AI Insights
How 3D-printed guns are spreading online

 Getty/BBC
Getty/BBC3D-printed guns could become “the weapon of choice” for criminals and violent extremists around the world, an expert has told the BBC. These DIY, untraceable firearms have been recovered in several recent criminal cases, including the alleged use of a partially 3D-printed gun in the killing of United Healthcare CEO Brian Thompson.
BBC Trending has investigated the global spread of 3D-printed guns across social media platforms including Telegram, Facebook and Instagram, as well as websites offering how-to guides.
3D-printed guns, often described as a type of “ghost” gun, are untraceable firearms that can be assembled using a 3D printer, downloadable blueprints and some basic materials. Designed to evade gun-control laws, the technology has advanced rapidly in the last decade, with the latest models capable of firing multiple rounds without their plastic components breaking.
According to Nick Suplina of Everytown, a US-based gun control organisation, 3D-printed guns could become the “weapon of choice” for people planning acts of violence: “The materials have gotten better, the cost has gone down, and the ease of access of these blueprints is at a high,” he said.
BBC Trending’s investigation began with advertisements for guns on Instagram and Facebook. In October 2024, the Tech Transparency Project, a non-profit that monitors technology companies, found hundreds of gun ads – including for 3D-printed and other ghost guns – appearing on Meta’s platforms, in violation of its policies.
Meta declined to comment on the findings at the time. Several months later, BBC Trending found similar gun adverts still showing as active in Meta’s ad database.
 Meta/BBC
Meta/BBCMany of these gun adverts directed potential customers to Telegram or WhatsApp channels. On Telegram, we found channels displaying a variety of guns for sale. Some of these appeared to be 3D-printed. One Telegram account with over 1,000 subscribers claimed to ship weapons globally.
BBC Trending contacted the account, which called itself “Jessy”, to confirm whether it would be willing to break the law by shipping 3D-printed guns to the UK. Within an hour, Jessy offered us a Liberator or a Glock switch.
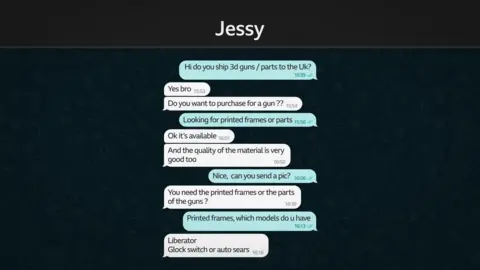
A glock switch (also known as an auto sear) is a small, sometimes 3D-printed part that converts a pistol into an automatic weapon.
The Liberator, designed in 2013 by “crypto-anarchist” Cody Wilson, is the world’s first widely available 3D-printed gun, capable of firing a single shot.
Jessy claimed he could smuggle the weapon through UK customs, asked for payment of £160 in bitcoin, then suggested a bank transfer to a UK account we couldn’t trace.
When we later contacted Jessy, identifying ourselves as the BBC, he acknowledged that selling weapons in the UK is illegal but sounded unapologetic.
“I run my business, sell some straps [slang for weapons] online,” he said.
We did not proceed with the transaction to test Jessy’s claims. While his casual attitude suggested he might have been a scammer, his ability to advertise on Meta and operate on Telegram highlights apparent loopholes that real gun dealers could exploit.
When contacted, Meta told the BBC that the adverts we highlighted had been “automatically disabled in line with our policies”, and that inclusion in its ad library “doesn’t necessarily mean the ad is still live or visible”.
Telegram said that Jessy’s account had been proactively removed for breaching its policies. A spokesperson added: “The sale of weapons is explicitly forbidden by Telegram’s terms of service and is removed whenever discovered. Moderators empowered with custom AI and machine learning tools proactively monitor public parts of the platform and accept reports in order to remove millions of pieces of harmful content each day, including the sale of weapons.”
Concerningly though, people seeking 3D-printed guns don’t need to buy readymade ones through social media. They can assemble their own. Models like the FGC-9 are designed using only 3D-printed plastic and repurposed metal components, with no commercially available gun parts required.
“You are essentially becoming a DIY gunsmith,” says Dr Rajan Basra, a researcher at King’s College London. However, “It’s not as easy as printing off a sheet of A4 paper in your office printer.”
As the BBC has previously reported, there are websites offering free step-by-step guides and downloadable blueprints for building 3D-printed guns.
One such guide was written by Matthew Larosiere, a gun rights attorney in Florida. He’s associated with the global pro-3D-printed gun community, which has many members in the USA who see the Second Amendment right to bear arms as a human right.
BBC Trending challenged him about why he is sharing information to help people build a lethal weapon.
He replied: “It’s just information. It’s ones and zeros. The fact that the information has a use case that makes you uncomfortable, I understand and I sympathise with that, but that doesn’t make it correct to say it’s anything more than information.”
Asked about the risk of this “information” being used in a school shooting or massacre, he replied: “I thank God that has not happened.” He cited Myanmar as a country where, in his view, 3D-printed guns have served a positive cause.
 Getty
GettyMyanmar is currently the only known case of 3D-printed guns being used in active military conflict. The FGC-9’s use by resistance fighters against the junta has been widely reported.
But as BBC Burmese’s Hnin Mo discovered, many of these groups have since stopped using 3D-printed guns. This is despite resistance forces producing hundreds of FGC-9s in 2022 and 2023, which cost over ten times less than machine guns on the black market.
The rebel leaders Hnin Mo spoke to cited the junta’s tight control over imports of essential materials like glue and metal. Additionally, these groups now have more conventional weapons at their disposal, such as RPGs or machine guns.
The Myanmar example demonstrates the limitations of current 3D-printed guns for military use. But globally, their spread is clear. Several countries are considering laws to criminalise the possession of blueprints. There are also calls for 3D printer manufacturers to block the printing of gun parts, in the same way that conventional printers restrict the printing of currency. But whether such measures can be effective remains to be seen.
Additional reporting by Hnin Mo, BBC Burmese
AI Insights
Spain Leads Europe in Adopting AI for Vacation Planning, Study Shows

Spain records higher adoption of Artificial Intelligence – AI in vacation planning than the European average, according to the 2025 Europ Assistance-Ipsos barometer.
The study finds that 20% of Spanish travelers have used AI-based tools to organize or book their holidays, compared with 16% across Europe.
The research highlights Spain as one of the leading countries in integrating digital tools into travel planning. AI applications are most commonly used for accommodation searches, destination information, and itinerary planning, indicating a shift in how tourists prepare for trips.
Growing Use of AI in Travel
According to the survey, 48% of Spanish travelers using AI rely on it for accommodation recommendations, while 47% use it for information about destinations. Another 37% turn to AI tools for help creating itineraries. The technology is also used for finding activities (33%) and booking platform recommendations (26%).
Looking ahead, the interest in AI continues to grow. The report shows that 26% of Spanish respondents plan to use AI in future travel planning, compared with 21% of Europeans overall. However, 39% of Spanish participants remain undecided about whether they will adopt such tools.
Comparison with European Trends
The survey indicates that Spanish travelers are more proactive than the European average in experimenting with AI for holidays. While adoption is not yet universal, Spain’s figures consistently exceed continental averages, underscoring the country’s readiness to embrace new technologies in tourism.
In Europe as a whole, AI is beginning to make inroads into vacation planning but at a slower pace. The 2025 Europ Assistance-Ipsos barometer suggests that cultural attitudes and awareness of technological solutions may play a role in shaping adoption levels across different countries.
Changing Travel Behaviors
The findings suggest a gradual transformation in how trips are organized. Traditional methods such as guidebooks and personal recommendations are being complemented—and in some cases replaced—by AI-driven suggestions. From streamlining searches for accommodation to tailoring activity options, digital tools are expanding their influence on the traveler experience.
While Spain shows higher-than-average adoption rates, the survey also reflects caution. A significant portion of travelers remain unsure about whether they will use AI in the future, highlighting that trust, familiarity, and data privacy considerations continue to influence behavior.
The Europ Assistance-Ipsos barometer confirms that Spain is emerging as a frontrunner in adopting AI for travel planning, reflecting both a strong appetite for digital solutions and an evolving approach to how holidays are designed and booked.
Photo Credit: ProStockStudio / Shutterstock.com
AI Insights
NBA star Tristan Thompson is bringing artificial intelligence to basketball fans

Listen and subscribe to Financial Freestyle on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, or wherever you find your favorite podcasts.
Tristan Thompson is well-recognized for his career in the NBA, having played for teams like the Cleveland Cavaliers, the Boston Celtics, and the Los Angeles Lakers, to name a few. He was even part of the team that earned an NBA championship in 2016. But while Thompson’s basketball reputation precedes him, off the court, he’s focusing on his various entrepreneurial ventures.
When asked by Yahoo Finance’s Financial Freestyle podcast host Ross Mac if he would invest his final dollar in artificial intelligence or the blockchain, Thompson picked the industry that’s already projected to be worth $3.6 trillion by 2034.
“You see what Mark Zuckerberg’s paying for all these AI gurus? So I might go AI,” he said (see the full episode above; listen below).
This embedded content is not available in your region.
Thompson has already made AI one of his entrepreneurial ventures with the launch of TracyAI, an artificial intelligence that’s meant to offer real-time NBA analysis and predictive insights.
“Imagine a sports analyst or commentator on steroids,” he explained to Mac. “What I mean by that is having all the high-level analytics that you cannot get from NBA.com and ESPN … the analytics are coming from the professional teams. We have certain data and access to certain companies that only professional sports teams have access to. And I was able to pull that data with my resources and put it into the AI agent.”
Thompson saw the venture as “low-hanging fruit,” as it was one of the few areas he hadn’t yet noticed artificial intelligence being worked into. Though AI is slowly finding its way into the sports industry, TracyAI offers basketball fans access to statistics and projections they may not have had through the typical channels, creating a unique fan experience.
Though Thompson admitted AI has created some of its own controversies, it’s a venture where he’s ready to invest some of his financial resources to capitalize on the industry’s projected rapid growth.
“For me, it’s like, if [AI is] covering so many sectors, how come it hasn’t got into sports?” Thompson said. “This is an opportunity where I can be a visionary and a pioneer … I’ve always had this grind, build-up mentality, so it just migrated easily into Web3. If you look at Daryl Morey, he said he used AI agents to curate his Sixers roster … that just shows you that’s the first domino effect into something great.”
AI Insights
No, AI Is Not Better Than a Good Doctor

Search the internet and you will find countless testimonials of individuals using AI to get diagnoses their doctors missed. And while it is important for individuals to take ownership of their healthcare and use all available resources, it is just as important to understand the process behind an AI diagnosis.
If you ask AI to figure out what ails you based on inputting a series of symptoms, the AI will use mathematical probability to calculate the appropriate sequence of words that would generate the most valuable output given the specific prompt. The AI has no intrinsic or learned understanding of what “body,” “illness,” “pain,” or “disease” mean. Such practically meaningful concepts to humans are, to the bot, just letters encountered in the training set frequently paired with other letters.
New research on AI’s lack of medical reasoning
Recently, a team of researchers set out to investigate whether AIs that achieved near-perfect accuracy on medical benchmarks like MedQA actually reasoned through medical problems or simply exploited statistical patterns in their training data. If doctors and patients more widely rely on AI tools for diagnosis, it becomes critical to understand the capability of AI when faced with novel clinical scenarios.
The researchers took 100 questions from MedQA, a standard dataset of multiple-choice medical questions collected from professional medical board exams, and replaced the original correct answer choice with “None of the other answers.” If the AI was simply pattern-matching to its training data, the change should prove devastating to its accuracy. On the other hand, if there was reasoning behind its answers the negative effect should be minimal.
Sure enough, they found that when an AI was faced with a question that deviates from the familiar answer patterns it was trained on, there was a substantive decline in accuracy, from 80% to 42% accuracy. This is because AI today are still just probability calculators, not artful thinkers.
Artful medical practitioners see, hear, feel, and recognize medical conditions in ways they are often not consciously aware of. While an AI would be thrown off by an unfamiliar description of symptoms, good doctors listen to the specific word choices of patients and try to understand. They appreciate how societal factors can impact health, trusting both their own intuitions and those of the patient. They pay close attention to all the presenting symptoms in an open-minded manner, as opposed to algorithmically placing the patient in a generic diagnostic box.
Healing is more than a single task
And yet, algorithmic supremacists are as confident as ever in their belief that human healthcare providers will be replaced by machines. In 2016, at the Machine Learning and Market for Intelligence Conference in my hometown of Toronto, Geoffrey Hinton took the mic to confidently assert: “If you work as a radiologist, you are like Wile E. Coyote in the cartoon. You’re already over the edge of the cliff, but you haven’t yet looked down … People should stop training radiologists now. It’s just completely obvious that in five years deep learning is going to do better than radiologists.”
Seven years later, well past the five-year deadline, Kevin Fischer, CEO of Open Souls, attacked Hinton’s erroneous AI prediction, explaining how tech boosters home in on a single behavior against some task and then extrapolate broader implications based on that single task alone. The reality is that reducing any job, especially a wildly complex job that requires a decade of training, to a handful of tasks is absurd.
As Fischer explains, radiologists have a 3D world model of the brain and its physical dynamics in their head, which they use when interpreting the results of a scan. An AI tasked with analysis is simply performing 2D pattern recognition. Furthermore, radiologists have a host of grounded models they use to make determinations, and, when they think artfully, one of the most important is whether something “feels” off. A large part of their job is communicating their findings with fellow human physicians. Further, human radiologists need to see only a single example of a rare and obscure condition to both remember it and identify it in the future, unlike algorithms, which struggle with what to do with statistical outliers.
So, by all means, use whatever tools you can access to help your wellness. But be mindful of the difference between a medical calculator and an artful thinker.
-
Tools & Platforms3 weeks ago
Building Trust in Military AI Starts with Opening the Black Box – War on the Rocks
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoThe Guardian view on Trump and the Fed: independence is no substitute for accountability | Editorial
-

 Ethics & Policy1 month ago
Ethics & Policy1 month agoSDAIA Supports Saudi Arabia’s Leadership in Shaping Global AI Ethics, Policy, and Research – وكالة الأنباء السعودية
-

 Events & Conferences3 months ago
Events & Conferences3 months agoJourney to 1000 models: Scaling Instagram’s recommendation system
-

 Jobs & Careers2 months ago
Jobs & Careers2 months agoMumbai-based Perplexity Alternative Has 60k+ Users Without Funding
-

 Funding & Business2 months ago
Funding & Business2 months agoKayak and Expedia race to build AI travel agents that turn social posts into itineraries
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoVEX Robotics launches AI-powered classroom robotics system
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoHappy 4th of July! 🎆 Made with Veo 3 in Gemini
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoOpenAI 🤝 @teamganassi
-

 Mergers & Acquisitions2 months ago
Mergers & Acquisitions2 months agoDonald Trump suggests US government review subsidies to Elon Musk’s companies


