Education
How Schools Are Helping Students Feel Safe Enough to Attend Class Amid Immigration Raids

From parents’ fraught decisions over whether they can safely send their children to class to reports of districts losing families to self-deportation, schools around the country are responding to the ripple effects touched off by the Trump administration’s aggressive immigration raids.
More specifically, they are trying to counteract the resulting fear that’s keeping students away from campuses — a continuation of what they saw in the spring as the immigration authorities ramped up apprehensions and deportations. Estimates put the number of K-12 students who did not have legal status in the U.S. at roughly 620,000 in 2021, about 1 percent of public school students.
Since the start of this new school year, education leaders and immigration advocacy groups have highlighted the challenges that schools and families are facing in light of ICE sweeps in their communities. Anxiety is higher following a recent Supreme Court decision allowing federal agents in Los Angeles to question people about their immigration status based solely on factors like their race, ethnicity or language spoken.
Speakers during recent panels hosted by America’s Voice and Advancement Project, an immigrants’ and civil rights organization, respectively, discussed what they believe should be schools’ role in ensuring parents and students feel safe.
The Effects of Fear
Fear caused by the visibility of immigration apprehensions can impact any child, clinical child psychologist Allison Bassett Ratto said during an America’s Voice panel, but immigrant children in particular are facing psychological harm. The resulting stress and trauma could be short- or long-term, she adds, and they can develop conditions like post-traumatic stress disorder whether they witness violence directly in person, or online.
“What they see are their classmates, their family members, their neighbors often being apprehended in violent and confusing ways while going about their daily lives, and this for children creates a sense that nowhere and no one is safe,” Bassett Ratto said. “Young children don’t understand who is at risk of being detained in this way, so this creates a sense of fear and worry that they or their families could be next.”
Noel Candelaria, the National Education Association’s secretary-treasurer and a special education teacher, said that children of immigrant parents feel unsafe in their own communities and “unsure of who they will find or not find when they get home from school.”
“Every student, cada estudiante, deserves to feel safe at school,” Candelaria said.
Alberto Carvalho, superintendent of the Los Angeles Unified School District, feels a personal connection to the issue. He’s spoken publicly about his experience living without legal status in the U.S. after graduating high school in his native Portugal. He was homeless in Miami for a time, eventually becoming a teacher and later superintendent of the Miami-Dade school district.
“As a once-undocumented immigrant, as someone who grew up in poverty and slept under a bridge, I cannot speak or address anyone without recognizing the impact that education has had on my life and that thousands of students are facing the same challenges and the same traumatic abuse I felt as a teenager alone in this country,” Carvalho said. “We are asserting the fundamental rights that belong to our children as prescribed and interpreted in the Constitution.”
Researchers have found that stress can impede normal childhood development, and instability like that caused by the Trump administration’s current immigration policies can interfere with children’s ability to focus and learn while in school.
“What we see in terms of school impacts is that when a child is managing trauma, anxiety or intense stress, it significantly impacts their ability to pay attention because that is like a vice on their brain,” Bassett Ratto said. “Fundamentally, it puts them in this fight or flight, the survival mode where math class or their band instructor is unfortunately moving to the back burner as they try and just get through their day over the long term.”
Fedrick Ingram, the American Federation of Teachers’ secretary-treasurer and a high school band director in Miami, described feeling a dissonance between the fear caused by immigration arrests and the normalcy of the school day.
“Unfortunately, we’re up against what we’ve not seen in the country in a long time, where we are traumatizing students and then asking them to go home and do school work in a traumatized situation,” Ingram said. “What many of our lawmakers have done is point fingers at our educators, point fingers at our students and say, ‘You didn’t pass this test,’ or ‘You didn’t do enough.’ They fail to understand these kids will bring those traumas to school and try to do the best they can, and we’re forcing them to try to process these things faster than they should, so shame on this administration.”
Attendance Struggles
Schools have a responsibility to protect students that goes beyond ensuring they can safely get into the building, Kristal Moore Clemons said. She is national director of the Children Defense Fund’s Freedom Schools program.
“This means superintendents, principals, school board members must establish clear procedures for how their staff should respond if ICE agents appear on school grounds,” she said during the Advancement Project panel. “This means taking the time to teach all students in all districts what their rights are if they are ever approached or questioned by immigration officials.”
Carvalho said that Los Angeles public schools have seen a slight enrollment dip, but concrete numbers on attendance won’t be available until mid-month. Prior to the school year’s start, he added, the district went on a communication blitz to reassure parents their children would be safe while en route to and inside their schools. The effort included adding more bus routes, increasing the number of mental health and legal aid professionals available to families, and helping parents understand their rights in case of an encounter with immigration agents.
“We prevented DHS agents from coming into our schools to talk to a first grader and second grader. What danger do elementary kids pose to national security?” he said. “I hope the community feels from us that we are that protective space, that our schools are those safe zones.”
Ingram noted that Miami-Dade County Public Schools saw enrollment drop by more than 13,000 students this fall, the result of not only immigration policy but also declining birth rates and families leaving for more affordable locales. The superintendent has promised not to lay off teachers as a result of any funding shortfalls.
“While we can’t attribute all of that to the immigration fight, we know that there’s a significant portion of people who are just not sending their students to school because of fear of deportation, because of fear of what will happen at home or because of tracing or what have you,” he said. “Where those dollar figures add up is there are fewer teachers, there are fewer programs and there’s less funding for students overall. And so anytime you get this particular kind of issue or this particular kind of trauma and stress to a school system, it hurts everybody from top to bottom.”
Adaku Onyeka-Crawford, director of the Opportunity to Learn Program at Advancement Project, said during a panel hosted by her organization that she’s seen families in the Washington, D.C., area show support by walking students to school in groups.
“They walk together to school to make sure that they get to school safely and aren’t afraid of being stopped or detained while just going to school,” Onyeka-Crawford said. “However, we don’t see that commitment coming from district leadership. We want them to make sure that these resources are available to all students, because we are just seeing that parents and school leadership need that support from the district and aren’t receiving it.”
Education
‘I regret pushing my daughter into school until she broke’

Ben SchofieldPolitics correspondent, BBC East
 Ben Schofield/BBC
Ben Schofield/BBCThe start of the school year saw the Education Secretary Bridget Phillipson warn parents about the need for children to attend classes.
Data suggests half of pupils who missed lessons in the first week of term last year went on to become persistently absent.
But school leaders say they are seeing more children who find attending school too traumatic.
What is it like having a child with what psychologists call emotionally based school avoidance and what should be done to help?
 Family handout
Family handoutThe final time Julie took her daughter to school in July 2023, a member of staff congratulated her.
Rosie, who was then eight, was “wearing a dirty pyjama top, a pair of jogging bottoms, a pair of trainers with no socks, she had her headphones on, she was holding a teddy”, Julie recalls.
“I walked into school and the [special needs co-ordinator] then said to me ‘well done, you got her here’.”
But for Julie, 48, it was not a “win”.
“She couldn’t even speak, she hadn’t eaten, she had maybe three or four hours sleep.
“But I’d done a good job as a parent for making her go to school?”
 Family handout
Family handoutAt the time Rosie, who has autism, was in Year Three at a primary school in Northamptonshire.
Julie says her daughter had struggled with the school environment since her time in nursery and is now educated out of school.
Rosie, she recalls, was “in fight and flight the whole time” she was in the classroom, which “just overwhelmed her”.
Eventually Rosie was “begging not to leave” the house for school and was self-harming, sometimes on the school run.
“She would have night terrors – she would be up screaming, if she went to sleep at all.
“It just felt as if I was walking her into the lion’s den every single day,” she says.
Meanwhile, Julie and her husband James received letters and home visits from school staff about Rosie’s attendance.
“It was very lonely.
“All of a sudden there’s these letters and people are talking about fines and I was lost.”
On that final say Julie says she “dragged” Rosie to school because “that was the expectation”.
Now she wishes she had taken Rosie out of school earlier.
“But I also feel that if I hadn’t have got to the point… where she broke, I would never have known if it had worked,” she says.
 Ben Schofield/BBC
Ben Schofield/BBCBased on Rosie’s reaction to school, an educational psychologist who assessed her noted she had “emotionally based school avoidance” or EBSA, a condition school leaders say they are encountering more.
Anna Hewes, the head teacher of Prince William School, a 1,400-pupil secondary in Oundle, Northamptonshire, says schools are seeing a “big increase” in EBSA among pupils in Year Seven, Eight and Nine.
The transition to secondary school is, she adds, a “key time” and at the start of the school year EBSA is “at the forefront of our minds because of the new year sevens coming through”.
The “noises, the bustling nature of a school – the busyness, all the classes walking around” make it a “real challenge” for those with sensory needs, she says.
But more generally “it’s very tough to be a teenager these days”.
Smartphones and social media, she adds, mean “young people can’t escape anymore”.
“It definitely is a post-Covid spike and these young people are genuinely really struggling to step over the threshold of the school and sometimes leave their bedrooms.”
 DJ McLaren/BBC
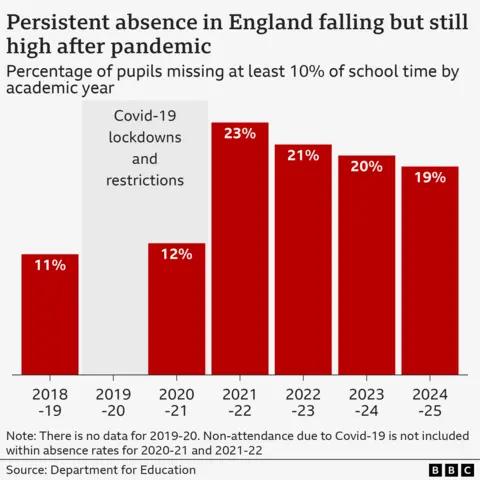
DJ McLaren/BBCAcross England, rates of “persistent absence” – when pupils miss 10% or more of lessons – have remained high since the pandemic.
Last academic year almost 19% of pupils were persistently absent, compared with 11% in 2018/19.
Mrs Hewes says EBSA is a “significant part” of the issue.
A lack of reliable data, however, means it is difficult to know how big a part.
Mrs Hewes says Prince William Academy prioritises “inclusion” and has recruited an assistant head teacher for “belonging”.
It has also opened a specialist “school-within-a-school” for pupils with EBSA, funded by North Northamptonshire Council. Four students have been enrolled so far and by 2028 it expects to see 48.
Jenny Nimmo, the head of inclusion at East Midlands Academy Trust, which runs Prince William Academy, says the unit will have more “homely” classrooms and on-site mental health provision.
She hopes it will be “future proof” because EBSA “isn’t going away”.
There are, she adds, “more and more young people” with “emotionally based school avoidance and indeed anxiety”.
 Ben Schofield/BBC
Ben Schofield/BBCThe Compass Centre in Luton also help pupils with EBSA access education.
Dr Joanne Summers, Luton Borough Council’s principal educational psychologist, says the condition can appear suddenly but “when you look back, there has been anxiety around being in school” and one incident might be a “catalyst”.
Intervening early, she adds, is important, as falling behind on school work and losing contact with friends can make anxiety worse.
Dr Summers says Luton has been trying to move away from seeing school absences as “defiance and truancy”.
“We are being curious about what’s going on for that young person, why is it that they are behaving in this way,” she adds.
 Ben Schofield/BBC
Ben Schofield/BBCGeoff Barton, a former head teacher in Suffolk and previous general secretary of the Association of School and College Leaders, says there should be more “emphasis on the humanity of our schools” rather than “draconian discipline” over absences.
He is researching special educational needs (Send) provision for the left-leaning think tank the Institute for Public Policy Research.
He says the people he is speaking to are “universally saying” that anxiety among pupils has increased.
But the “age of anxiety” is only one reason for persistent absence.
Another is poverty, while he says there is also a “long shadow in education of Covid” when “schools started to feel a bit more of an optional decision”.
Cornelia Andrecut, the executive director of children’s services for North Northamptonshire Council, said the authority has offered training courses for schools to learn strategies to support children with EBSA.
The government says it will spend £740m creating “more specialist places in mainstream schools” and placing Send leads in 1,000 new family hubs.
A Department for Education spokesperson says: “Schools should take a ‘support first’ approach for children who are facing barriers to regular school attendance, and we are expanding access to mental health support teams in all schools, ensuring that every pupil has access to early support services in their community.”
 Family handout
Family handoutFor Julie, taking Rosie out of school was “not a lifestyle choice” but was prompted by “trauma and distress” that her daughter is still recovering from.
Does she regret pushing Rosie to attend school?
“Yeah – definitely.
“I always wonder if there was a bit of trust broken between us as mum and daughter when I still took her into that place when it was that bad.”
Education
Earl Richardson, who spotlighted HBCU funding disparities, dies : NPR

Earl Richardson was the president of Morgan State University between 1984 and 2010.
Morgan State University
hide caption
toggle caption
Morgan State University
Earl Richardson was a Black college president — “armed with history,” as a colleague described him — when he led a 15-year-long lawsuit that ended in a historic settlement for four Black schools in Maryland and put a spotlight on funding disparities for all of the nation’s historically Black colleges and universities (HBCUs).
Richardson’s death, at 81, was announced on Saturday by Morgan State University, located in Baltimore, where he served as president when he helped organize the lawsuit that began in 2006. It was settled in 2021 when the state of Maryland agreed to give $577 million in supplemental funding over 10 years to four HBCUs.
Richardson led Morgan State from 1984 to 2010 and he had long chafed at stretching the little funding he got from the state. In the lawsuit, plaintiffs argued that Maryland had historically underfunded its Black colleges and had put them at a disadvantage by starting and boosting similar programs at nearby majority-white schools.
David Burton, one of the plaintiffs, told NPR that the case was compared to Brown v. Board of Education, the landmark lawsuit that brought up similar issues of disparities in educational opportunities for Black students, but the Maryland case raised the issues for students in higher education.
In 1990, when Richardson was a new school president, students took over the administration building for six days to protest the school’s dilapidated classrooms and dorms, with roofs that leaked and science labs stocked with outdated equipment.
Edwin Johnson was one of those student protesters. “We originally were protesting against Morgan’s administration,” including Richardson, he said. “But then after we dig and do a little research, we find out it’s not our administration, but it’s the governor down in Annapolis that isn’t equipping the administration with what they need to appropriately run the school.”
The protest ended when the students marched 34 miles to Annapolis to demand a meeting with the governor.
Richardson, who spoke of taking part in civil rights demonstrations when he was in school, had subtly guided the students to the correct target, said Johnson, who is now the university’s historian and special assistant to the provost.
That protest helped pave the way to the future, historic lawsuit.
Because Richardson was the university’s president, and an employee of the state, he couldn’t sue the state. So, a coalition of students and former students was created, the Coalition for Equity and Excellence in Maryland Higher Education Inc., to serve as the plaintiff.
Still, Richardson was the visionary behind the lawsuit, said Burton, a Morgan State alumnus and now a strategic planner for businesses. “He was armed with history,” Burton said.
“Dr. Richardson knew where the skeletons were,” Burton added. He was “a force that the state could not reckon with because of his institutional knowledge.”
At one point, during the trial, state attorneys objected to Richardson’s presence in the courtroom and asked the judge to make him leave, even though he had a right to be there as an expert witness, said Jon Greenbaum, then the chief counsel of the Lawyer’s Committee for Civil Rights Under Law, who helped argue the lawsuit.
Richardson stayed in the courtroom and “because this was really a desegregation case,” said Greenbaum, he provided historical detail that became critical to the arguments made by the lawyers representing the plaintiffs.
The funding that resulted, and Richardson’s leadership, jump-started what is now called on campus “Morgan’s Renaissance.” Or sometimes, said Johnson: “Richardson’s Renaissance” — because during Richardson’s presidency, enrollment doubled, the campus expanded with new buildings and new schools were added, including a school of architecture and a school of social work.
Richardson’s work put a spotlight, too, on the funding disparities faced by HBCUs across the country. They are more likely than other schools to rely upon federal, state and local funding — money that has faced budget cuts in recent years. Compared to other universities and colleges, HBCUs get a higher percentage of their revenue from tuition and less from private gifts and grants, according to one study.
In testimony before the U.S. House of Representatives in 2008, Richardson emphasized the mission of HBCUs when he told lawmakers that Black schools like his educated the most talented Black students but also sought to attract students who didn’t consider, or thought they couldn’t afford, to go to college. “We can make them the scientists and the engineers and the teachers and the professors — all of those things,” he said. But only if “we can have our institutions develop to a level of comparability and parity so that we are as competitive as other institutions.”
Education
How millions of dollars in funding cuts will impact Hispanic Serving Institutions
Chancellor Sonya Christian of the California Community College system talks about the impact of funding cuts for students.
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoThe Guardian view on Trump and the Fed: independence is no substitute for accountability | Editorial
-
Tools & Platforms1 month ago
Building Trust in Military AI Starts with Opening the Black Box – War on the Rocks
-

 Ethics & Policy2 months ago
Ethics & Policy2 months agoSDAIA Supports Saudi Arabia’s Leadership in Shaping Global AI Ethics, Policy, and Research – وكالة الأنباء السعودية
-

 Events & Conferences4 months ago
Events & Conferences4 months agoJourney to 1000 models: Scaling Instagram’s recommendation system
-

 Jobs & Careers3 months ago
Jobs & Careers3 months agoMumbai-based Perplexity Alternative Has 60k+ Users Without Funding
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoHappy 4th of July! 🎆 Made with Veo 3 in Gemini
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoVEX Robotics launches AI-powered classroom robotics system
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoMacron says UK and France have duty to tackle illegal migration ‘with humanity, solidarity and firmness’ – UK politics live | Politics
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoOpenAI 🤝 @teamganassi
-

 Funding & Business3 months ago
Funding & Business3 months agoKayak and Expedia race to build AI travel agents that turn social posts into itineraries


