AI Insights
General-purpose LLMs can be used to track true critical findings

General-purpose large language models (LLMs), such as GPT-4, can be adapted to detect and categorize multiple critical findings within individual radiology reports, using minimal data annotation, researchers have reported.
A team led by Ish Talati, MD, of Stanford University, with colleagues from the Arizona Advanced AI and Innovation (A3I) Hub and Mayo Clinic Arizona, retrospectively evaluated two “out-of-the-box” LLMs — GPT-4 and Mistral-7B — to see how well they might perform at classifying findings indicating medical emergency or requiring immediate action, among others. Their results were published on September 10 in the American Journal of Roentgenology.
Timely critical findings communication can be challenging due to the increasing complexity and volume of radiology reports, the authors noted. “Workflow pressures highlight the need for automated tools to assist in critical findings’ systematic identification and categorization,” they said.
The study demonstrated that few-shot prompting, incorporating a small number of examples for model guidance, can aid general-purpose LLMs in adapting to the medical task of complex categorization of findings into distinct actionable categories.
To that end, Talati and colleagues evaluated GPT-4 and Mistral-7B on more than 400 radiology reports selected from the MIMIC-III database of deidentified health data from patients in the intensive care unit (ICU) at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center from 2001 to 2012.
Analysis included 252 radiology reports of varying modalities (56% CT, ~30% radiography, 9% MRI, for example) and anatomic regions (mostly chest, pelvis, and head).
The reports were divided into a prompt engineering tuning set of 50, a holdout test set of 125, and a pool of 77 remaining reports used as examples for few-shot prompting. An external test set consisted of 180 chest x-ray reports extracted from the CheXpert Plus database.
With a board-certified radiologist and software separately, manual reviews of the reports classified them at consensus into one of three categories:
- True critical finding (new, worsening, or increasing in severity since prior imaging)
- Known/expected critical finding (a critical finding that is known and unchanged, improving, or decreasing in severity since prior imaging)
- Equivocal critical finding (an observation that is suspicious for a critical finding but that is not definitively present based on the report)
The models analyzed the submitted report and provided structured output containing multiple fields, listing model-identified critical findings within each of the three categories, according to the group. Evaluation included automated text similarity metrics (BLEU-1, ROUGE-F1, G-Eval) and manual performance metrics (precision, recall) in the three categories.
|
Precision and recall comparison for LLMs tracking true critical findings |
||
|
Type of test set and classification |
GPT-4 |
Mistral-7B |
|
Precision |
||
| Holdout test set, true critical findings |
90.1% |
75.6% |
| Holdout test set, known/expected critical findings |
80.9% |
34.1% |
| Holdout test set, equivocal critical findings |
80.5% |
41.3% |
| External test set, True critical findings |
82.6% |
75% |
| External test set, known/expected critical findings |
76.9% |
33.3% |
| External test set, equivocal critical findings |
70.8% |
34% |
|
Recall |
||
| Holdout test set, true critical findings |
86.9% |
77.4% |
| Holdout test set, known/expected critical findings |
85% |
70% |
| Holdout test set, equivocal critical findings |
94.3% |
74.3% |
| External test set, True critical findings |
98.3% |
93.1% |
| External test set, known/expected critical findings |
71.4% |
92.9% |
| External test set, equivocal critical findings |
85% |
80% |
“GPT-4, when optimized with just a small number of in-context examples, may offer new capabilities compared to prior approaches in terms of nuanced context-dependent classifications,” Tatali and colleagues wrote. “This capability is crucial in radiology, where identification of findings warranting referring clinician alerts requires differentiation of whether the finding is new or already known.”
Though promising, further refinement is needed before clinical implementation, the group noted. In addition, the group highlighted a role for electronic health record (EHR) integration to inform more nuanced categorization in future implementations.
Furthermore, additional technical development remains required before potential real-world applications, the group said.
See all metrics and the complete paper here.
AI Insights
Mapping the power of AI across the patient journey
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming clinical care, offering healthcare leaders new tools to improve workflows through automation and enhance patient outcomes with more accurate diagnoses and personalized treatments. This resource provides a framework for understanding how AI is applied across the patient journey, from pre-visit interactions to post‑visit monitoring and ongoing care. It focuses on actionable use cases to help healthcare organizations evaluate AI technologies holistically, balance innovation with feasibility, and navigate the evolving landscape of AI in healthcare.
For a deeper exploration of any specific use case featured in this infographic, check out our comprehensive compendium. It offers detailed insights into these technologies, including their benefits, implementation considerations, and evolving role in healthcare.
AI Insights
West Alabama school district looks to strengthen AI policy

TUSCALOOSA, Ala. (WBRC) – One west Alabama school district is working to update its policy on artificial intelligence (AI).
Tuscaloosa City Schools wants to hear from parents when it comes to how they handle AI, a growing system that continues to evolve.
The school district has a committee studying best-use practices and a major part of that study is surveying parents on how they think AI could be strengthened to improve teaching and learning.
Central High School English teacher Rachael James is the first to admit just the mere mention of AI intimidated her a bit.
“There is definitely that intimidation factor,” said James.
But AI is here to stay, and James felt the best way to tackle it is to confront it head on with crystal clarity.
James learned early on that for teachers, AI is simply another resource – another avenue – to find apps that help do their jobs better.
“AI allows us to create different tools to address different learning styles and it also makes some of the legwork in education a little easier with creating lesson plans we need to run our classes smoothly,” said James.
But like any new thing, there is a chance it could be abused and harmful.
“Safety and privacy are most important,” said Tuscaloosa City Schools Superintendent Dr. Mike Daria.
Dr. Daria says the school district is sending out surveys to parents to get their feedback on how to make the use of AI better, stronger and safer in the classroom.
“We know it’s evolving very quickly and we believe it’s important to have input from our parents on the way we use it. A big part of that is AI literacy so our students can understand AI, navigate it, interpret it, discern what it is and what it’s not,” said Dr. Daria.
But what about the teacher-student relationship? Could artificial intelligence damage the synergy?
“There is that fear. However, being able to educate, even if computers take over, there still has to be human engagement in some shape, form or fashion,” said James.
Either way, the future is here and James is on the front line and mastering it along the way.
“The goal is not to be afraid of AI,” said James.
School district leaders said parents have until September 26 to complete the survey.
Get news alerts in the Apple App Store and Google Play Store or subscribe to our email newsletter here.
Copyright 2025 WBRC. All rights reserved.
AI Insights
Artificial intelligence (AI) for trusted computing and cyber security
Summary points:
- New software security system enhances protection for NVIDIA Jetson-powered embedded AI systems.
- Secures AI models and sensitive data through encrypted APIs, process isolation, and secure OS features.
- Includes anti-rollback protection, automatic OS recovery, and centralized web-based monitoring tools for edge devices.
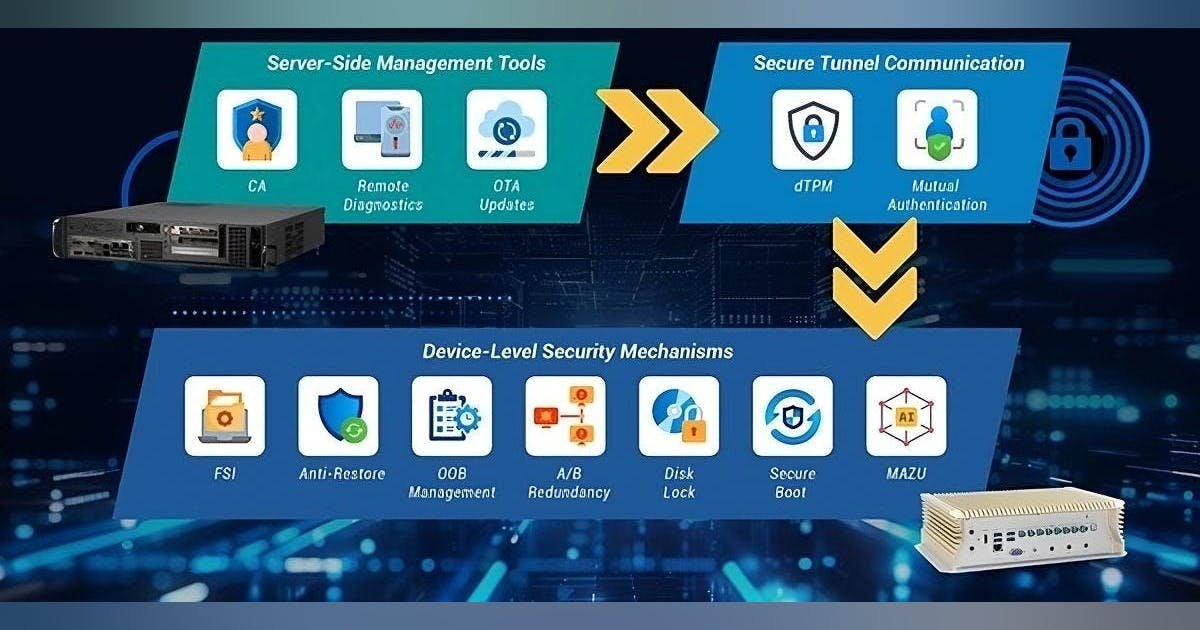
TAIPEI, Taiwan – AAEON Technology in Taipei, Taiwan, is introducing a software security system for the company’s embedded artificial intelligence (AI) systems powered by NVIDIA Jetson system-on-modules.
The cyber security system is built on a three-tiered architecture with components that protect data at the edge and in the cloud. It is available as part of the board support package for SKUs of AAEON’s BOXER-8621AI, BOXER-8641AI-Plus, and the BOXER-8651AI-Plus Edge AI systems.
The most notable component of this trusted computing product is a trusted execution environment (TEE) named MAZU to protect AI models and application data by separating files, processes, and algorithms within protected execution zones.
Sensitive assets
Using MAZU enables users to isolate machine learning algorithms while running standard applications. It also gives access to sensitive assets through certified APIs with encrypted communications, secure OS, and certificate validation.
Other mechanisms include anti-restore protection, A/B redundancy partitioning, and disk lock to prevent hackers from reverting system software to previous versions. It reverts to a stable OS image if a device fails, and encrypts data storage on edge devices.
The package contains server-side management tools to manage edge devices at the server, including a web-based UI that monitors several edge systems from one server.
For more information contact AAEON online at https://www.aaeon.com/en/article/detail/software_security_framework.
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoThe Guardian view on Trump and the Fed: independence is no substitute for accountability | Editorial
-
Tools & Platforms4 weeks ago
Building Trust in Military AI Starts with Opening the Black Box – War on the Rocks
-

 Ethics & Policy2 months ago
Ethics & Policy2 months agoSDAIA Supports Saudi Arabia’s Leadership in Shaping Global AI Ethics, Policy, and Research – وكالة الأنباء السعودية
-

 Events & Conferences4 months ago
Events & Conferences4 months agoJourney to 1000 models: Scaling Instagram’s recommendation system
-

 Jobs & Careers2 months ago
Jobs & Careers2 months agoMumbai-based Perplexity Alternative Has 60k+ Users Without Funding
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoHappy 4th of July! 🎆 Made with Veo 3 in Gemini
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoVEX Robotics launches AI-powered classroom robotics system
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoMacron says UK and France have duty to tackle illegal migration ‘with humanity, solidarity and firmness’ – UK politics live | Politics
-

 Funding & Business2 months ago
Funding & Business2 months agoKayak and Expedia race to build AI travel agents that turn social posts into itineraries
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoOpenAI 🤝 @teamganassi

