AI Insights
Let AI Decide Whether You Should Be Covered or Not

Donald Trump says he is Making America Great Again, which seems like it might be code for: making everything shittier, less affordable, and less efficient. Certainly, when it comes to the realm of public services, the White House seems to be doing everything in its power to make the century-old social welfare programs—like Social Security and Medicare—significantly less helpful.
The latest unfortunate example of this unfurled itself this week with the announcement of a new pilot program being trialed by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. The pilot, which the New York Times reports is scheduled to begin next year in six different states, will use artificial intelligence software to determine whether certain kinds of coverage are “appropriate” or not. In a press release on the agency’s website that feels very DOGE-like, the CMS notes that its new program will “Target Wasteful, Inappropriate Services in Original Medicare.” It reads:
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) is announcing a new Innovation Center model aimed at helping ensure people with Original Medicare receive safe, effective, and necessary care.
Yes, you wouldn’t want to have unnecessary care, would you? That would be terrible. The press release continues:
Through the Wasteful and Inappropriate Service Reduction (WISeR) Model, CMS will partner with companies specializing in enhanced technologies to test ways to provide an improved and expedited prior authorization process relative to Original Medicare’s existing processes, helping patients and providers avoid unnecessary or inappropriate care and safeguarding federal taxpayer dollars.
Prior authorization is the process whereby medical providers are required to check with insurance companies before providing certain types of care. Traditionally, folks enjoying public benefits with Original Medicare do not need to worry about this sort of thing, but for those using the more “modernized” program, Medicare Advantage, they seem to be getting hit with it all the time. In this case, recipients who are receiving Original Medicare will still be subjected to prior authorization through the pilot program. The AI algorithms will be used to determine whether the care recipients are getting represents an “appropriate” expenditure of “federal taxpayer dollars.” This is all packaged by the government as if it’s doing you some sort of favor. The press release states:
The WISeR Model will test a new process on whether enhanced technologies, including artificial intelligence (AI), can expedite the prior authorization processes for select items and services that have been identified as particularly vulnerable to fraud, waste, and abuse, or inappropriate use.
The New York Times notes that algorithms of this sort have been subjected to litigation, while also noting that the AI companies involved “would have a strong financial incentive to deny claims,” and the new pilot has already been referred to as an “AI death panels” program. Gizmodo reached out to the government for information.
AI Insights
Bitcoin Proxy’s Chief Seeks Funding Fix as ‘Flywheel’ Falters
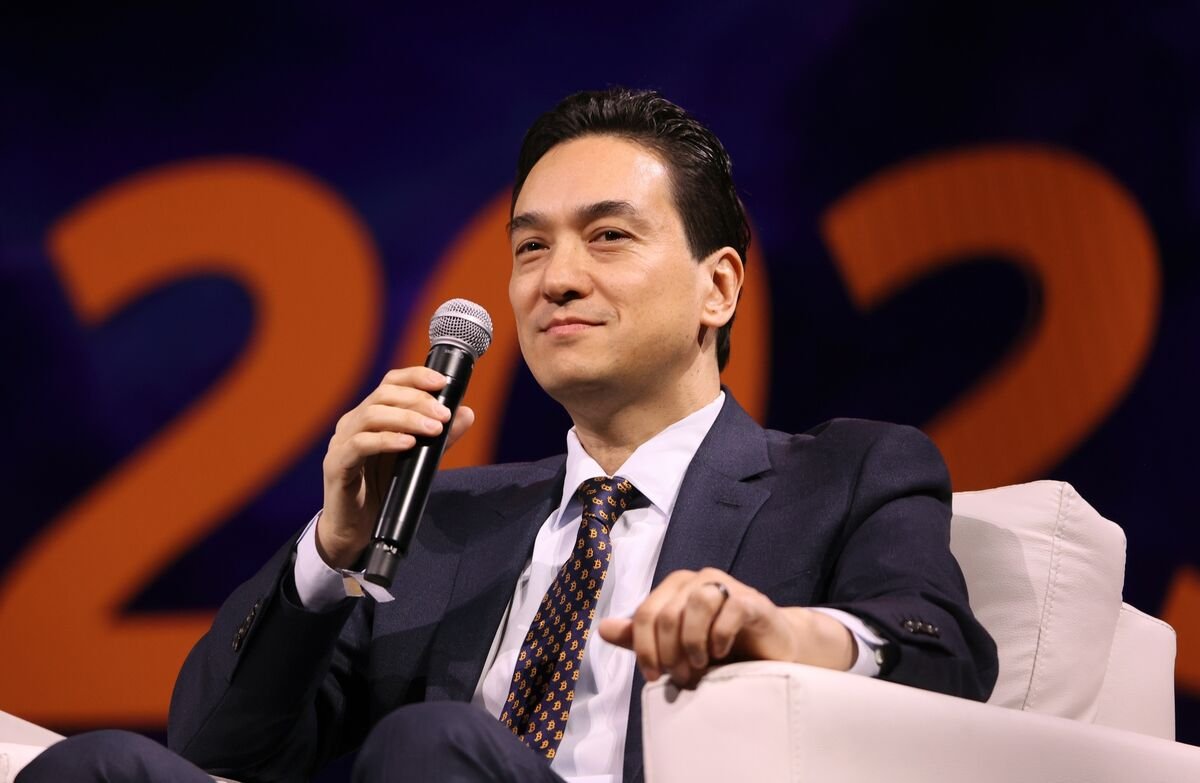

Simon Gerovich, who turned a struggling Japanese hotelier into a Bitcoin stockpiler and investor darling, is feeling the heat.
Source link
AI Insights
Anthropic Settles Landmark Artificial Intelligence Copyright Case

Anthropic’s settlement came after a mixed ruling on the “fair use” where it potentially faced massive piracy damages for downloading millions of books illegally. The settlement seems to clarify an important principle: how AI companies acquire data matters as much as what they do with it.
After warning both the district court and an appeals court that the potential pursuit of hundreds of billions of dollars in statutory damages created a “death knell” situation that would force an unfair settlement, Anthropic has settled its closely watched copyright lawsuit with authors whose books were allegedly pirated for use in Anthropic’s training data. Anthropic’s settlement this week in a landmark copyright case may signal how the industry will navigate the dozens of similar lawsuits pending nationwide. While settlement details remain confidential pending court approval, the timing reveals essential lessons for AI development and intellectual property law.
The settlement follows Judge William Alsup’s nuanced ruling that using copyrighted materials to train AI models constitutes transformative fair use (essentially, using copyrighted material in a new way that doesn’t compete with the original) — a victory for AI developers. The court held that AI models are “like any reader aspiring to be a writer” who trains upon works “not to race ahead and replicate or supplant them — but to turn a hard corner and create something different.”
(For readers unfamiliar with copyright law, “fair use” is a legal doctrine that allows limited use of copyrighted material without permission for purposes like criticism, comment, or — as courts are now determining — AI training. A key test is whether the new use “transforms” the original work by adding something new or serving a different purpose, rather than simply copying it. Think of it as the difference between a critic quoting a novel to review it versus someone photocopying the entire book to avoid buying it.)
After ruling in Anthropic’s favor on this issue, Judge Alsup drew a bright line at acquisition methods. Anthropic’s downloading of over seven million books from pirate sites like LibGen constituted infringement, the judge ruled, rejecting Anthropic’s “research purpose” defense: “You can’t just bless yourself by saying I have a research purpose and, therefore, go and take any textbook you want.”
The settlement’s timing suggests a pragmatic approach to risk management. While Anthropic could claim vindication on training methodology, defending its acquisition methods before a jury posed substantial financial exposure. Statutory damages for willful infringement can reach $150,000 per work, creating potential liability for Anthropic totaling in the billions.
Anthropic is still facing copyright suits from music publishers, including Universal Music Corp. and Concord Music Group Inc., as well as Reddit. The settlement with authors removes one of Anthropic’s many legal challenges. Lawyers for the plaintiffs said, “[t]his historic settlement will benefit all class members,” promising to announce details in the coming weeks.
This settlement solidifies the principles established in Judge Alsup’s prior ruling: how AI companies acquire training data matters as much as what they do with it. The court’s framework permits AI systems to learn from human cultural output, but only through legitimate channels.
For practitioners advising AI projects and companies, the lesson is straightforward: document data sources meticulously and ensure the legitimate acquisition of data. AI companies that previously relied on scraped or pirated content face strong incentives to negotiate licensing agreements or develop alternative training approaches. Publishers and authors gain leverage to demand compensation, even as the fair use doctrine limits their ability to block AI training entirely.
The Anthropic settlement marks neither a total victory nor a defeat for either side, but rather a recognition of the complex realities governing AI and intellectual property. It also remains to be seen what impact it will have on similar pending cases, including whether this will create a pattern of AI companies settling when facing potential class actions. In this new landscape, the legitimacy of the process matters as much as the innovation of the outcome. That balance will define the next chapter of AI development. Under Anthropic, it is apparent that to maximize chances of AI models constituting fair use, developers should use a bookstore, not a pirate’s flag.
AI Insights
AI-powered stethoscopes can detect 3 types of heart conditions within seconds, say researchers – Anadolu Ajansı
-
Tools & Platforms3 weeks ago
Building Trust in Military AI Starts with Opening the Black Box – War on the Rocks
-

 Ethics & Policy1 month ago
Ethics & Policy1 month agoSDAIA Supports Saudi Arabia’s Leadership in Shaping Global AI Ethics, Policy, and Research – وكالة الأنباء السعودية
-

 Events & Conferences3 months ago
Events & Conferences3 months agoJourney to 1000 models: Scaling Instagram’s recommendation system
-

 Jobs & Careers2 months ago
Jobs & Careers2 months agoMumbai-based Perplexity Alternative Has 60k+ Users Without Funding
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoThe Guardian view on Trump and the Fed: independence is no substitute for accountability | Editorial
-

 Funding & Business2 months ago
Funding & Business2 months agoKayak and Expedia race to build AI travel agents that turn social posts into itineraries
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoVEX Robotics launches AI-powered classroom robotics system
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoHappy 4th of July! 🎆 Made with Veo 3 in Gemini
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoOpenAI 🤝 @teamganassi
-

 Jobs & Careers2 months ago
Jobs & Careers2 months agoAstrophel Aerospace Raises ₹6.84 Crore to Build Reusable Launch Vehicle