of webinars about starting businesses, offered jointly to students at Pitt and Carnegie Mellon, the most popular installment is about how to found a startup on a student visa, said Rhonda Schuldt, director of Pitt’s Big Idea Center, in a storefront on Forbes Avenue in the Innovation District.

Some international undergraduates continue into graduate school or take jobs with companies that sponsor them so they can keep working on their ideas, Schuldt said.
“They want to stay in Pittsburgh and build businesses here,” she said.
There are clear worries that this momentum could come to a halt if the supply of international students continues a slowdown that began even before the new Trump term, thanks to visa processing delays and competition from other countries.
The number of international graduate students dropped in the fall by 2 percent, before the presidential election, according to the Institute of International Education. Further declines are expected following the government’s pause on student visa interviews, publicity surrounding visa revocations and arrests and cuts to federal research funding.

It’s too early to know what will happen this fall. But D. Sole co-founder Saisri Akondi has heard from friends who planned to come to the United States that they can’t get visas. “Most of these students wanted to start companies,” she said.
“I would be lying if I said nothing has changed,” said Akondi, who has been accepted into a master’s degree program in business administration at the Stanford University Graduate School of Business under her existing student visa, though she said her company will stay in Pittsburgh. “The fear has increased.”
This could affect whether tech companies continue to come to Pittsburgh, said Russo, at least unless and until more Americans are better prepared for and recruited into tech-related graduate programs. That’s something universities have not yet begun to do, since the unanticipated threat to their international students erupted only in March, and that would likely take years.

“Who’s going to do the research? Who’s going to be in these teams?” asked Russo. “We’re hurting ourselves deeply.”
The impact could transcend the research and development ecosystem. “I think we’ll see almost immediate ramifications in Pittsburgh in terms of higher-skilled, higher-wage companies hiring here,” said Sean Luther, at InnovatePGH. “And that affects the grocery shops, the barbershops, the real estate.”
There are other, more nuanced impacts.

“Whether we like it or not, it’s a global world. It’s a global economy. The problems that these students want to solve are global problems,” Schuldt said. “And one of the things that is really important in solving the world’s problems is to have a robust mix of countries, of cultures — that opportunity to learn how others see the world. That is one of the most valuable things students tell us they get here.”
Pittsburgh is a prime example of a place whose economy is vulnerable to a decline in the number of international students, said Brookings’ Muro. But it’s not unique.
“These scholars become entrepreneurs. They’re adding to the U.S. economy new ideas and new companies,” he said. Without them, “the economy would be smaller. Research wouldn’t get done. Journal articles wouldn’t be written. Patents wouldn’t be filed. Fewer startups would occur.”
The United States, said Muro, “has cleaned up by being the absolute central place for this. The system has been incredibly beneficial to the United States. The hottest technologies are inordinately reliant on these excellent minds from around the world. And their being here is critical to American leadership.”
Contact writer Jon Marcus at 212-678-7556, jmarcus@hechingerreport.org or jpm.82 on Signal.
This story about international students was produced by The Hechinger Report, a nonprofit, independent news organization focused on inequality and innovation in education. Sign up for our higher education newsletter. Listen to our higher education podcast.
Education
First week ‘critical’ to avoid children missing school later, parents told

Hazel ShearingEducation correspondent
 Getty Images
Getty ImagesPupils in England who missed school during the first week back in September 2024 were more likely to miss large parts during the rest of the year, figures suggest.
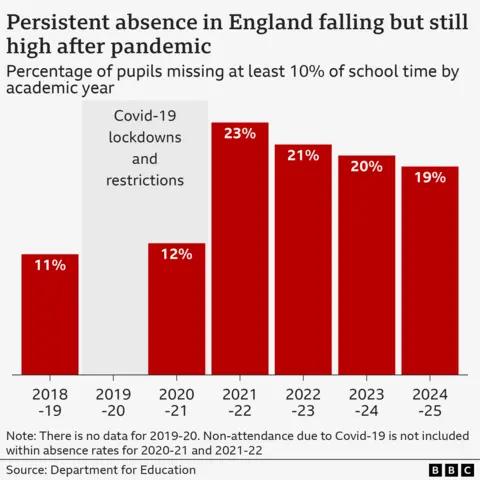
More than half (57%) of pupils who were partially absent in week one became “persistently absent” – missing at least 10% of school, according to government data first seen by the BBC.
By contrast, of pupils who fully attended the first week, 14% became persistently absent.
Education Secretary Bridget Phillipson said schools and parents should “double down” to get children in at the start of the 2025 term, which is this week for most English schools.
A head teachers’ union said more support was needed “outside of the school gates” to boost attendance.
Schools have always grappled with attendance issues, but they became much worse after the pandemic in 2020 and schools closed to most pupils during national lockdowns.
Attendance has improved since, but it remains a bigger problem than before Covid.
Overall, about 18% of pupils were persistently absent in the 2024-25 school year, down from a peak of 23% in 2021-22 but higher than the pre-Covid levels of about 11%.
The Department for Education (DfE) said the data from the first week of the 2024-25 school year showed the start of term was “critical” for tackling persistent absence.
Karl Stewart, head teacher at Shaftesbury Junior School in Leicester, said his school’s attendance rates were higher than average and but there was a “definite dip” in the two years after Covid.
“I get why. Some of that wasn’t necessarily parents not wanting to send them in. It was because either they had got Covid or other things, they were saying, ‘We’ll just keep them off now to be sure’,” he said.
The school has incentives like awards and class competitions to keep absence rates down, and Mr Stewart said attendance had more or less returned to pre-Covid levels.
“When we have the children in every day the results are just better,” he said.
“If you’re here, that gives you more time for your teacher to notice you, for us to see all that good behaviour [and] that really hard work – and that’s what we want.”
But, like lots of schools, he said some parents still took their children on unauthorised term-time holidays to make the most of cheaper costs.
Others, he said, have taken children for medical treatments overseas to avoid NHS waiting lists.

The education secretary said that while attendance improved last year, absence levels “remain critically high, putting at risk the life chances of a whole generation of young people”.
“Every day of school missed is a day stolen from a child’s future,” Phillipson said.
“As the new term kicks off, we need schools and parents to double down on the energy, the drive and the relentlessness that’s already boosted the life chances of millions of children, to do the same for millions more.”
The DfE said 800 schools were set to be supported by regional school improvement teams – through attendance and behaviour hubs.
These hubs are made up of 90 exemplary schools which will offer support to improve struggling schools through training sessions, events and open days.
It said it had appointed the first 21 schools that will lead the programme.
However, Pepe Di’Iasio, general secretary of the Association of School and College Leaders, said attendance hubs were not a “silver bullet” and a more “strategic approach” was needed.
“I think the government has worked really hard to improve attendance and it continues to be a priority for them, but there’s certainly more to do,” he told the BBC.
“So many of the challenges that [school leaders] are facing come from beyond the school gates – children suffering with high levels of anxiety, issues around mental health.”
He said school leaders wanted quicker access to support for those pupils and specialist staff in schools, but pupils also needed “great role models” in the community through youth clubs and volunteer groups.
The Conservatives said Labour’s Schools Bill had dismantled a “system that has driven up standards for decades”.
Shadow education secretary Laura Trott said: “Behaviour and attendance are two of the biggest challenges facing schools and it’s about time the government acted.”
She added: “There must be clear consequences for poor behaviour not just to protect the pupils trying to learn, but to recognise when mainstream education isn’t the right setting for those causing disruption.”
Additional reporting by Nathan Standley
Education
AI in the classrooms: How Bangladeshi schools are adapting to a new digital era
The recent explosion of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has pervaded numerous industries, going from a futuristic concept to an everyday reality. However, the impact of AI on schooling has been exceptionally staggering.
From helping students complete assignments to reshaping the way teachers think about homework and exams, AI is beginning to redefine education all over the world.
Bangladesh is no different.
Artificial Intelligence isn’t just coming to Bangladeshi classrooms—it’s already here. While its promise of convenience and quick solutions is quite alluring to students, the ever-growing presence of AI in schools has raised difficult questions: is learning actually taking place anymore or is it being replaced by answers generated not from thought, but from machines?
In schools across Bangladesh, AI tools like ChatGPT have quietly revolutionised how students complete their homework, how teachers prepare lessons, and how institutions rethink education altogether.
Is it a blessing or a bane?
Students have quickly adapted to using advanced AI chatbots like ChatGPT, making AI an unavoidable and integral part of academic life. From essays to homework, students are increasingly finding ways to rely on AI not just to work faster, but to sidestep studying altogether.
Many schools and educators have now been forced to accept that resisting AI is no longer an option. Schools must adapt to the new reality or risk becoming redundant.
Yafa Rahman, Vice Principal and Senior Business Studies Teacher of Adroit International School, told The Business Standard, “Talks about integrating AI in the school curriculum is a global concern, and my school has had meetings with Pearson Education on how to do that in the best possible manner as well as train teachers to use AI in a beneficial way while being able to spot unethical AI use. This is an ongoing discussion, and we will see many changes soon.”
Yafa explained that her school also employs AI tools to structure assignments and class content. Rather than banning AI altogether, she believes in channelling students’ fascination with technology into meaningful learning. “Students rely on technology so much that if we incorporate any technology into the learning process, students instantly become more interested,” she said.
Rethinking the curriculum
The convenience of AI comes with a heavy cost. Teachers are reporting a surge in AI-generated assignments. Entire essays, reports, and even personal reflections are being turned in with no human touch. And it’s getting harder to spot the difference.
Educators have responded by rethinking the very structure of education in the country. Oral assessments, in-class essays, and presentations have become increasingly common, as schools seek to test students’ independent thinking rather than their ability to reproduce AI-generated answers.
“For assignments meant to show knowledge and understanding, I’ve returned to using pencil and paper to prevent AI use. For reflective assignments, I encourage students to use AI but remind them to think critically. You do not always have to agree with what AI generated, and key facts and figures must be checked with reliable sources,” said Olivier Gautheron, a Science Teacher at International School Dhaka (ISD) who has earned the “AI Essentials for Educators” certification from Edtech Teachers in the US.
This hybrid approach reflects a wider consensus among educators that AI should not be ignored but incorporated responsibly, encouraging students to refine their critical faculties alongside their digital literacy.
It’s no longer just about stopping AI from being used. It’s about guiding how it’s used.
AI detection
Detecting AI-generated work isn’t straightforward. In universities, plagiarism software and AI detectors are standard. But in schools, teachers often rely on their personal knowledge of each student’s writing style and capability, using their instincts to identify when a student’s writing does not look like their own.
But Gautheron warns against over-reliance on intuition, preferring restraint over wrongful accusations.
“I believe it all comes down to knowing your students and their abilities,” he said. “There’s a high chance of mistakenly identifying student work as AI-generated when it’s not.”
He recalled an incident when he suspected a student of using AI, only to learn that the child had simply used software to improve grammar without altering the ideas. “This is perfectly acceptable, as the purpose of the assignment was for students to generate their own ideas,” he added.
He believes the solution lies not in advanced software but in dialogue. “Although software exists to detect AI, there are other softwares to make them undetectable. I believe that the best way to detect inappropriate use of AI is asking your students directly. If I feel that a student’s work quality is very different from previous tasks, simply asking them to clarify a few ideas of their work is enough.”
For resource-constrained schools, this approach is also pragmatic, since not every institution can afford detection software.
AI for teachers
Just like students, teachers are also increasingly turning to AI for lesson planning and content creation
Emran Taher, Cambridge examiner and senior English instructor at Mastermind School, sees AI as a game-changer.
“It is not just the students who use AI. Teachers and schools are using it too. I can keep my syllabus up-to-date and incorporate more relevant topics and examples instead of just relying on textbooks. This helps grab students’ interest while reducing issues like bunking classes.”
He also uses AI for personalised instruction. By feeding student data—age, class level, strengths, and weaknesses—into AI tools, he receives tailored recommendations that help him address individual needs. “There are no bad students, only bad teachers,” he said.
Striking the right balance
AI’s presence in schools reveals a tension: the same tool that can personalise learning and spark creativity can also be used to bypass real thinking. This balancing act between embracing innovation and preserving the essence of education appears to be the defining challenge of AI use.
However, there is no turning back. AI is already embedded in how schools operate. What matters now is how educators choose to respond. As Bangladeshi schools navigate this shift, teacher training, investment in digital infrastructure, and the development of ethical guidelines will all be crucial.
Some see AI as a threat to academic honesty. Others see it as a catalyst for overdue change in the old, rigid education system. But everyone realises that the role of teachers must evolve to address the new digital landscape.
-
Tools & Platforms3 weeks ago
Building Trust in Military AI Starts with Opening the Black Box – War on the Rocks
-

 Ethics & Policy1 month ago
Ethics & Policy1 month agoSDAIA Supports Saudi Arabia’s Leadership in Shaping Global AI Ethics, Policy, and Research – وكالة الأنباء السعودية
-

 Events & Conferences3 months ago
Events & Conferences3 months agoJourney to 1000 models: Scaling Instagram’s recommendation system
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoThe Guardian view on Trump and the Fed: independence is no substitute for accountability | Editorial
-

 Jobs & Careers2 months ago
Jobs & Careers2 months agoMumbai-based Perplexity Alternative Has 60k+ Users Without Funding
-

 Funding & Business2 months ago
Funding & Business2 months agoKayak and Expedia race to build AI travel agents that turn social posts into itineraries
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoVEX Robotics launches AI-powered classroom robotics system
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoHappy 4th of July! 🎆 Made with Veo 3 in Gemini
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoOpenAI 🤝 @teamganassi
-

 Mergers & Acquisitions2 months ago
Mergers & Acquisitions2 months agoDonald Trump suggests US government review subsidies to Elon Musk’s companies