Tools & Platforms
Tech Giants Invest Billions in AI Infrastructure Boom

In the heart of Silicon Valley, the race to dominate artificial intelligence is accelerating at a breakneck pace, with tech giants pouring unprecedented sums into infrastructure and development. Recent earnings reports from major players like Microsoft, Meta, Amazon, and Alphabet reveal a collective commitment to AI that is reshaping corporate budgets and investor expectations. This surge in spending is not just about keeping up; it’s a strategic bet on AI as the next foundational technology, akin to the internet or cloud computing.
Microsoft, in particular, has emerged as a frontrunner, reporting robust revenue growth driven by its AI initiatives. In its latest quarterly earnings, the company highlighted how Azure, its cloud platform, is benefiting from AI demand, with revenues soaring. This comes amid announcements of massive capital expenditures aimed at expanding data centers equipped for AI workloads.
Escalating Investments in AI Infrastructure
According to a report from CNBC, Microsoft anticipates spending $80 billion on AI-enabled data centers in fiscal 2025, with over half of that investment targeted within the U.S. This figure represents a significant uptick from previous years, underscoring the company’s confidence in AI’s revenue potential. Brad Smith, Microsoft’s Vice Chair and President, emphasized in a blog post on Microsoft On the Issues that this spending is key to harnessing AI’s transformative power for economic growth and global leadership.
Industry-wide, the trend is even more pronounced. A post on X from analyst Beth Kindig noted Microsoft’s $80 billion projection, up nearly 60% from 2024, while another from Tsarathustra highlighted comparative spending: Amazon at $65 billion, Google at $49 billion, and Meta at $31 billion over the past year. These investments are fueling a boom in data center construction, chip procurement, and software development, as companies vie for supremacy in generative AI and machine learning applications.
Microsoft’s Revenue Boom from AI
Delving into Microsoft’s financials, the company’s AI business has surpassed an annual revenue run rate of $13 billion, marking a 175% year-over-year increase, as stated by CEO Satya Nadella in a recent earnings call summarized on X by Quartr. Azure’s growth stands out, with a 31% rise, contributing to overall revenue climbing 12% and earnings before interest and taxes up 17%. This performance is detailed in a New York Times article, which notes a $27.2 billion quarterly profit, alleviating investor concerns about the payoff from hefty AI investments.
Yet, this spending spree isn’t without risks. As reported in WebProNews, Big Tech’s collective $344 billion outlay for 2025 focuses on data centers and chips, but faces hurdles like regulatory scrutiny and energy demands. Despite these, tangible returns are emerging, particularly in healthcare and productivity tools, signaling that the AI bubble fears may be overstated.
Comparative Spending Across Tech Titans
Looking beyond Microsoft, Meta’s projected $65 billion in capital expenditures for 2025, as mentioned in X posts from Oguz O. and Flows Invest, reflects a similar all-in approach. Amazon’s $97 billion and Google’s $70 billion add to a hyperscaler total nearing $320 billion, primarily for AI infrastructure. A Gizmodo article titled “Silicon Valley’s AI Spend Goes Berserk as Microsoft Starts Cashing In” captures this frenzy, noting how quarterly earnings from these firms are tied by booming AI investments, with Microsoft beginning to reap substantial rewards.
Silicon Valley’s AI fervor is also evident in stock movements. Microsoft’s shares surged following its earnings, as covered by Silicon Valley, with the company planning over $30 billion in quarterly spending on AI data centers. This has propelled Microsoft toward a $4 trillion valuation, per an X post from Assad Dar, amid expectations of over $400 billion in industry-wide AI spend for 2025.
Implications for Industry and Economy
For industry insiders, this spending trend signals a shift toward AI-centric business models. Microsoft’s Copilot and Azure integrations are driving adoption across sectors, with cloud revenue hitting $168 billion annually, as per an X update from Marvin Labs. However, job cuts—9,000 at Microsoft alone, according to CEO Today Magazine—highlight the human cost of this pivot, balancing efficiency gains with workforce disruptions.
Economically, the U.S. stands to benefit, with much of the investment staying domestic. Yet, as Industry Leaders Magazine points out, this expansion is geared toward cloud and AI-driven growth, potentially widening the tech divide globally. Investors are watching closely, with AI’s promise of revolutionizing industries from healthcare to finance justifying the bets, even as total capex surges to $364 billion across Big Tech, per an X post from AFV GLOBAL.
Future Outlook and Challenges
Looking ahead, Microsoft’s guidance for fiscal 2025 anticipates double-digit revenue growth, with Intelligent Cloud revenues projected between $28.6 billion and $28.9 billion for Q1, as shared on X by Evan. This optimism is tempered by the need for sustained innovation and regulatory navigation. The company’s $100 billion-plus AI bet, including partnerships and acquisitions, positions it to lead, but competition from OpenAI-backed ventures and rivals like Google intensifies the stakes.
In conclusion, Silicon Valley’s AI spending bonanza, led by Microsoft’s revenue successes, marks a pivotal era. As these investments translate into real-world applications, the tech sector’s trajectory will define the next decade’s economic powerhouses, rewarding those who invest wisely while challenging laggards to catch up.
Tools & Platforms
AI stethoscope could detect heart conditions in seconds
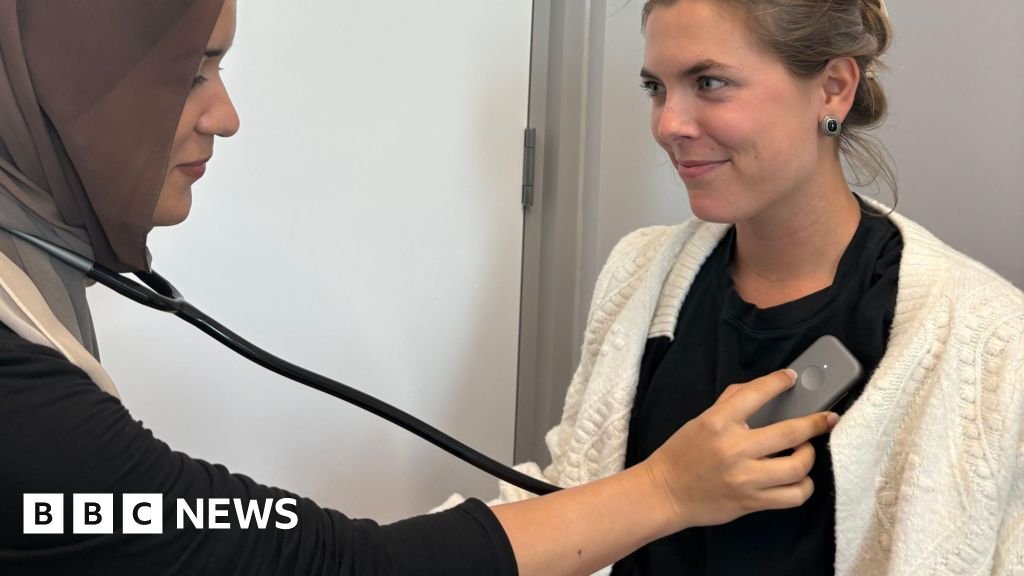
Stethoscopes powered by artificial intelligence (AI) could help detect three different heart conditions in seconds, researchers say.
The original stethoscope, invented in 1816, allows doctors to listen to the internal sounds of a patient’s body.
But now a British team have designed one that can spot heart failure, heart valve disease and abnormal heart rhythms almost instantly.
The breakthrough AI-powered tool could be a “real game-changer” resulting in patients being treated sooner, the researchers say, with plans to roll the device out across the country.
The new device replaces the traditional chest piece with a device around the size of a playing card. It uses a microphone to analyse subtle differences in heartbeat and blood flow that the human ear cannot detect.
The study by Imperial College London and Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust involved more than 200 GP surgeries in London.
More than 12,000 patients from 96 surgeries were examined with the AI stethoscope and were then compared to patients from 109 GP surgeries where the technology was not used.
Those examined with the device were 2.33 times more likely to be diagnosed with heart failure in the next 12 months, researchers said.
Abnormal heartbeat patterns, which have no symptoms but can increase stroke risk, were 3.5 times more detectable with the AI stethoscopes, while heart valve disease was 1.9 times more detectable.
Dr Sonya Babu-Narayan, clinical director at the British Heart Foundation (BHF) and consultant cardiologist, said: “This is an elegant example of how the humble stethoscope, invented more than 200 years ago, can be upgraded for the 21st century”.
Such innovations are vital “because so often this condition is only diagnosed at an advanced stage when patients attend hospital as an emergency”, she said.
“Given an earlier diagnosis, people can access the treatment they need to help them live well for longer.”
The findings have been presented to thousands of doctors at the European Society of Cardiology annual congress in Madrid, the world’s largest heart conference.
There are plans to roll out the new stethoscopes to GP practices in Wales, south London and Sussex.
Tools & Platforms
Taco Bell is having second thoughts about relying on AI at the drive-through

Taco Bell’s chief digital officer says the company is having an “active conversation” about when to use and not to use AI.
The company has apparently rolled out voice AI-powered ordering at more than 500 drive-throughs, leading to unflattering viral moments like someone ordering 18,000 water cups in order to “bypass” the AI and get connected to a human server.
Chief Digital and Technology Officer Dane Matthews told The Wall Street Journal that even he has mixed experiences with technology: “Sometimes it lets me down, but sometimes it really surprises me.”
Overall, it sounds like Taco Bell is still deciding how broadly to deploy AI at the drive-through, with leeway for different franchisees to do things their own way. For example, rather than relying on AI exclusively, Matthews said it might make sense to have a human handle drive-through orders at busy restaurants with long lines.
“For our teams, we’ll help coach them: at your restaurant, at these times, we recommend you use voice AI or recommend that you actually really monitor voice AI and jump in as necessary,” he said.
Tools & Platforms
Amazon blocks AI bots from major tech companies amid commerce battle

Amazon has intensified its campaign to block artificial intelligence companies from accessing its e-commerce platform, according to updates discovered on August 21, 2025, to the retail giant’s robots.txt file. The company recently added six more AI-related crawlers to its publicly available restrictions, targeting bots from Meta, Google, Huawei, Mistral and other technology firms.
According to independent analyst Juozas Kaziukėnas, who first spotted the changes, Amazon’s updated code now explicitly prohibits these companies from scraping data from the world’s largest online marketplace. “Amazon is desperately trying to stop AI companies from training models on its data,” Kaziukėnas wrote in a LinkedIn post on Thursday.
Subscribe PPC Land newsletter ✉️ for similar stories like this one. Receive the news every day in your inbox. Free of ads. 10 USD per year.
The August 21 update expands previous restrictions Amazon implemented at least a month earlier against crawlers from Anthropic’s Claude, Perplexity, and Google’s Project Mariner agents, according to The Information. These robots.txt files function as standard website instructions for automated crawlers, though restrictions operate on an advisory basis rather than as enforceable barriers.
Amazon maintains a $56 billion advertising business built around shoppers browsing its marketplace. The company generates revenue through sponsored product listings, display advertisements, and video content across its ecosystem. Third-party AI tools that bypass Amazon’s storefront could potentially undermine both website traffic and advertising revenue streams.
Kaziukėnas suggested the timing of these restrictions may be too late to prevent AI model training. “I think it is too late to stop AI training — Amazon’s data is already in the datasets ChatGPT and others are using,” he noted. “But Amazon is definitely not interested in helping anyone build the future of AI shopping. If that is indeed the future, Amazon wants to build it itself.”
The restrictions come as Amazon develops its own artificial intelligence shopping tools, including Rufus, a chatbot currently testing advertising features according to Adweek reporting from last year. Amazon has also been testing its own “buy-for-me” feature that can purchase items from third-party websites for customers, positioning the company to control how AI integrates with shopping on its platform.
Industry experts view these developments through the lens of competitive dynamics in AI-powered commerce. Eric Seufert, analyst at Mobile Dev Memo, argued on social media platform X that blocking AI agents serves Amazon’s business interests. “The fundamental flaw with ‘agentic commerce’ or ‘agentic advertising’ is that it violates the motivations of retail outlets to 1) control the customer relationship and 2) monetize their first-party data with advertising,” Seufert wrote on August 29.
Seufert emphasized that retail platforms lack commercial motivation to allow unrestricted third-party agent access. “Amazon and Shopify are blocking AI agents because they want to retain ownership of discovery,” he explained. “This natural inclination has surfaced repeatedly in history: walled gardens operate with more attractive economics than open advertising ecosystems because first-party privileges confer such significant commercial advantages.”
Advertising technology expert Karsten Weide offered a contrasting perspective on the long-term effectiveness of these blocking strategies. “Ultimately, blocking personal shopping bots will be a losing defensive battle,” Weide posted on X on August 30. “First it’s going to be drip drip drip in niches, giving competitive advantages to smaller, specialized retailers, but eventually it’ll turn into a stream, then a torrent.”
Weide predicted fundamental changes in consumer commerce patterns driven by AI agents. “A lot of consumer commerce will go through agents. Why would I spend a hour on the machine just to find the best offer for Brooks sneakers size 10?” he questioned. According to Weide’s analysis, brands will lose direct customer relationships but gain connections with “machine servants” that execute purchases on behalf of consumers.
The shift toward AI-mediated commerce could reshape advertising strategies, according to industry observers. Weide suggested that “D/R advertising will fade. Brand advertising will gain in importance as we want to influence consumers before they tell their agent what to do.” This transformation would prioritize brand awareness campaigns over direct response advertising formats that currently dominate digital marketing spending.
Shopify, Amazon’s primary competitor in e-commerce technology, has taken a different approach to AI agents. According to Modern Retail reporting from July, Shopify introduced warning language to merchants’ robots.txt files rather than outright blocking specific companies. Shopify’s “Robot & agent policy” requires “buy-for-me” agents to include human review steps and directs developers to integrate Shopify’s checkout technology into their tools.
Buy ads on PPC Land. PPC Land has standard and native ad formats via major DSPs and ad platforms like Google Ads. Via an auction CPM, you can reach industry professionals.
The e-commerce platform has also pursued partnership opportunities with AI companies. Shopify has partnered with Perplexity and reportedly is preparing to integrate with OpenAI to enable transactions through AI chatbots, according to The Financial Times. This collaborative approach contrasts with Amazon’s more restrictive stance toward third-party AI tools.
PPC Land previously reported that over 35% of leading websites now block OpenAI’s GPTBot, with varied blocking rates for other AI crawlers. The trend began shortly after OpenAI announced GPTBot on August 7, 2023, with major sites including Amazon, Quora, The New York Times, and CNN implementing blocks within two weeks.
Other major retailers have not followed Amazon’s approach to AI bot restrictions. Walmart and eBay have not made changes blocking AI bots from their sites, according to a review of their robots.txt files conducted by Modern Retail. This divergence suggests different strategic approaches to balancing competitive positioning with potential benefits from AI-powered shopping tools.
Recent analysis by HUMAN Security found that 80% of companies utilizing the cybersecurity firm’s platform chose to block known large language model user-agents outright. The report, published in July 2024, analyzed over one quadrillion online interactions throughout 2023, revealing widespread wariness among businesses toward AI-powered web crawlers.
The implications extend beyond immediate competitive concerns to fundamental questions about data ownership and monetization in the AI economy. As Seufert noted, “Retail platforms have no commercial motivation to allow third-party agents, broadly and without restriction, to browse their catalogue or to make purchases directly. If agentic commerce takes shape, it’s likely to occur through narrowly-scoped, explicit partnerships that tilt in favor of the platforms.”
Amazon’s approach reflects broader tensions in the technology industry over AI training data access. McKinsey’s Technology Trends Outlook 2025 identified agentic AI as the most significant emerging trend for marketing organizations, representing a shift toward autonomous systems that can independently manage complex workflows.
The effectiveness of robots.txt restrictions depends entirely on voluntary compliance from AI companies. Well-behaved crawlers typically respect these advisory blocks, but enforcement mechanisms remain limited. As Kaziukėnas observed, “Amazon is a treasure trove of e-commerce data. It is notable that Amazon seems to be the only one actively fighting this.”
Amazon’s stance becomes more significant considering the company’s own artificial intelligence investments. The company reported 22% growth in advertising revenue to $15.7 billion in Q2 2025, with substantial investments in AI-powered tools that optimize campaign performance while reducing operational complexity for advertisers.
The timing of Amazon’s expanded AI bot restrictions coincides with increasing regulatory attention on AI companies’ data collection practices. US Attorneys General from 44 jurisdictions recently warned artificial intelligence companies about accountability for exploitation of children through predatory AI products, demonstrating growing governmental oversight of AI development practices.
For the marketing community, these developments signal potential disruption to existing digital advertising models that rely on open data access and traditional customer acquisition funnels. As PPC Land has documented, the intersection of AI technology and advertising continues evolving rapidly, with platforms implementing new tools and restrictions that reshape how brands reach consumers.
The battle over AI access to e-commerce data reflects deeper questions about the future of online shopping and advertising. Whether Amazon’s defensive approach proves successful in maintaining its competitive position, or whether alternative pathways emerge for AI-powered shopping tools, will likely determine how consumers interact with digital commerce in the coming years.
Subscribe PPC Land newsletter ✉️ for similar stories like this one. Receive the news every day in your inbox. Free of ads. 10 USD per year.
Timeline
- August 7, 2023: OpenAI announces GPTBot, triggering widespread blocking by major websites within two weeks
- July 2024: Shopify introduces robots.txt warnings for merchants’ sites requiring human review for “buy-for-me” agents
- July 31, 2024: HUMAN Security reports 80% of companies block AI language models
- May 16, 2025: Amazon’s AI system begins scanning brand websites for compliance violations
- July 2025: Amazon blocks Anthropic’s Claude, Perplexity, and Google’s Project Mariner agents
- July 27, 2025: McKinsey identifies agentic AI as top trend reshaping marketing
- August 21, 2025: Amazon adds six more AI-related crawlers to robots.txt file, including Meta, Google, and Huawei
- August 29, 2025: Eric Seufert publishes analysis of “agentic commerce” fundamental flaws
- August 30, 2025: Karsten Weide predicts blocking shopping bots will be “losing defensive battle”
Subscribe PPC Land newsletter ✉️ for similar stories like this one. Receive the news every day in your inbox. Free of ads. 10 USD per year.
PPC Land explains
Robots.txt: A standard protocol file that websites use to communicate instructions to web crawlers and automated bots about which parts of their site should or should not be accessed. While these instructions operate on an advisory basis rather than enforceable restrictions, well-behaved crawlers typically respect these guidelines. Amazon’s robots.txt file serves as the primary mechanism for blocking AI companies from accessing its e-commerce data, though compliance depends entirely on voluntary cooperation from the crawlers.
AI Crawlers: Automated software programs deployed by artificial intelligence companies to systematically browse and collect data from websites for training large language models and other AI systems. These crawlers, such as OpenAI’s GPTBot, Anthropic’s Claude bot, and Google’s various AI agents, identify themselves when accessing websites, allowing site owners to make informed decisions about blocking or allowing access to their content.
Agentic Commerce: An emerging model where artificial intelligence agents autonomously conduct shopping activities on behalf of consumers, including product research, price comparisons, and purchase decisions. This concept represents a fundamental shift from traditional e-commerce where consumers directly interact with retail websites, potentially disrupting established customer acquisition and advertising models that depend on direct consumer engagement with brand websites.
E-commerce Data: The comprehensive information generated by online retail platforms, including product listings, pricing, customer reviews, inventory levels, and purchasing patterns. For Amazon, this data represents both a competitive advantage and the foundation of its advertising business, making it a valuable resource that AI companies seek to access for training models and developing shopping assistance tools.
First-party Data: Information that companies collect directly from their own customers through owned channels such as websites, mobile apps, and retail locations. Amazon’s first-party data includes shopping behaviors, preferences, and transaction history that enables targeted advertising and personalized experiences. This data becomes more valuable when companies can prevent third-party access and maintain exclusive relationships with customers.
Advertising Business: Amazon’s rapidly growing revenue stream that generated $15.7 billion in Q2 2025, representing 22% year-over-year growth. This business model relies on brands paying for sponsored product listings, display advertisements, and video content placement across Amazon’s ecosystem. The advertising business faces potential disruption if AI agents bypass Amazon’s storefront and reduce the platform’s ability to monetize customer discovery and purchase decisions.
Shopping Chatbot: AI-powered conversational interfaces that assist consumers with product discovery, recommendations, and purchase decisions. Amazon’s Rufus represents the company’s entry into this category, currently testing advertising features that could generate revenue while maintaining customer relationships. These tools compete directly with third-party AI shopping agents by providing similar assistance within the platform’s controlled environment.
Walled Gardens: Closed digital ecosystems where platforms maintain exclusive control over user data, advertising inventory, and customer relationships. Amazon operates as a walled garden by restricting third-party access to its customer data while developing internal tools that compete with external services. This approach generates more attractive economics compared to open systems because first-party privileges provide significant commercial advantages in advertising and data monetization.
Web Scraping: The automated process of extracting data from websites using software programs that systematically access and download information. AI companies use web scraping to collect training data from e-commerce platforms, though this practice faces increasing restrictions as websites implement blocking mechanisms. The effectiveness of scraping depends on whether target websites implement technical barriers and whether scrapers respect voluntary restrictions like robots.txt files.
Customer Relationship: The direct connection between brands or retailers and their customers, encompassing data collection, communication channels, and influence over purchase decisions. Amazon’s blocking of AI agents reflects concerns about losing customer relationships to intermediary services that could reduce the platform’s ability to collect first-party data and monetize customer interactions through advertising and personalized experiences.
Subscribe PPC Land newsletter ✉️ for similar stories like this one. Receive the news every day in your inbox. Free of ads. 10 USD per year.
Summary
Who: Amazon, the world’s largest e-commerce platform, implementing restrictions against AI companies including Meta, Google, Huawei, Mistral, Anthropic, and Perplexity.
What: Amazon added six more AI-related crawlers to its robots.txt file on August 21, 2025, expanding previous restrictions to prevent artificial intelligence companies from scraping e-commerce data from its marketplace.
When: The latest updates were discovered August 21, 2025, building on restrictions implemented at least a month earlier targeting other AI companies’ crawlers.
Where: Changes apply to Amazon’s publicly available robots.txt file that provides instructions to automated web crawlers attempting to access the retail giant’s sprawling website and marketplace.
Why: Amazon seeks to protect its $56 billion advertising business built around shoppers browsing its site while developing its own AI shopping tools like Rufus chatbot and “buy-for-me” features, preventing third-party AI tools from bypassing its storefront and undermining both traffic and ad revenue.
-
Tools & Platforms3 weeks ago
Building Trust in Military AI Starts with Opening the Black Box – War on the Rocks
-

 Ethics & Policy1 month ago
Ethics & Policy1 month agoSDAIA Supports Saudi Arabia’s Leadership in Shaping Global AI Ethics, Policy, and Research – وكالة الأنباء السعودية
-

 Events & Conferences3 months ago
Events & Conferences3 months agoJourney to 1000 models: Scaling Instagram’s recommendation system
-

 Jobs & Careers2 months ago
Jobs & Careers2 months agoMumbai-based Perplexity Alternative Has 60k+ Users Without Funding
-

 Funding & Business2 months ago
Funding & Business2 months agoKayak and Expedia race to build AI travel agents that turn social posts into itineraries
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoVEX Robotics launches AI-powered classroom robotics system
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoHappy 4th of July! 🎆 Made with Veo 3 in Gemini
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoOpenAI 🤝 @teamganassi
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoThe Guardian view on Trump and the Fed: independence is no substitute for accountability | Editorial
-

 Jobs & Careers2 months ago
Jobs & Careers2 months agoAstrophel Aerospace Raises ₹6.84 Crore to Build Reusable Launch Vehicle