Tools & Platforms
Gen AI: Faster Than a Speeding BulletNot So Great at Leaping Tall Buildings
FEATURE
Gen AI: Faster Than a Speeding BulletNot So Great at Leaping Tall Buildings
by Christine Carmichael
This article was going to be a recap of my March 2025 presentation at the Computers in Libraries conference (computersinlibraries.infotoday.com).
However, AI technology and the industry are experiencing not just rapid
growth, but also rapid change. And as we info pros know, not all change is
good. Sprinkled throughout this article are mentions of changes since March, some in the speeding-bullet category, others in the not-leaping-tall-buildings one.
Getting Started
I admit to being biased—after all, Creighton University is in my hometown of Omaha—but what makes Creighton special is how the university community lives out its Jesuit values. That commitment to caring for the whole person, caring for our common home, educating men and women to serve with and for others, and educating students to be agents of change has never been more evident in my 20 years here than in the last 2–3 years.
An adherence to those purposes has allowed people from across the campus to come together easily and move forward quickly. Not in a “Move fast and break things” manner, but with an attitude of “We have to face this together if we are going to teach our students effectively.” The libraries’ interest in AI officially started after OpenAI launched ChatGPT-3.5 in November 2022.
Confronted with this new technology, my library colleagues and I gorged ourselves on AI-related information, attending workshops from different disciplines, ferreting out article “hallucinations,” and experimenting with ways to include information about generative AI (gen AI) tools in information literacy instruction sessions. Elon University shared its checklist, which we then included in our “Guide to Artificial Intelligence” (culibraries.creighton.edu/AI).
(Fun fact: Since August 2024, this guide has received approximately 1,184 hits—it’s our fourth-highest-ranked guide.)
 |
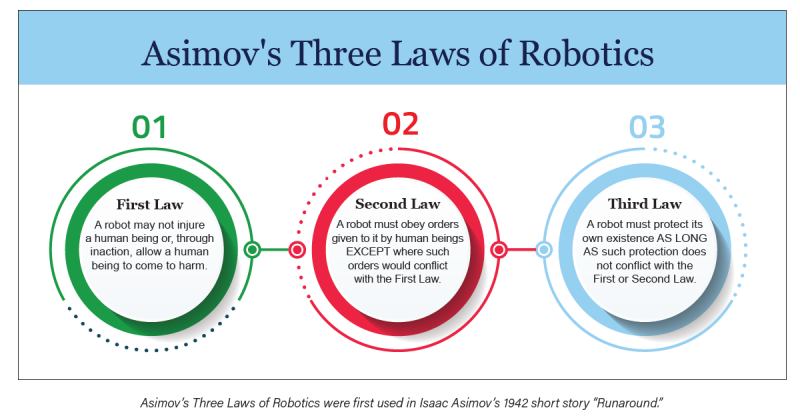
Two things inspired and convinced me to do more and take a lead role with AI at Creighton. First was my lifelong love affair with science fiction literature. Anyone familiar with classic science fiction should recognize Asimov’s Three Laws of Robotics. First used in Isaac Asimov’s 1942 short story “Runaround,” they are said to have come from the Handbook of Robotics, 56th Edition, published in 2058. Librarians should certainly appreciate this scenario of an author of fiction citing a fictional source. In our current environment, where gen AI “hallucinates” citations, it doesn’t get more AI than that!
Whether or not these three laws/concepts really work in a scientific sense, you could extrapolate some further guidance for regulating development and deployment of these new technologies to mitigate harm. Essentially, it’s applying the Hippocratic oath to AI.
 |
The second inspiration came from a February 2023 CNN article by Samantha Murphy Kelly (“The Way We Search for Information Online Is About to Change”; cnn.com/2023/02/09/tech/ai-search/index.html), which claims that the way we search for information is never going to be the same. I promptly thought to myself, “Au contraire, mon frère, we have been here before,” and posted a response on Medium (“ChatGPT Won’t Fix the Fight Against Misinformation”; medium.com/@christine.carmichael/chatgpt-wont-fix-the-fight-against-misinformation-15c1505851c3).
What Happened Next
Having a library director whose research passion is AI and ethics enabled us to act as a central hub for convening meetings and to keep track of what is happening with AI throughout the campus. We are becoming a clearinghouse for sharing information about projects, learning opportunities, student engagement, and faculty development, as well as pursuing library-specific projects.
After classes started in the fall 2024, the director of Magis Core Curriculum and the program director for COM 101—a co-curricular course requirement which meets oral communication and information literacy learning objectives—approached two research and instruction librarians, one being me. They asked us to create a module for our Library Encounter Online course (required in COM 101) to explain some background of AI and how large language models (LLMs) work. The new module was in place for spring 2025 classes.
In November 2024, the library received a $250,000 Google grant, which allowed us to subscribe to and test three different AI research assistant tools—Scopus, Keenious, and Scite. We split into three teams, each one responsible for becoming the experts on a particular tool. After presenting train-the-trainer sessions to each other, we restructured our teams to discuss the kinds of instruction options we could use: long, short, online (bite-sized).
We turned on Scopus AI in late December 2024. Team Scopus learned the tool’s ins and outs and describe it as “suitable for general researchers, upper-level undergraduates, graduate/professional students, medical residents, and faculty.” Aspects of the tool are particularly beneficial to discovering trends and gaps in research areas. One concern the team has remains the generation of irrelevant references. The team noticed this particularly when comparing the same types of searches in “regular” Scopus vs. Scopus AI.
Team Keenious was very enthusiastic and used an evaluation rubric from Rutgers University (credit where it’s due!). The librarians’ thoughts currently are that this tool is doing fairly well at “being a research recommendation tool” for advanced researchers. It has also successfully expanded the “universe” of materials used in systematic reviews. However, reservations remain as to its usefulness for undergraduate assignments, particularly when that group of students may not possess the critical thinking skills necessary to effectively use traditional library resources.
Scite is the third tool in our pilot. The platform is designed to help researchers evaluate the reliability of research papers using three categories: citations supporting claims, citations contrasting claims, and citations without either. Team Scite.ai” liked the tool, but recognized that it has a sizable learning curve. One Team Scite.ai member summed up their evaluation like this: “Much like many libraries, Scite.ai tries to be everything to everyone, but it lacks the helpful personal guide-on-the-side that libraries provide.”
The official launch and piloting the use of these tools began in April 2025 for faculty. We will introduce them to students in the fall 2025 semester. However, because the Scopus AI tool is already integrated and sports a prominent position on the search page, we anticipate folks using that tool before we get an opportunity to market it.
The Google funding also enabled the Creighton University Libraries to partner with several departments across campus in support of a full-day faculty development workshop in June. “Educating the Whole Person in an AI-Driven World” brought almost 150 faculty and staff together for the common purpose of discerning (another key component of Jesuit education) where and how we will integrate AI literacies into the curriculum. In addition to breakout sessions, we were introduced to a gen AI SharePoint site, the result of a library collaboration with the Center for Faculty Excellence.
ETHICS AND AI
Our director is developing a Jesuit AI Ethics Framework. Based on Jesuit values and Catholic Social Teaching, the framework also addresses questions asked by Pope Francis and the Papal Encyclical, Laudato si’, which asks us to care for our common home by practicing sustainability. Because of our extensive health sciences programs, a good portion of this ethical framework will focus on how to maintain patient and student privacy when using AI tools.
Ethics is a huge umbrella. These are things we think bear deeper dives and reflection:
The labor question: AI as a form of automation
We had some concerns and questions about AI as it applies to the workforce. Is it good if AI takes people’s jobs or starts producing art? Where does that leave the people affected? Note that the same concerns were raised about automation in the Industrial Revolution and when digital art tablets hit the market.
Garbage in, garbage out (GIGO): AIs are largely trained on internet content, and much of that content is awful.
We were concerned particularly about the lack of transparency: If we don’t know what an AI model is trained on, if there’s no transparency, can we trust it—especially for fields like healthcare and law, where there are very serious real-word implications? In the legal field, AI has reinforced existing biases, generally assuming People of Color (POCs) to be guilty.
Availability bias is also part of GIGO. AIs are biased by the nature of their training data and the nature of the technology itself (pattern recognition). Any AI trained on the internet is biased toward information from the modern era. Scholarly content is biased toward OA, and OA is biased by different field/author demographics that indicate who is more or less likely to publish OA.
AI cannot detect sarcasm, which may contribute to misunderstanding about meaning. AI chatbots and LLMs have repeatedly shown sexist, racist, and even white supremacist responses due to the nature of people online. What perspectives are excluded from training data (non-English content)? What about the lack of developer diversity (largely white Americans and those from India and East Asia)?
Privacy, illegal content sourcing, financial trust issues
Kashmir Hill’s 2023 book, Your Face Belongs to Us: A Secretive Startup’s Quest to End Privacy (Penguin Random House), provides an in-depth exposé on how facial recognition technology is being (mis)used. PayPal founder Peter Thiel invested $200,000 into a company called SmartCheckr, which eventually became Clearview AI, specializing in facial recognition. Thiel was a Facebook board member with a fiduciary responsibility at the same time that he was investing money in a company that was illegally scraping Facebook content. There is more to the Clearview AI story, including algorithmic bias issues with facial recognition. Stories like this raise questions about how to regulate this technology.
Environmental impacts
What about energy and water use and their climate impacts? This is from Scientific American: “A continuation of the current trends in AI capacity and adoption are set to lead to NVIDIA shipping 1.5 million AI server units per year by 2027. These 1.5 million servers, running at full capacity, would consume at least 85.4 terawatt-hours of electricity annually—more than what many small countries use in a year, according to the new assessment“ (scientificamerican.com/article/the-ai-boom-could-use-a-shocking-amount-of-electricity).
In May 2025, MIT Technology Review released a new report, “Power Hungry: AI and Our Energy Future” (technologyreview.com/supertopic/ai-energy-package), which states, “The rising energy cost of data centers is a vital test case for how we deal with the broader electrification of the economy.”
It’s Not All Bad News
There are days I do not even want to open my newsfeed because I know I will find another article detailing some new AI-infused horror, like this one from Futurism talking about people asking ChatGPT how to administer their own facial fillers (futurism.com/neoscope/chatgpt-advice-cosmetic-procedure-medicine). Then there is this yet-to-be-peer-reviewed article about what happens to your brain over time when using an AI writing assistant (“Your Brain on ChatGPT: Accumulation of Cognitive Debt When Using an AI Assistant for Essay Writing Task”; arxiv.org/pdf/2506.08872v1). It is reassuring to know that there are many, many people who are not invested in the hype, who are paying attention to how gen AI is or is not performing.
There are good things happening. For instance, ResearchRabbit and Elicit, two well-known AI research assistant tools, use the corpus of Semantic Scholar’s metadata as their training data. Keenious, one of the tools we are piloting, uses OpenAlex for its training corpus.
On either coast of the U.S. are two outstanding academic research centers focusing on ethics: Santa Clara University’s Markkula Center for Applied Ethics (scu.edu/ethics/focus-areas/internet-ethics) and the Berkman Klein Center for Internet and Society at Harvard University (cyber.harvard.edu).
FUTURE PLANS
We have projects and events planned for the next 2 years:
- Library director and School of Medicine faculty hosting a book club using Teaching With AI: Navigating the Future of Education
- Organizing an “unconference” called Research From All Angles Focusing on AI
- Hosting a Future of Work conference with Google
- Facilitating communities of practice around different aspects of AI: teaching, research, medical diagnostics, computing, patient interaction, etc.
As we get further immersed, our expectations of ourselves need to change. Keeping up with how fast the technology changes will be nigh on impossible. We must give ourselves and each other the grace to accept that we will never “catch up.” Instead, we will continue to do what we excel at—separating the truth from the hype, trying the tools for ourselves, chasing erroneous citations, teaching people to use their critical thinking skills every time they encounter AI, learning from each other, and above all, sharing what we know.
Tools & Platforms
I Interned at Google, but Chose to Start My Career at an AI Startup

This as-told-to essay is based on a conversation with Advait Maybhate, a software engineer. The following has been edited for length and clarity. Business Insider has verified his employment and academic history.
When I graduated from the University of Waterloo with my bachelor’s degree in 2023, I had done about a dozen tech internships.
Internships are a big deal at Waterloo, and students usually do six during their time there. I started doing internships before I enrolled and took some gap semesters to squeeze in a couple more stints.
To me, internships meant exploring varied fields, from gaming to fintech. I also got to intern at companies of different scales, from early-stage startups to mature Big Tech companies.
The first summer internship I did at Waterloo was at Google. Interning there was an eye-opening experience. I got to work on Google Search, a product that billions of people, including myself, use every single day.
When I took up the internship, like any freshman, I just thought it would be cool to work at a big company and ship big products. I ended up interning at Google twice, first in the summer of 2019, and then during the following summer in 2020.
During my internships at Google, I learned a lot, particularly about operating as a software engineer on large-scale products. That included learning how to write unit tests and good technical design documents. Big companies are great at that.
That said, I didn’t enjoy the bureaucracy that came with working in a Big Tech company. If you are shipping something on Google Search, you cannot break Google Search. That is just one of the underlying rules.
I understand why things have to be slow at that scale. It’s just that for someone who wants to learn fast and try out different things, it can feel limiting.
Even for my internship projects, it took a few months just for the code to get shipped. Although the projects were technically done, we still had to conduct A/B testing experiments and get sign-offs before the code could be deployed.
Going from Big Tech to startups
That experience eventually set me on the path toward working at startups. I chose to focus on AI because I wanted to be at the edge of what technology can do.
I was initially an AI skeptic. I didn’t buy into the hype of how it could change everything. It was only when I started using AI on a day-to-day basis that I began to appreciate how it could usher in a fundamental shift in the way we work.
It also helps that working on AI is fun and exciting. There are new advancements in space every week, and the frontier of what we can do just keeps going further.
I ended up doing two internships at two AI startups before I graduated. The first one was at Warp, an AI agent platform for developers, and the second one was at Ramp, a fintech startup that uses AI to automate financial operations.
I received full-time offers from both Warp and Ramp and chose to work at Warp. Both were great companies, but I wanted to work at Warp because I wanted to be part of a startup that was in a relatively early stage of development.
Ramp was at a much more mature stage than Warp at the time, and was focused on scaling up. Warp, on the other hand, was still trying to figure things out. On a personal level, I wanted to see how a startup goes through that process. I wanted to grapple with questions like, “How does pricing work? How does the business model work?”
That is harder to see at a mature startup, where all of these things have already been figured out and growth is the priority.
So far, working at Warp for the past two years has lived up to my expectations. We ship code every week. I could be working on something on Tuesday, and it gets shipped out on Thursday. I work maybe 60 to 70 hours a week. It’s a very different kind of velocity and cadence than at Big Tech.
In the near term, I want to continue to work on AI because it’s one of the most rapidly expanding areas in tech. Companies like Warp and its competitors, Cursor and Cognition, are all expanding very rapidly.
I am somewhat tempted to launch my own startup, but I think it’s difficult to gain market share in this hyper-competitive space. That’s something I will give serious thought about in the future.
Do you have a story to share about working at an AI startup? Contact this reporter at ktan@businessinsider.com.
Tools & Platforms
China’s top social media platforms take steps to comply with new AI content labeling rules

China’s top social media platforms, including ByteDance Ltd.’s TikTok clone Douying and Tencent Holdings’ WeChat, rolled out new features today to try to comply with a new law that mandates all artificial intelligence content is clearly labeled as such.
The new content labeling rules mandate that all AI-generated content posted on social media is tagged with explicit markings visible to users. It applies to AI-generated text, images, videos and audio, and also requires that implicit identifiers, such as digital watermarks, are embedded in the content’s metadata.
The law, which was first announced in March by the Cyberspace Administration of China, reflects Beijing’s increased scrutiny of AI at a time when concerns are rising about misinformation, online fraud and copyright infringement.
According to a report in the South China Morning Post, the law comes amid a broader push by Chinese authorities to increase oversight of AI, as illustrated by the CAC’s 2025 Qinglang campaign, which aims to clean up the Chinese language internet.
WeChat, one of the most popular messaging platforms in China, which boasts more than 1.4 billion monthly active users globally, has said that all creators using its platform must voluntarily declare any AI-generated content they publish. It’s also reminding users to “exercise their own judgement” for any content that has not been flagged as AI generated.
In a post today, WeChat said it “strictly prohibits” any attempts to delete, tamper with, forge or conceal AI labels added by its own automated tools, which are designed to pick up any AI-generated content that’s not flagged by users who upload it. It also reminded users against using AI to spread false information or for any other “illegal activities.”
Meanwhile Douyin, which has around 766 million monthly active users, said in a post today that it’s encouraging users to add clear labels to every AI-generated video they upload to its platform. It will also attempt to flag AI-generated content that isn’t flagged by users by checking its source via its metadata.
Several other popular social media platforms made similar announcements. For instance, the microblogging site Weibo, often known as China’s Twitter, said on Friday it’s adding tools for users to tag their own content, as well as a button for users to report “unlabeled AI content” posted by others.
RedNote, the e-commerce-based social media platform, issued its own statement on Friday, saying that it reserves the right to add explicit and implicit identifiers to any unidentified AI-generated content it detects on its platform.
Many of China’s best known AI tools are also moving to comply with the new law. For instance, Tencent’s AI chatbot Yuanbao said on Sunday it has created a new labeling system for any content it generates on behalf of users, adding explicit and implicit tags to text, videos and images. In its statement, it also advised users that they should not attempt to remove the labels it automatically adds to the content it creates.
When the CAC announced the law earlier this year, it said its main objectives were to implement robust AI content monitoring, enforce mandatory labeling and apply penalties to anyone who disseminates misinformation through AI or uses the technology to manipulate public opinion. It also pledged to crack down on deceptive marketing that uses AI, and strengthen online protections for underage users.
The European Union is set to implement its own AI content labeling requirements in August 2026, as part of the EU AI Act, which mandates that any content “significantly generated” by AI must be labeled to ensure transparency. The U.S. has not yet mandated AI content labels, but a number of social media platforms, such as Meta Platforms Inc., are implementing their own policies regarding the tagging of AI-generated media.
Photo: WeChat
Support our mission to keep content open and free by engaging with theCUBE community. Join theCUBE’s Alumni Trust Network, where technology leaders connect, share intelligence and create opportunities.
- 15M+ viewers of theCUBE videos, powering conversations across AI, cloud, cybersecurity and more
- 11.4k+ theCUBE alumni — Connect with more than 11,400 tech and business leaders shaping the future through a unique trusted-based network.
About SiliconANGLE Media
Founded by tech visionaries John Furrier and Dave Vellante, SiliconANGLE Media has built a dynamic ecosystem of industry-leading digital media brands that reach 15+ million elite tech professionals. Our new proprietary theCUBE AI Video Cloud is breaking ground in audience interaction, leveraging theCUBEai.com neural network to help technology companies make data-driven decisions and stay at the forefront of industry conversations.
Tools & Platforms
Surge in Alibabas Volume Amid Tech Shifts and AI Investments

Nvidia dropped solidly by -3.32%, with the trading volume of 42.33B. UAE AI company G42 is seeking to diversify its chip supply beyond Nvidia, including negotiations with tech giants like Amazon AWS, Google, Meta, Microsoft, and xAI for its planned AI park. Google is reportedly leading in these discussions.
2. Tesla (Nasdaq: TSLA)
Tesla dropped solidly by -3.50%, with the trading volume of 27.32B. Tesla’s CEO Elon Musk states that 80% of Tesla’s value will depend on the Optimus robot. Despite challenges in Europe, including executive resistance and competition, Tesla lowered Model 3 prices in China, marking its long-range version’s debut with a price cut.
3. Alibaba Group Holding Limited (NYSE: BABA)
Alibaba Group Holding Limited surged by 12.90%, with the trading volume of 10.94B. Alibaba plans to invest over 380 billion yuan in the next three years to boost its computing power industry, impacting domestic AI infrastructure. Its Q1 FY 2026 financial report showed a 10% revenue growth and a 76% net profit increase, exceeding expectations.
4. Microsoft (Nasdaq: MSFT)
Microsoft dipped mildly by -0.58%, with the trading volume of 10.63B. UAE AI company G42 is diversifying chip supplies to reduce dependency on Nvidia, engaging with tech giants like Amazon AWS, Google, Meta, Microsoft, and Elon Musk’s xAI for a planned AI park, with Google’s negotiations being the most advanced.
5. Apple (Nasdaq: AAPL)
Apple dipped mildly by -0.18%, with the trading volume of 9.16B. Apple is expanding its retail footprint in India with a new store, Apple Hebbal, set to open in Bangalore on September 2. This follows the openings of Apple BKC in Mumbai and Apple Saket in Delhi. Apple also plans to remove physical SIM card slots in more countries for the iPhone 17 series.
6. Alphabet (Nasdaq: GOOGL)
Alphabet gained mildly by 0.60%, with the trading volume of 8.44B. UAE’s AI company G42 is seeking to diversify its chip suppliers to reduce reliance on Nvidia. They are negotiating with major tech companies including Amazon AWS, Google, Meta, Microsoft, and Elon Musk’s xAI, with Google likely to sign a computing power procurement deal soon.
7. Palantir Technologies (NYSE: PLTR)
Palantir Technologies dipped mildly by -0.89%, with the trading volume of 7.27B. South Korean retail investors showed significant interest in Palantir Technologies, with substantial net purchases over the past week.
8. Meta Platforms (Nasdaq: META)
Meta Platforms dipped mildly by -1.65%, with the trading volume of 6.70B. Meta and Scale AI’s partnership faced challenges as major investment leads to strained relations and data quality concerns. Additionally, Meta plans to release a smart glasses SDK, diverging from trends by opting for LCoS over Micro LED technology.
9. Broadcom (Nasdaq: AVGO)
Broadcom dropped solidly by -3.65%, with the trading volume of 6.42B. Broadcom (AVGO.US) is expected to report a 21% revenue increase to $15.82 billion for Q3, with EPS projected at $1.66. Oppenheimer reaffirmed its “outperform” rating, raising the target price to $325. The AI business could exceed $5 billion in revenue.
10. Marvell Technology (Nasdaq: MRVL)
Marvell Technology plunged by -18.60%, with the trading volume of 6.19B. Company XYZ announced plans for global expansion, focusing on emerging markets and sustainable initiatives. New partnerships aim to enhance technological capabilities, while leadership emphasizes innovation and growth potential.
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoThe Guardian view on Trump and the Fed: independence is no substitute for accountability | Editorial
-
Tools & Platforms3 weeks ago
Building Trust in Military AI Starts with Opening the Black Box – War on the Rocks
-

 Ethics & Policy1 month ago
Ethics & Policy1 month agoSDAIA Supports Saudi Arabia’s Leadership in Shaping Global AI Ethics, Policy, and Research – وكالة الأنباء السعودية
-

 Events & Conferences3 months ago
Events & Conferences3 months agoJourney to 1000 models: Scaling Instagram’s recommendation system
-

 Jobs & Careers2 months ago
Jobs & Careers2 months agoMumbai-based Perplexity Alternative Has 60k+ Users Without Funding
-

 Funding & Business2 months ago
Funding & Business2 months agoKayak and Expedia race to build AI travel agents that turn social posts into itineraries
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoVEX Robotics launches AI-powered classroom robotics system
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoHappy 4th of July! 🎆 Made with Veo 3 in Gemini
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoOpenAI 🤝 @teamganassi
-

 Mergers & Acquisitions2 months ago
Mergers & Acquisitions2 months agoDonald Trump suggests US government review subsidies to Elon Musk’s companies


