AI Research
NIH Taps UT Southwestern Medical Center for $23M North Texas Alzheimer’s Disease Research Hub » Dallas Innovates

The leadership team for UT Southwestern’s new North Texas Alzheimer’s Disease Research Center includes principal investigator Dr. Ihab Hajjar (left), O’Donnell Brain Institute director Dr. William Dauer, and neurology chair Dr. Elan Louis. Their work will push the frontier of dementia research, as well as support community outreach and training for caregivers. [Photos: UT Southwestern Medical Center]
North Texas is the newest federal front line in the fight against Alzheimer’s and dementia.
The National Institute of Health has awarded UT Southwestern a $23 million, five-year grant from the National Institute on Aging to establish the North Texas Alzheimer’s Disease Research Center (ADRC). The designation makes it one of 37 such centers nationwide and the second in Texas, according to an announcement.
The new center, based at UT Southwestern Medical Center, will be a focal point for research that could reset how the disease is detected and treated. Scientists plan to probe how cardiometabolic conditions like high blood pressure accelerate dementia, train AI to hear vocal cues of cognitive decline, and build digital replicas of patients to test therapies.
Texas by the numbers
Texas, which is the nation’s second most populous state, has the third-highest number of Alzheimer’s patients, the second-highest Alzheimer’s-related deaths, and the highest dementia burden score, according to UTSW. The dementia burden score is a measure of the emotional and psychological toll on caregivers.
That reality, paired with UT Southwestern’s long-standing strength in neurology and its Peter O’Donnell Jr. Brain Institute, laid the groundwork for the designation.
Tackling cardiometabolic factors in dementia and more
Each Alzheimer’s Disease Research Center operates with a unique theme. In North Texas, the focus will be on advancing the national agenda by exploring how cardiometabolic factors, especially hypertension, contribute to Alzheimer’s and related dementias. Hypertension affects nearly 120 million Americans, according to UTSW.
The center also plans to use AI voice analysis to discover vocal changes that accompany cognitive decline. Researchers will develop “digital twin” technology to create virtual representations of patients, which will help distinguish between factors associated with normal aging and those linked to dementias, according to Dr. Ihab Hajjar, principal investigator of the new center.
“Being named an ADRC is not only an indication of scientific excellence, but also highlights an intentional commitment to research Alzheimer’s disease and cognitive impairment in our community,” said Hajjar, who is professor of neurology and internal medicine at UT Southwestern, in a statement.
Hajjar said the designation gives North Texas “the chance to make an unprecedented leap in understanding and treating Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias.”

Dr. Ihab Haijar [Photo: UT Southwestern Medical Center]
North Texas collaboration in the dementia fight
The designation is designed in collaboration with UT Dallas and UT Arlington.
The North Texas ADRC will not only enable new science but also “enhance scientific and clinical collaborations locally and nationally” while creating education opportunities for researchers, clinicians, and learners, according to UTSW.
Dr. William T. Dauer, director of the Peter O’Donnell Jr. Brain Institute, points to the new designation as proof of what can happen when institutions combine their strengths.
“This designation reflects the power of bringing together outstanding scientists, clinicians, and community partners to tackle one of the most urgent societal challenges,” Dauer said in the announcement. “It will strengthen our ability to link discoveries from O’Donnell Brain Institute laboratories with the needs of patients and families in North Texas and beyond, accelerating progress against Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias.”
Dr. Elan D. Louis, chair and professor of neurology and an investigator in the O’Donnell Brain Institute, noted that the ADRC reflects momentum already underway across his department.
“Our new ADRC reflects a growing emphasis in the Department of Neurology on learning about, understanding, and treating a group of disorders that affect millions of elderly people nationwide,” Louis said.
Feeding a national data engine for dementia research
The research generated by all ADRCs will feed into communal datasets that are made publicly available to spur collaboration and speed discovery. Hajjar said those shared efforts could offer “hope to patients with dementia and their loved ones.”
Dementia research is a core area within UTSW, and the new center builds on a decade of work by the O’Donnell Brain Institute.
UTSW also notes its No. 9 ranking for Neurology & Neurosurgery on U.S. News & World Report’s Best Hospitals list and 12 nationally ranked specialties, the most of any hospital in Texas. To date, its faculty have received six Nobel Prizes and include 24 members of the National Academy of Sciences, 23 members of the National Academy of Medicine, and 13 Howard Hughes Medical Institute Investigators.
Leadership brings specialized expertise
UTSW said the center’s leadership team brings long-standing expertise in neurological research with distinct but complementary focuses. Dr. Dauer holds the Lois C.A. and Darwin E. Smith Distinguished Chair in Neurological Mobility Research. Dr. Hajjar holds the Pogue Family Distinguished University Chair in Alzheimer’s Disease Clinical Research and Care, in Memory of Maurine and David Weigers McMullan. Dr. Louis holds the Linda and Mitch Hart Distinguished Chair in Neurology.
The ADRCs were established in 1984 as congressionally designated NIH Centers of Excellence. The mission includes improving detection, diagnosis, treatment, prevention, and care for patients and families. Each center tailors its theme to local populations and scientific priorities.
The North Texas center joins another Texas ADRC, a collaboration between UT Health San Antonio and The University of Texas Rio Grande Valley designated in 2021, strengthening the state’s role in national dementia research efforts.
Don’t miss what’s next. Subscribe to Dallas Innovates.
Track Dallas-Fort Worth’s business and innovation landscape with our curated news in your inbox Tuesday-Thursday.
AI Research
Coming for Your Job or Improving Your Performance?

Epic’s Electronic Medical Record and Ancillary Systems Release AI Upgrades
Epic Systems announced a host of artificial intelligence (AI) tools last month at its annual conference. With its more than 300 million patient records (in a country with <400 million people) and more than 3500 different hospital customers, Epic has either released or is currently working on more than 200 different AI tools.1
Their vast data stores are being used to create predictive models and train their own AI tools. The scale of Epic and AI and what it can be used for is both exciting and frightening.
Optimizing Tools to Reduce the Burden of Health Care Administration
Typically, Epic Systems and other technology solution providers’ first entry into AI implementation comes in the form of reducing menial tasks and attempting to automate patient-customer interactions. In my discussions with health care administrators, it is not uncommon for them to attribute 40% to 60% of the cost of health care to administrative tasks or supports. For every physician, there are generally at least 3 full-time equivalencies (workforce members) needed to support that physician’s work, from scheduling to rooming patients to billing and a host of other support efforts.
About the Author
Troy Trygstad, PharmD, PhD, MBA, is the executive director of CPESN USA, a clinically integrated network of more than 3500 participating pharmacies. He received his PharmD and MBA degrees from Drake University and a PhD in pharmaceutical outcomes and policy from the University of North Carolina. He has recently served on the board of directors for the Pharmacy Quality Alliance and the American Pharmacists Association Foundation. He also proudly practiced in community pharmacies across the state of North Carolina for 17 years.
Reducing Cost and Improving Patient-Customer Experience
Reducing administration should reduce costs. Early-entry AI tools are generally aimed at reducing administrative cost, while simultaneously improving the patient experience extramural to the care delivery process (the bump in customer experience is the side benefit, not the motivation). In fact, all of us are more likely to be assigned an AI assistant as a customer than to use one as a health care provider at this juncture. AI is currently deployed over multiple sectors and customer service scenarios, interacting with us indirectly in recent years and now more directly as time passes. Remember that Siri and Alexa continue to grow just like humans, and now there are thousands and thousands of these AI bots. There is a strong possibility that if you answer a spam phone call, the “person” on the other end of the line is an AI tool (being?) and not a human.
Will AI Be an Antidote to Health Care Professional Burnout?
Charting is a drag. Ask any medical provider and one of their least favorite tasks is writing patient encounters for documentation’s sake rather than for the sake of patient care. I’ve personally known hundreds of physicians over my 2 decades of collaborating with them and the majority do most of their charting during off hours (thanks to technology), eating into their work-life balance and wellbeing. A recent study of providers using AI tools for charting found a 40% reduction in documentation burden and better and more complete charting.2 Could AI reduce the burden of menial pharmacy tasks that take away from patient care as well? Very likely yes.
But what if the business model doesn’t change? The biggest lie ever told in pharmacy was that technology was going to free pharmacists to provide patient care without a subsequent workflow and economic model to support it. Therefore, our profession went from filling 150 prescriptions a day to 300 a day to, in some cases, up to 500 per day per pharmacist. The only thing the technology did was increase the throughput of the existing business model. It didn’t support a new model at all.
That is the concern of many physicians as well. Will AI merely increase the number of encounters expected of them or will it actually improve their care delivery and practice satisfaction? That’s a question explored in a recent Harvard Business School article that points to upcoding bias (documentation of higher levels of care to bill more revenue), reduction in administrative cost, and reduced clerical full-time equivalents as the seeming “wins” for health systems administrators thus far, rather than better and more cost-efficient care delivery overall.3 Unsurprisingly to pharmacists, the business model is driving AI use, not the desired practice model.
AI as the New “Peripheral Brain” and Decision Support System
Those of us of a certain age remember a time in pharmacy school when we first entered the practice world under the supervision of a preceptor. At that time, the “peripheral brain” was a notebook that contained the latest prescribing guidelines, infectious disease–drug matches, and other clinical information. Then along came a handheld electronic version of it. Then came Google. Then the implementation of cloud computing. And now AI.
AI is already in place for many physicians and other health care providers, and I fear pharmacy may actually be late to the game in an arms race to make the drug assessment–prescribing–filling process even more efficient. But efficient at what? Administrative tasks? Order entry? Prior authorization documentation?
What About the Effects on Health System and Community Pharmacy Practice?
What if the rest of the world views the practice of pharmacy as consisting entirely of administrative tasks and not assessment and care delivery? If the AI tool is the physician’s peripheral brain, why is there a need for the pharmacist to make recommendations or find drug therapy problems? If the AI tool is instructing the care manager on which medications the care team needs to gather information about and report back to the peripheral brain, why have a pharmacist on the team? There will be many who say, “Oh, AI will absolutely replace the need for pharmacists because they don’t (actually) deliver care. They are a means of medication distribution and a great source of knowledge of medications, but AI will be better at that.”
Too Little Discussion and Planning Not Underway in Pharmacy Circles
The AI takeover is not some distant future reality. The reality is weeks and months away, not years and decades. Nvidia (the chipmaker essential for AI processing) has seen its stock price rise more than 900% in the past 3 years as investors awaken to the speed with which AI is moving. AI is already starting to move from helper to replacement for many jobs and we could see AI agents doing research autonomously within 6 to 18 months and becoming the experts in every field of study known to humans by 2030 (or sooner).
What are we doing in the pharmacy world to prepare, take advantage of, and plant our flag as the medication optimization experts that utilize AI better than anyone else? As far as I can tell at this juncture, we’ve given AI a passing glance and are waiting for AI to come to us, rather than aligning and integrating with AI at the outset.
AI Could Be the Best and Worst Thing for Pharmacy. We Must Learn Lessons From the Past.
There is so much work to do, from regulatory discussions with our state boards of pharmacy to scoping the future of practice alongside technology solution providers to teaching the next generation of pharmacists as well as those already in practice about how to use AI to deliver safer, more effective, and more innovative care.
And above all, practice follows the business model. If provider status was important pre-AI, it has become critical post AI. If we are a profession of clerical work, we will be replaced. If we are a profession of providers, we will harness the immense capabilities of our future AI assistants. No more “This will save you time so you can care for patients” baloney, when there is no economic support model for care delivery sizable enough to employ a quarter of a million pharmacists. We should all be demanding to see evidence of the billable time from our employers, policy makers, and regulators. That is the only sustainable path when the peripheral brain is in the cloud and is the known universe’s best version of it.
REFERENCES
1. What health care provisions of the One Big Beautiful Bill Act mean for states. National Academy for State Health Policy. July 8, 2025. Accessed July 21, 2025. https://nashp.org/what-health-care-provisions-of-the-one-big-beautiful-bill-act-mean-for-states/
2. Graham J. The big, beautiful health care squeeze is here: what that means for your coverage. Investor’s Business Daily. July 18, 2025. Accessed July 21, 2025. https://www.investors.com/news/big-beautiful-bill-trump-budget-health-care-coverage/
3. Constantino AK. Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer to sell blockbuster blood thinner Eliquis at 40% discount. CNBC. July 17, 2025. Accessed July 21, 2025. https://www.cnbc.com/2025/07/17/bristol-myers-squibb-pfizer-to-sell-eliquis-at-40percent-discount.html
AI Research
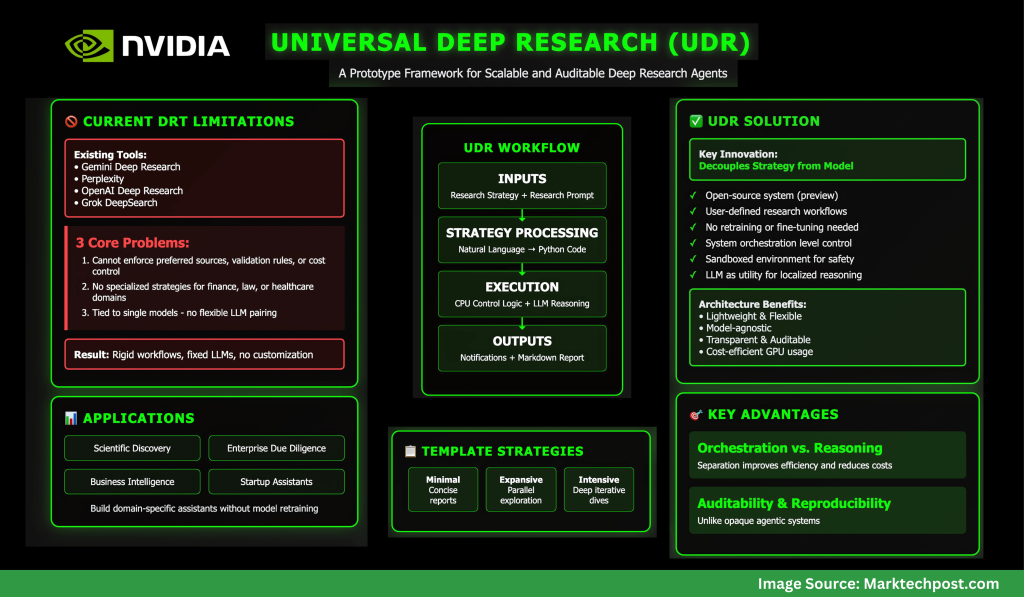
NVIDIA AI Releases Universal Deep Research (UDR): A Prototype Framework for Scalable and Auditable Deep Research Agents
Why do existing deep research tools fall short?
Deep Research Tools (DRTs) like Gemini Deep Research, Perplexity, OpenAI’s Deep Research, and Grok DeepSearch rely on rigid workflows bound to a fixed LLM. While effective, they impose strict limitations: users cannot define custom strategies, swap models, or enforce domain-specific protocols.
NVIDIA’s analysis identifies three core problems:
- Users cannot enforce preferred sources, validation rules, or cost control.
- Specialized research strategies for domains such as finance, law, or healthcare are unsupported.
- DRTs are tied to single models, preventing flexible pairing of the best LLM with the best strategy.
These issues restrict adoption in high-value enterprise and scientific applications.
What is Universal Deep Research (UDR)?
Universal Deep Research (UDR) is an open-source system (in preview) that decouples strategy from model. It allows users to design, edit, and run their own deep research workflows without retraining or fine-tuning any LLM.
Unlike existing tools, UDR works at the system orchestration level:
- It converts user-defined research strategies into executable code.
- It runs workflows in a sandboxed environment for safety.
- It treats the LLM as a utility for localized reasoning (summarization, ranking, extraction) instead of giving it full control.
This architecture makes UDR lightweight, flexible, and model-agnostic.
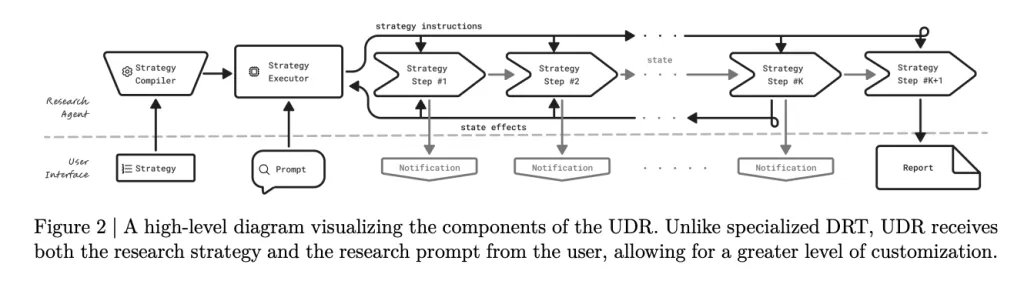
How does UDR process and execute research strategies?
UDR takes two inputs: the research strategy (step-by-step workflow) and the research prompt (topic and output requirements).
- Strategy Processing
- Natural language strategies are compiled into Python code with enforced structure.
- Variables store intermediate results, avoiding context-window overflow.
- All functions are deterministic and transparent.
- Strategy Execution
- Control logic runs on CPU; only reasoning tasks call the LLM.
- Notifications are emitted via
yieldstatements, keeping users updated in real time. - Reports are assembled from stored variable states, ensuring traceability.
This separation of orchestration vs. reasoning improves efficiency and reduces GPU cost.
What example strategies are available?
NVIDIA ships UDR with three template strategies:
- Minimal – Generate a few search queries, gather results, and compile a concise report.
- Expansive – Explore multiple topics in parallel for broader coverage.
- Intensive – Iteratively refine queries using evolving subcontexts, ideal for deep dives.
These serve as starting points, but the framework allows users to encode entirely custom workflows.

What outputs does UDR generate?
UDR produces two key outputs:
- Structured Notifications – Progress updates (with type, timestamp, and description) for transparency.
- Final Report – A Markdown-formatted research document, complete with sections, tables, and references.
This design gives users both auditability and reproducibility, unlike opaque agentic systems.
Where can UDR be applied?
UDR’s general-purpose design makes it adaptable across domains:
- Scientific discovery: structured literature reviews.
- Enterprise due diligence: validation against filings and datasets.
- Business intelligence: market analysis pipelines.
- Startups: custom assistants built without retraining LLMs.
By separating model choice from research logic, UDR supports innovation in both dimensions.
Summary
Universal Deep Research signals a shift from model-centric to system-centric AI agents. By giving users direct control over workflows, NVIDIA enables customizable, efficient, and auditable research systems.
For startups and enterprises, UDR provides a foundation for building domain-specific assistants without the cost of model retraining—opening new opportunities for innovation across industries.
Check out the PAPER, PROJECT and CODE. Feel free to check out our GitHub Page for Tutorials, Codes and Notebooks. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 100k+ ML SubReddit and Subscribe to our Newsletter.
Asif Razzaq is the CEO of Marktechpost Media Inc.. As a visionary entrepreneur and engineer, Asif is committed to harnessing the potential of Artificial Intelligence for social good. His most recent endeavor is the launch of an Artificial Intelligence Media Platform, Marktechpost, which stands out for its in-depth coverage of machine learning and deep learning news that is both technically sound and easily understandable by a wide audience. The platform boasts of over 2 million monthly views, illustrating its popularity among audiences.
AI Research
GAO Review Finds 94 Federal AI Adoption Requirements
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoThe Guardian view on Trump and the Fed: independence is no substitute for accountability | Editorial
-
Tools & Platforms4 weeks ago
Building Trust in Military AI Starts with Opening the Black Box – War on the Rocks
-

 Ethics & Policy2 months ago
Ethics & Policy2 months agoSDAIA Supports Saudi Arabia’s Leadership in Shaping Global AI Ethics, Policy, and Research – وكالة الأنباء السعودية
-

 Events & Conferences4 months ago
Events & Conferences4 months agoJourney to 1000 models: Scaling Instagram’s recommendation system
-

 Jobs & Careers2 months ago
Jobs & Careers2 months agoMumbai-based Perplexity Alternative Has 60k+ Users Without Funding
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoHappy 4th of July! 🎆 Made with Veo 3 in Gemini
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoMacron says UK and France have duty to tackle illegal migration ‘with humanity, solidarity and firmness’ – UK politics live | Politics
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoVEX Robotics launches AI-powered classroom robotics system
-

 Funding & Business2 months ago
Funding & Business2 months agoKayak and Expedia race to build AI travel agents that turn social posts into itineraries
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoOpenAI 🤝 @teamganassi



![Organoids without blood vessels can't grow larger than sesame seeds—about 3 millimeters—before dying from lack of oxygen and nutrients. UNT and Stanford researchers say they've solved this problem. Seeds pictured above are not to scale. [Image: Pinchai Puntong/istockphoto]](https://aistoriz.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/Sesame-Seed-organoid-science-iStock-1487667097-970x464.jpg)