Education
How Pakistani students are reshaping global mobility

A new study from ApplyBoard has shown the number of students leaving Pakistan to join universities in countries such as the UK and US has grown exponentially in the past few years, with student visas issued to Pakistani students bound for the ‘big four’ nearly quadrupling from 2019 to 2025.
“One of the most striking findings is just how rapid and resilient Pakistan’s growth has been across major study destinations,” ApplyBoard CEO Meti Basiri told The PIE News.
“The rise of Pakistani students is a clear signal that global student mobility is diversifying beyond traditional markets like India and China,” he said.
The question is, why?
A large factor is Pakistan’s young population – 59%, or roughly 142.2 million people, are between the ages of five and 24, making it one of the youngest populations in Asia.
Additionally, due to economic challenges faced by Pakistan, many young people see international education as a necessity in order to succeed financially, even with Pakistan’s economic growth and gradual stabilisation – which has a possibility of slightly decreasing the overall movement between countries in the future.
The UK has remained the most popular destination for Pakistani students even through Covid-19, with Pakistan rising to become the UK’s third largest source country in 2024.
Visas issued to Pakistani students have grown from less than 5,500 to projected 31,000 this year, an increase of over 550% from 2019 to 35,501 in 2024.
Some 83% of students chose postgraduate programs, with the most popular being business courses, but in recent years statistics show a shift towards computing and IT courses.
This trend aligns with the growth of the UK’s tech sector, which is now worth more than 1.2 trillion pounds, with graduates set to aid further growth in the coming years.
“In the US, F-1 visas for Pakistani students are on track to hit an all-time high in FY2025,” said Basiri, with STEM subjects the most popular among the cohort.
This aligns with the US labour market, where STEM jobs have grown 79% in the last 30 years.
Basiri highlighted the “surprising” insight that postgraduate programs now make up the majority of Pakistani enrolments, particularly in fields of IT, engineering and life sciences. “This reflects a deliberate and career-driven approach to international education,” he said.
Such an approach is true of students across the world, who are becoming “more intentional, choosing destinations and programs based on affordability, career outcomes, and visa stability, not just brand recognition,” said Basiri.
The rise of Pakistani students is a clear signal that global student mobility is diversifying beyond traditional markets like India and China
Meti Basiri, ApplyBoard
Canada, unlike the US and UK, has welcomed far fewer Pakistani students, most likely due to the introduction of international student caps. ApplyBoard also suspects Pakistani student populations to drop further in the coming years, it warned.
Similarly, the amount of visas issued to Pakistani students has also dropped in Australia after high demand following the pandemic.
Germany, however, has experienced rising popularity, a 70% increase in popularity over five years amongst Pakistani students.
One of the biggest factors for this is their often tuition-free public post secondary education, according to ApplyBoard, as well as the multitude of engineering and technology programs offered in Germany.
What’s more, though smaller in scale, the UAE has seen a 7% increase in Pakistani students in recent years, thanks, in part to “geographic proximity, cultural familiarity and expanding institutional capacity,” said Basiri.
Education
Bridget Phillipson: parents must do more about bad behaviour and attendance in schools | Education policy

Parents and caregivers “need to do more” to reverse post-Covid trends of poor attendance and behaviour in schools, the education secretary has said, announcing new measures to support schools in England before the start of the new school year.
Bridget Phillipson unveiled a UK government programme on Sunday targeting 800 schools attended by about 600,000 pupils, beginning with an initial wave of 21 schools that will serve as attendance and behaviour hubs.
The struggling schools will have access to support from headteachers who have tackled the problems successfully in their own schools. The whole programme is expected to support 5,000 schools, including intensive support for 500.
Phillipson said: “I am calling on parents, schools and families to join us in playing their part to get children in class and ready to learn for the start of the new school term.
“We have already made progress with 5m more days in school this year, and are backing parents and supporting schools through our plan for change.
“But we all need to do more, and when it comes to getting kids in and behaving – this includes mums, dads and carers too.”
Data showed seven out of every 30 classroom minutes were lost to disruption, the department of education said in a statement. A survey by the NASUWT teaching union this year found four in five of more than 5,800 members felt the number of pupils exhibiting violent and abusive behaviour at school had increased, and government figures show suspensions and exclusions in England rose to a record high in the 2023-2024 school year.
Overall absence rates declined in the autumn of 2024-2025 compared with the previous year, but the number of “severely absent” pupils – those missing more than 50% of school days – increased from 142,000 to 148,000.
Writing in the Sunday Telegraph, Phillipson said she was particularly concerned about white working-class children, the demographic group with one of the highest overall absence and suspension rates.
Newly released statistics from the National Behaviour Survey show that one in 10 white children on free school meals in England was suspended in the 2023-24 academic year. It was the highest suspension rate of any group except Gypsy, Roma and Traveller pupils, who are far fewer in number.
She said: “For far too many white working-class children, opportunity is out of reach,” with statistics showing “one in 10 white children on free school meals were suspended last year, with suspension rates five times higher than their peers”.
“These children are swimming upstream against a staggering, entrenched class divide that sees them disproportionately kicked out of education or not attending in the first place.”
Persistent school absence or periods of suspension are directly linked to quality of life in adulthood: by the age of 24, children who were suspended at school were three times as likely as their peers to be on sickness benefits, and on average earn £10,000 a year less by the age of 28.
Phillipson announced two attendance and behaviour ambassadors would support the new programme: Tom Bennett, who has previously advised the Department for Education on behaviour, and former pupil referral unit headteacher Jayne Lowe.
The government’s schools white paper, expected to be published in the autumn, will also set out further plans to tackle bad behaviour.
Education
A largely invisible role of international students: Fueling the innovation economy

PITTSBURGH — Saisri Akondi had already started a company in her native India when she came to Carnegie Mellon University to get a master’s degree in biomedical engineering, business and design.
Before she graduated, she had co-founded another: D.Sole, for which Akondi, who is 28, used the skills she’d learned to create a high-tech insole that can help detect foot complications from diabetes, which results in 6.8 million amputations a year.
D.Sole is among technology companies in Pittsburgh that collectively employ a quarter of the local workforce at wages much higher than those in the city’s traditional steel and other metals industries. That’s according to the business development nonprofit the Pittsburgh Technology Council, which says these companies pay out an annual $27.5 billion in salaries alone.
A “significant portion” of Pittsburgh’s transformation into a tech hub has been driven by international students like Akondi, said Sean Luther, head of InnovatePGH, a coalition of civic groups and government agencies promoting innovation businesses.
“Next Happens Here,” reads the sign above the entrance to the co-working space where Luther works and technology companies are incubated, in an area near Carnegie Mellon and the University of Pittsburgh dubbed the Pittsburgh Innovation District. The neighborhood is filled with people of various ethnicities speaking a variety of languages over lunch and coffee.
What might happen next to the international students and graduates who have helped fuel this tech economy has become an anxiety-inducing subject of those conversations, as the second presidential administration of Donald Trump brings visa crackdowns, funding cuts and other attacks on higher education — including here, in a state that voted for Trump.
Related: Interested in innovations in higher education? Subscribe to our free biweekly higher education newsletter.
Inside the bubble of the universities and the tech sector, “there’s so much support you get,” Akondi observed, in a gleaming conference room at Carnegie Mellon. “But there still is a part of the population that asks, ‘What are you doing here?’ ”
Much of the ongoing conversation about international students has focused on undergraduates and their importance to university revenues and enrollment. Many of these students — especially in graduate schools — fill a less visible role in the economy, however. They conduct research that can lead to commercial applications, have skills employers need and start a surprising number of their own companies in the United States.

“The high-tech engineering and computer science activities that are central to regional economic development today are hugely dependent on these students,” said Mark Muro, a senior fellow at the Brookings Institution who studies technology and innovation. “If you go into a lab, it will be full of non-American people doing the crucial research work that leads to intellectual property, technology partnerships and startups.”
Some 143 U.S. companies valued at $1 billion or more were started by people who came to the country as international students, according to the National Foundation for American Policy, a nonprofit that conducts research on immigration and trade. These companies have an average of 860 employees each and include SpaceX, founded by Elon Musk, who was born in South Africa and graduated from the University of Pennsylvania.
Whether or not they invent new products or found businesses of their own, international graduates are “a vital source” of workers for U.S.-based tech companies, the National Science Foundation reported last year in an annual survey on the state of American science and engineering.

It’s supply and demand, said Dave Mawhinney, a professor of entrepreneurship at Carnegie Mellon and founding executive director of its Swartz Center for Entrepreneurship, which helps many of that school’s students do research that can lead to products and startups. “And the demand for people with those skills exceeds the supply.”
States with the most international students
California: 140,858
New York: 135,813
Texas: 89,546
Massachusetts: 82,306
Illinois: 62,299
Pennsylvania: 50,514
Florida: 44,767
Source: NAFSA: Association of International Educators. Figures are from the 2023-24 academic year, the most recent available.
Related: So much for saving the planet. Climate careers, and many others, evaporate for class of 2025
That’s in part because comparatively few Americans are going into fields including science, technology, engineering and math. Even before the pandemic disrupted their educations, only 20 percent of college-bound American high school students were prepared for college-level courses in these subjects. U.S. students scored lower in math than their counterparts in 21 of the 37 participating nations of the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development on an international assessment test in 2022, the most recent year for which the outcomes are available.
One result is that international students make up more than a third of master’s and doctoral degree recipients in science and engineering at American universities. Two-thirds of U.S. university graduate students and more than half of workers in AI and AI-related fields are foreign born, according to Georgetown University’s Center for Security and Emerging Technology.
“A real point of strength, and a reason our robotics companies especially have been able to grow their head counts, is because of those non-native-born workers,” said Luther, in Pittsburgh. “Those companies are here specifically because of that talent.”
International students are more than just contributors to this city’s success in tech. “They have been drivers” of it, Mawhinney said, in his workspace overlooking the studio where the iconic children’s television program “Mister Rogers’ Neighborhood” was taped.
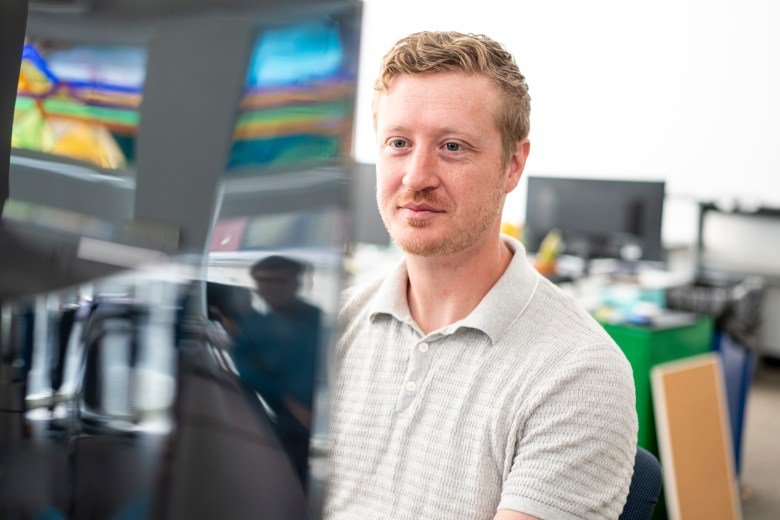

“Every year, 3,000 of the smartest people in the world come here, and a large proportion of those are international,” he said of Carnegie Mellon’s graduate students. “Some of them go into the research laboratories and work on new ideas, and some come having ideas already. You have fantastic students who are here to help you build your company or to be entrepreneurs themselves.”
Boosters of the city’s tech-driven turnaround say what’s been happening in Pittsburgh is largely unappreciated elsewhere. It followed the effective collapse of the steel industry in the 1980s, when unemployment hit 18 percent.
In 2006, Google opened a small office at Carnegie Mellon to take advantage of the faculty and student expertise in computer science and other fields there and at neighboring higher education institutions; the company later moved to a nearby former Nabisco factory and expanded its Pittsburgh workforce to 800 employees. Apple, software and AI giant SAP and other tech firms followed.
“It was the talent that brought them here, and so much of that talent is international,” said Audrey Russo, CEO of the Pittsburgh Technology Council.
Sixty-one percent of the master’s and doctoral students at Carnegie Mellon come from abroad, according to the university. So do 23 percent of those at Pitt, an analysis of federal data shows.
Related: International students are rethinking coming to the US. That’s a problem for colleges
The city has become a world center for self-driving car technology. Uber opened an advanced research center here. The autonomous vehicle company Motional — a joint venture between Hyundai and the auto parts supplier Aptiv — moved in. So did the Ford- and Volkswagen-backed Argo AI, which eventually dissolved, but whose founders went on to create the Pittsburgh-based self-driving truck developer Stack AV. The Ford subsidiary Latitude AI and the autonomous flight company Near Earth Autonomy also are headquartered in Pittsburgh.
Among other tech firms with homes here: Duolingo, which has 830 employees and is worth an estimated $22 billion. It was co-founded by a professor at Carnegie Mellon and a graduate of the university who both came to the United States as international students, from Guatemala and Switzerland, respectively.
InnovatePGH tracks 654 startups that are smaller than those big conglomerates but together employ an estimated 25,000 workers. Unemployment in Pittsburgh (3.5 percent in April) is below the national average (3.9 percent). Now Pitt and others are developing Hazelwood Green, which includes a former steel mill that closed in 1999, into a new district housing life sciences, robotics and other technology companies.
In a series of webinars about starting businesses, offered jointly to students at Pitt and Carnegie Mellon, the most popular installment is about how to found a startup on a student visa, said Rhonda Schuldt, director of Pitt’s Big Idea Center, in a storefront on Forbes Avenue in the Innovation District.

Some international undergraduates continue into graduate school or take jobs with companies that sponsor them so they can keep working on their ideas, Schuldt said.
“They want to stay in Pittsburgh and build businesses here,” she said.
There are clear worries that this momentum could come to a halt if the supply of international students continues a slowdown that began even before the new Trump term, thanks to visa processing delays and competition from other countries.
The number of international graduate students dropped in the fall by 2 percent, before the presidential election, according to the Institute of International Education. Further declines are expected following the government’s pause on student visa interviews, publicity surrounding visa revocations and arrests and cuts to federal research funding.

It’s too early to know what will happen this fall. But D. Sole co-founder Saisri Akondi has heard from friends who planned to come to the United States that they can’t get visas. “Most of these students wanted to start companies,” she said.
“I would be lying if I said nothing has changed,” said Akondi, who has been accepted into a master’s degree program in business administration at the Stanford University Graduate School of Business under her existing student visa, though she said her company will stay in Pittsburgh. “The fear has increased.”
This could affect whether tech companies continue to come to Pittsburgh, said Russo, at least unless and until more Americans are better prepared for and recruited into tech-related graduate programs. That’s something universities have not yet begun to do, since the unanticipated threat to their international students erupted only in March, and that would likely take years.
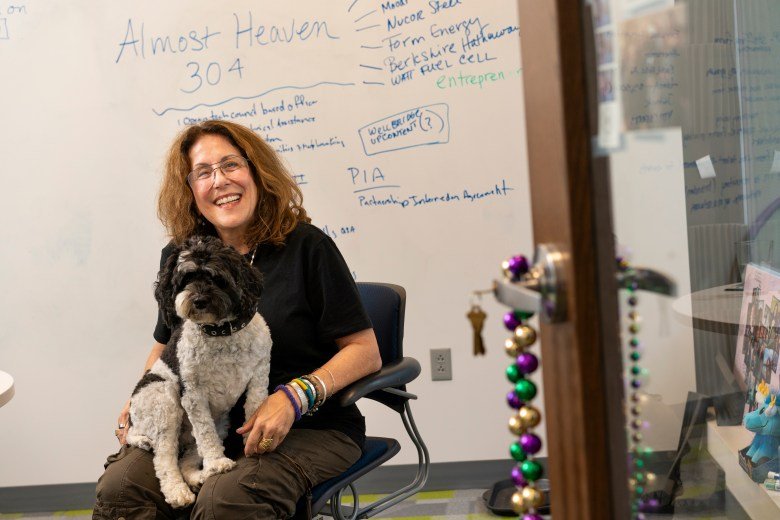

“Who’s going to do the research? Who’s going to be in these teams?” asked Russo. “We’re hurting ourselves deeply.”
The impact could transcend the research and development ecosystem. “I think we’ll see almost immediate ramifications in Pittsburgh in terms of higher-skilled, higher-wage companies hiring here,” said Sean Luther, at InnovatePGH. “And that affects the grocery shops, the barbershops, the real estate.”
There are other, more nuanced impacts.

“Whether we like it or not, it’s a global world. It’s a global economy. The problems that these students want to solve are global problems,” Schuldt said. “And one of the things that is really important in solving the world’s problems is to have a robust mix of countries, of cultures — that opportunity to learn how others see the world. That is one of the most valuable things students tell us they get here.”
Pittsburgh is a prime example of a place whose economy is vulnerable to a decline in the number of international students, said Brookings’ Muro. But it’s not unique.
“These scholars become entrepreneurs. They’re adding to the U.S. economy new ideas and new companies,” he said. Without them, “the economy would be smaller. Research wouldn’t get done. Journal articles wouldn’t be written. Patents wouldn’t be filed. Fewer startups would occur.”
The United States, said Muro, “has cleaned up by being the absolute central place for this. The system has been incredibly beneficial to the United States. The hottest technologies are inordinately reliant on these excellent minds from around the world. And their being here is critical to American leadership.”
Contact writer Jon Marcus at 212-678-7556, jmarcus@hechingerreport.org or jpm.82 on Signal.
This story about international students was produced by The Hechinger Report, a nonprofit, independent news organization focused on inequality and innovation in education. Sign up for our higher education newsletter. Listen to our higher education podcast.
Education
First week ‘critical’ to avoid children missing school later, parents told

Hazel ShearingEducation correspondent
 Getty Images
Getty ImagesPupils in England who missed school during the first week back in September 2024 were more likely to miss large parts during the rest of the year, figures suggest.
More than half (57%) of pupils who were partially absent in week one became “persistently absent” – missing at least 10% of school, according to government data first seen by the BBC.
By contrast, of pupils who fully attended the first week, 14% became persistently absent.
Education Secretary Bridget Phillipson said schools and parents should “double down” to get children in at the start of the 2025 term, which is this week for most English schools.
A head teachers’ union said more support was needed “outside of the school gates” to boost attendance.
Schools have always grappled with attendance issues, but they became much worse after the pandemic in 2020 and schools closed to most pupils during national lockdowns.
Attendance has improved since, but it remains a bigger problem than before Covid.
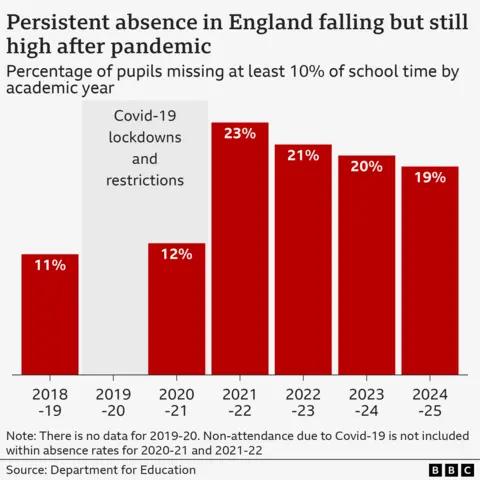
Overall, about 18% of pupils were persistently absent in the 2024-25 school year, down from a peak of 23% in 2021-22 but higher than the pre-Covid levels of about 11%.
The Department for Education (DfE) said the data from the first week of the 2024-25 school year showed the start of term was “critical” for tackling persistent absence.
Karl Stewart, head teacher at Shaftesbury Junior School in Leicester, said his school’s attendance rates were higher than average and but there was a “definite dip” in the two years after Covid.
“I get why. Some of that wasn’t necessarily parents not wanting to send them in. It was because either they had got Covid or other things, they were saying, ‘We’ll just keep them off now to be sure’,” he said.
The school has incentives like awards and class competitions to keep absence rates down, and Mr Stewart said attendance had more or less returned to pre-Covid levels.
“When we have the children in every day the results are just better,” he said.
“If you’re here, that gives you more time for your teacher to notice you, for us to see all that good behaviour [and] that really hard work – and that’s what we want.”
But, like lots of schools, he said some parents still took their children on unauthorised term-time holidays to make the most of cheaper costs.
Others, he said, have taken children for medical treatments overseas to avoid NHS waiting lists.

The education secretary said that while attendance improved last year, absence levels “remain critically high, putting at risk the life chances of a whole generation of young people”.
“Every day of school missed is a day stolen from a child’s future,” Phillipson said.
“As the new term kicks off, we need schools and parents to double down on the energy, the drive and the relentlessness that’s already boosted the life chances of millions of children, to do the same for millions more.”
The DfE said 800 schools were set to be supported by regional school improvement teams – through attendance and behaviour hubs.
These hubs are made up of 90 exemplary schools which will offer support to improve struggling schools through training sessions, events and open days.
It said it had appointed the first 21 schools that will lead the programme.
However, Pepe Di’Iasio, general secretary of the Association of School and College Leaders, said attendance hubs were not a “silver bullet” and a more “strategic approach” was needed.
“I think the government has worked really hard to improve attendance and it continues to be a priority for them, but there’s certainly more to do,” he told the BBC.
“So many of the challenges that [school leaders] are facing come from beyond the school gates – children suffering with high levels of anxiety, issues around mental health.”
He said school leaders wanted quicker access to support for those pupils and specialist staff in schools, but pupils also needed “great role models” in the community through youth clubs and volunteer groups.
The Conservatives said Labour’s Schools Bill had dismantled a “system that has driven up standards for decades”.
Shadow education secretary Laura Trott said: “Behaviour and attendance are two of the biggest challenges facing schools and it’s about time the government acted.”
She added: “There must be clear consequences for poor behaviour not just to protect the pupils trying to learn, but to recognise when mainstream education isn’t the right setting for those causing disruption.”
Additional reporting by Nathan Standley
-
Tools & Platforms3 weeks ago
Building Trust in Military AI Starts with Opening the Black Box – War on the Rocks
-

 Ethics & Policy1 month ago
Ethics & Policy1 month agoSDAIA Supports Saudi Arabia’s Leadership in Shaping Global AI Ethics, Policy, and Research – وكالة الأنباء السعودية
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoThe Guardian view on Trump and the Fed: independence is no substitute for accountability | Editorial
-

 Events & Conferences3 months ago
Events & Conferences3 months agoJourney to 1000 models: Scaling Instagram’s recommendation system
-

 Jobs & Careers2 months ago
Jobs & Careers2 months agoMumbai-based Perplexity Alternative Has 60k+ Users Without Funding
-

 Funding & Business2 months ago
Funding & Business2 months agoKayak and Expedia race to build AI travel agents that turn social posts into itineraries
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoVEX Robotics launches AI-powered classroom robotics system
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoHappy 4th of July! 🎆 Made with Veo 3 in Gemini
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoOpenAI 🤝 @teamganassi
-

 Jobs & Careers2 months ago
Jobs & Careers2 months agoAstrophel Aerospace Raises ₹6.84 Crore to Build Reusable Launch Vehicle




















