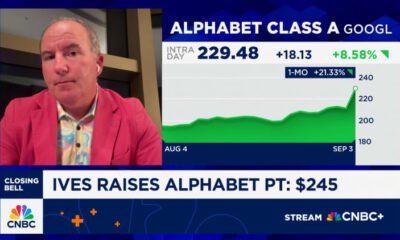
Business
Google unveils more realistic text-to-speech service by DeepMind’s AI
49
Google is launching a new AI voice synthesiser as part of its suite of machine learning cloud tools.
The service, named Cloud Text-to-Speech, will be available for any developer or business that needs voice synthesis on tap, whether that’s for an app, website, or virtual assistant. But what’s particularly interesting about this news is that Cloud Text-to-Speech is powered by WaveNet, software created by Google’s UK-based AI subsidiary DeepMind.
This is significant for two reasons. First, ever since Google bought DeepMind in 2014, it’s been exploring ways to turn the company’s AI talent into tangible products. So far, this has meant using DeepMind’s algorithms to reduce electricity costs in Google’s data centres by 40 percent and DeepMind’s forays into health care. But, directly integrating WaveNet into its cloud service is arguably more significant, especially as Google tries to win cloud business away from Amazon and Microsoft, presenting its AI skills as its differentiating factor.
Second, DeepMind’s AI voice synthesis tech is some of the most advanced and realistic in the business. Most voice synthesizers (including Apple’s Siri) use what’s called concatenative synthesis, in which a program stores individual syllables — sounds such as “ba,” “sht,” and “oo” — and pieces them together on the fly to form words and sentences. This method has gotten pretty good over the years, but it still sounds stilted.
Image: DeepMind A GIF showing how DeepMind’s WaveNet model has improved over the years.
WaveNet, by comparison, uses machine learning to generate audio from scratch. It actually analyzes the waveforms from a huge database of human speech and re-creates them at a rate of 24,000 samples per second. The end result includes voices with subtleties like lip smacks and accents. When Google first unveiled WaveNet in 2016, it was far too computationally intensive to work outside of research environments, but it’s since been slimmed down significantly, showing a clear pipeline from research to product.
WaveNet was first integrated into Google Assistant last October (although only in Japanese and English) and is now available for select voices in Cloud Text-To-Speech. Google says the new service offers 32 different voices capable of speaking 12 languages, and users are able to customize factors like pitch and speed. So, be prepared for a wave of new, realistic computer voices to argue with and boss around. You can check out how WaveNet sounds for yourself below.
Here’s an industry-leading synthesized voice:
And here’s the same sentence from WaveNet:
Here’s another rival’s voice synthesizer, this time speaking Japanese:
And again, here’s the same sentence from WaveNet:
Business
C3.ai Unveils Agentic Process Automation to Transform Business Workflows

C3.ai, Inc. (NYSE:AI) is one of the Hot AI Stocks to Keep on Your Radar. On September 9, the company announced C3 AI Agentic Process Automation, a new product that leverages autonomous AI agents to handle business and operational workflows across enterprises.
The C3 AI Agentic Process Automation handles numerous types of business processes such as order-to-cash, customer service, invoice processing, debt collection, supplier onboarding, procurement, and employee onboarding, industrial operations, manufacturing operations, production planning, inventory management, and aircraft maintenance.
By replacing traditional robotic process automation tools with AI models, the C3 AI Agentic Process Automation allows enterprises to work with the reasoning capabilities of modern AI models with pre-determined steps and controls.
“C3 AI Agentic Process Automation is a breakthrough that will mark a decisive shift in the very nature of work. With our software, customers can handle key business processes from start to finish, making complex workflows efficient, reliable, and repeatable.” -Stephen Ehikian, CEO of C3 AI.
C3.ai, Inc. (NYSE:AI) is an enterprise artificial intelligence (AI) software company involved in building and operating enterprise-scale AI applications and accelerating digital transformation.
While we acknowledge the potential of AI as an investment, we believe certain AI stocks offer greater upside potential and carry less downside risk. If you’re looking for an extremely undervalued AI stock that also stands to benefit significantly from Trump-era tariffs and the onshoring trend, see our free report on the best short-term AI stock.
READ NEXT: 10 AI Stocks Gaining Attention on Wall Street and 10 Exciting AI Stocks to Watch Right Now
Disclosure: None.
Business
Zoho Contracts Brings AI and CRM Integration to Simplify Small Business Legal Workflows

At Zoho’s SMZ 2025 event, I sat down with Arjun Kesavan Balasubramanian from the Zoho Contracts team. Their conversation focused on how the platform’s newest features—including AI assistance and deeper CRM integration—are designed to save small businesses time, reduce risk, and improve transparency when handling contracts.
For small business owners, contracts are a constant part of operations. Every vendor agreement, client deal, or partnership relies on legal language that can be confusing and time-consuming. Traditionally, managing contracts requires a patchwork of tools, lawyers, and endless email threads. Zoho Contracts is aiming to change that by providing one unified platform for the entire contract lifecycle.
One Tool for the Entire Contract Lifecycle
Balasubramanian began by outlining what Zoho Contracts offers today:
“So Zoho Contracts is Zoho’s contract lifecycle management software. So, if you want to transform your entire contract lifecycle, if you want to have one tool to manage the contract requests, the collaboration, the approval negotiation signature and all of the post execution stages like amendments, renewals, extensions, termination and the contract analytics part. All of this is covered in one tool, which is Zoho Contracts.”
For small businesses, this means avoiding the chaos of juggling Word documents, email attachments, and multiple online tools. Instead, owners can initiate a contract request, collaborate internally, send it for approval, negotiate terms, and sign—all without leaving the platform. Post-execution tasks like renewals and amendments are tracked automatically.
AI Assistance for Contract Insights
One of the headline features from the 2025 update is the integration of large language models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT into the platform.
“The recent features that we launched with this update is basically our integration with LLMs like ChatGPT. So what that adds to the CLM system is it adds an additional layer of intelligence. So if you are working on a contract document, let’s say 50 pages long, it would be amazing to have an assistant that will tell you what are the key insights from this contract, right? Like it can summarize your contract. It can give you an update on what are the potential risks I have in this contract and it can extract what are the obligations you have in this particular contract so that AI assistant is a powerful feature.”
For small business owners who don’t have an in-house legal team, this is a big step forward. Instead of combing through dozens of pages, AI can highlight deadlines, risks, or unusual clauses in seconds.
Zoho also plans to introduce its own AI engine, Zia, to handle these tasks in a privacy-first way.
Where AI Fits—and Where Humans Still Matter
I asked the question many small business owners are thinking: Can AI really handle contract work without risk?
“That’s a good one. So if you think about it, you have an AI assistant that can summarize that can tell you what is the risk and what is not, but you still need a human judgment to validate whatever the AI is saying, because legal is this one sector where the nuances are a lot, right.”
Balasubramanian explained that while AI can suggest missing clauses, flag obligations, or summarize terms, humans remain essential for judgment. Industry regulations, company policies, and regional laws require context AI cannot fully capture.
In practice, AI reduces the time it takes for a business owner—or their lawyer—to make informed decisions. It speeds up drafting and reviewing but doesn’t eliminate the need for oversight.
Data Privacy and BYOK Integration
When it comes to AI, data privacy is always top of mind for small businesses. I pressed on this point, asking what data is shared with OpenAI when using the ChatGPT integration.
“Definitely. So this particular ChatGPT integration is covered as bring your own key integration. So if you already are using ChatGPT at your organization, you’re bringing that key and you’re enabling this integration with Zoho Contracts, right? So you’re already OK with ChatGPT processing that data to help you improve efficiency or make your contract management easier.”
This Bring Your Own Key (BYOK) approach means businesses maintain control. If they don’t want to use ChatGPT, they can opt out while still leveraging other features. Soon, Zoho’s own LLM will give businesses a private option that doesn’t use contract data for external training.
Balasubramanian emphasized:
“Exactly. Yeah. So what Zoho has achieved is trust, and that trust was built over 3 decades… when Zoho LLM is implemented into our system, the decision becomes very, very easy for our customers.”
CRM Integration for Sales and Legal Transparency
For many small businesses, contracts and customer relationships are tightly linked. Closing a deal often requires quick contract generation and approval. Zoho has deepened its integration with Zoho CRM to make this process seamless.
“So if you are a CRM user. And when you see that a deal is imminent, you can just create a record right from your deal, record in CRM and all of that information in CRM will be fetched. It will be automatically mapped into Zoho’s Contracts. A contract document will be generated and that document is also available as an attachment in Zoho CRM.”
This ensures sales teams don’t have to switch tools or chase down legal staff for paperwork. Contracts are automatically generated from CRM data, cutting down errors and improving speed.
Pre-Approved Templates and Clause Libraries
Another feature aimed at small businesses is the inclusion of templates and a clause library.
“We have 14 predefined templates and these templates are some of the commonly used contracts that any business would need, but actually we would still recommend the small businesses to actually do a check of whether these clauses are relevant for the industry that they are operating in.”
The benefit for small businesses is clear: rather than starting from scratch, they can use ready-made templates and adapt them for their industry. Balasubramanian noted that lawyers are still important but that Zoho Contracts can reduce legal dependencies by providing fallback clauses and pre-approved language.
I summarized it well:
“So more of a way to give a lawyer something that’s you know, 90% of the way there instead of starting from scratch.”
And Balasubramanian confirmed:
“Exactly. Exactly. It’s about reducing the dependency. It’s not about replacing lawyers.”
This approach cuts costs while ensuring negotiations move quickly. For example, if a customer requests a discount, fallback options are already documented. Sales staff don’t need to escalate every negotiation to managers or legal counsel.
Regional and Multi-Organization Support
Zoho Contracts has also expanded features to support businesses operating in multiple regions or managing different subsidiaries.
“We support multi organization. We have some regional settings covered now you can add files and URLs and attachments to your contract documents.”
For small businesses growing across borders—or simply managing multiple LLCs—this flexibility helps keep operations compliant without increasing complexity.
Practical Benefits for Small Businesses
Throughout the discussion, I pointed out how these updates can save business owners “a whole lot of time and effort.” That’s the central promise of Zoho Contracts: reduce headaches, speed up workflows, and improve legal preparedness without overwhelming owners or requiring full-time legal staff.
The combination of AI insights, CRM integration, and pre-approved templates provides a practical toolkit for:
-
Freelancers negotiating service contracts
-
Small retailers managing vendor agreements
-
Agencies drafting client proposals
-
Growing businesses dealing with renewals and amendments
By centralizing the contract process, Zoho Contracts helps ensure nothing slips through the cracks.
Trust as a Competitive Advantage
One theme that came up repeatedly was trust. Zoho has long emphasized privacy, and that principle is guiding its AI development. With many small businesses wary of where their data goes, Zoho’s commitment to in-house AI and transparent integrations is a differentiator.
Balasubramanian summed it up:
“Even though we have chat integration, people would still ask when is Zoho LLM coming? Because they would really want to switch. And yeah, that trust I think. Will definitely help the adoption of LLM as well.”
For small businesses, trust isn’t abstract—it directly impacts whether they feel safe using a platform for sensitive contracts.
Where to Learn More
As the interview wrapped up, Balasubramanian directed small businesses to explore the platform further:
“Yeah, people can learn more about Zoho Contracts at zoho.com/contracts.”
Final Takeaway for Small Business Owners
Zoho Contracts is positioning itself as more than just software—it’s a way for small businesses to work smarter with contracts. By combining AI, templates, CRM integration, and a privacy-focused approach, the platform provides a strong alternative to traditional, fragmented contract management.
Small business owners should see this as an opportunity to:
-
Cut down on manual legal tasks
-
Speed up deal closings
-
Reduce dependency on external counsel for routine negotiations
-
Improve compliance and risk awareness
-
Build a scalable foundation for growth
In the end, Zoho Contracts doesn’t remove the need for lawyers, but it does ensure that small businesses come to the table prepared—with better insights, faster processes, and fewer headaches.
Business
The “Boring” AI Business Model Making Millionaires in 2025

In 2025, while the world gushed about flashy robots, talking cars, and futuristic gadgets, a group of young people quietly built an AI business so unremarkable at first glance that almost nobody noticed it. It wasn’t glamorous, it didn’t have a viral video, and it didn’t try to predict the next big trend. But it was making millionaires out of regular people… people who had nothing but grit, curiosity, and patience.
This is the story of Maya and her “boring” AI model, and how it reshaped not only her life but the lives of thousands who followed her blueprint.
Maya was 27 in early 2024, living in a one-bedroom apartment above a grocery store in a crowded city. She had a degree in literature, not engineering, and worked as a night-shift clerk in a local print shop.
She had no investors, no startup culture contacts, and no idea how to code beyond simple website builders. But she had two assets few people had: relentless curiosity and the habit of looking for problems that nobody wanted to solve.
One evening, while scrolling through forums about small business challenges, she noticed dozens of owners complaining about repetitive, mundane tasks: sorting invoices, tagging emails, filing customer questions, and moving data from one platform to another. It wasn’t glamorous work. It wasn’t on the cover of magazines. But it was expensive and time-consuming.
And something clicked.
“What if AI could quietly do all these boring tasks?” she wondered.
While the tech world chased billion-dollar breakthroughs in self-driving cars and virtual universes, Maya started tinkering with the “unsexy” side of artificial intelligence. She didn’t try to build a sentient assistant. Instead, she built small, focused AI “micro-tools” that automated the ugly, tedious back-office work of everyday businesses.
Maya’s first tool wasn’t impressive. It was a simple AI model that read PDF invoices, extracted key data, and entered it into spreadsheets for small business owners. She found an open-source language model online, watched tutorials for weeks, and cobbled together an interface using no-code platforms. She spent nights testing it on free samples and begging café owners to try it.
Her first paying client was a family-run furniture shop. They hated doing paperwork at the end of every week. Maya’s tool reduced their 6-hour weekly process to 30 minutes. They paid her $50 a month. She danced around her apartment with joy.
But Maya didn’t stop. She built a second micro-tool to categorize customer emails into urgency levels. A third to predict low inventory items. Each small AI bot solved one tiny, boring problem. Together, they saved small businesses hundreds of hours.
By mid-2024, Maya had 47 clients paying $30-$200 a month. Not life-changing, but enough to quit her print shop job. She then created subscription tiers and white-labeled her micro-tools so other freelancers could sell them too. Her pitch wasn’t sexy; it was practical. “Save time. Save money. Grow quietly.”
This was the turning point.
A former schoolteacher named Daniel, 32, bought a license to resell Maya’s AI bots in his own city. He signed up 20 businesses in a month. He made more than he’d made teaching full-time. A retired accountant named Lucia, 58, did the same. She introduced the tools to her network of small retailers and built a six-figure income in a year.
The “boring” AI model had become a movement… not of tech moguls, but of ordinary people solving ordinary problems.
Maya’s philosophy was simple:
Don’t chase hype.
Solve persistent problems.
Keep costs low and margins healthy.
Let others partner and profit.
Instead of selling one giant software platform, she sold dozens of tiny, niche AI “workers” that anyone could subscribe to individually. This modular approach allowed even small-town businesses to adopt AI at their own pace.
By early 2025, hundreds of resellers around the world were using Maya’s framework to deliver micro-AI services. Some ran one-person operations; others built small agencies. They weren’t Silicon Valley founders… they were baristas, teachers, retirees, and college kids who saw a need and used Maya’s blueprint.
One such story was Sophie, a 21-year-old student who had grown up watching her parents run a bakery. Sophie bought Maya’s AI invoicing and scheduling tools, customized them with her own branding, and started selling them to bakeries and cafés in her region. Within six months, she’d replaced her part-time job income. Within a year, she was making $12,000 a month… enough to pay off her student loans before graduating.
Then there was Amir, 44, a former mechanic who lost his job during an economic downturn. He learned how to use Maya’s training materials, packaged AI bots for auto shops, and made more money in his first year of self-employment than he ever had before.
The model worked because it wasn’t glamorous. No flashy ads. No wild claims. Just steady value. Maya called it “AI plumbing”… building the pipes that let small businesses run smoother.
She focused on four principles:
1. Accessibility: Make it cheap and easy enough for non-tech people.
2. Education: Offer plain-language training and support.
3. Flexibility: Let resellers white-label and adjust pricing.
4. Community: Encourage sharing improvements and templates.
By mid-2025, Maya herself wasn’t just running a business. She was leading a decentralized movement of AI micro-entrepreneurs. Her own income grew into the millions, but she always reinvested in building better training and tools.
And yet Maya stayed humble. She still lived in a modest apartment, still answered customer support emails personally, and still said no to investors who wanted to “scale aggressively.” She believed the real revolution wasn’t another billion-dollar tech giant but thousands of small, empowered entrepreneurs earning honest incomes from useful AI tools.
Her success attracted skepticism. Some said it was too simple. Others thought the big companies would crush her. But Maya knew she was in a different lane. She wasn’t trying to win a popularity contest… she was trying to solve real problems.
And as the economy shifted in 2025, her approach turned out to be exactly what people needed: stability, low overhead, and the ability to start small.
By late 2025, analysts began to notice. Articles described the phenomenon of “boring AI” making quiet millionaires. But those inside the movement already knew: it wasn’t about hype. It was about mindset.
Maya often told her community:
“Find a problem. Build the simplest AI solution. Offer it to the people who need it most. Repeat. Don’t try to impress. Try to improve.”
It was a model anyone could adopt. A 19-year-old in Manila built AI tools for local fishermen to predict tide patterns. A 63-year-old in Nairobi used AI bots to help farmers monitor soil moisture. A single mom in Toronto built an AI appointment scheduler for local hair salons. The stories poured in, all rooted in the same principle: simple solutions, consistent effort, and community sharing.
Maya had proven something profound:
You don’t need to invent the next flying car to become successful. You can build “boring” tools that make life easier… and people will pay for that forever.
Moral of the Story
In a world obsessed with hype and spectacle, quiet consistency and practical problem-solving can outlast trends. The “boring” AI business model shows that success isn’t about dazzling innovation… it’s about meaningful impact. When you stop chasing fame and start solving real problems, you unlock a sustainable path to wealth, freedom, and purpose. Even the most ordinary ideas, applied persistently, can change lives… including your own.
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoThe Guardian view on Trump and the Fed: independence is no substitute for accountability | Editorial
-
Tools & Platforms4 weeks ago
Building Trust in Military AI Starts with Opening the Black Box – War on the Rocks
-

 Ethics & Policy2 months ago
Ethics & Policy2 months agoSDAIA Supports Saudi Arabia’s Leadership in Shaping Global AI Ethics, Policy, and Research – وكالة الأنباء السعودية
-

 Events & Conferences4 months ago
Events & Conferences4 months agoJourney to 1000 models: Scaling Instagram’s recommendation system
-

 Jobs & Careers2 months ago
Jobs & Careers2 months agoMumbai-based Perplexity Alternative Has 60k+ Users Without Funding
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoVEX Robotics launches AI-powered classroom robotics system
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoHappy 4th of July! 🎆 Made with Veo 3 in Gemini
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoMacron says UK and France have duty to tackle illegal migration ‘with humanity, solidarity and firmness’ – UK politics live | Politics
-

 Funding & Business2 months ago
Funding & Business2 months agoKayak and Expedia race to build AI travel agents that turn social posts into itineraries
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoOpenAI 🤝 @teamganassi