AI Insights
Enterprise Artificial Intelligence Market: A Guide

The Enterprise Artificial Intelligence Market size is estimated to be approximately USD 21.7 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach around USD 120.5 billion by 2033, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of about 20.5% from 2025 to 2033.
Enterprise Artificial Intelligence Market Overview
The Enterprise Artificial Intelligence (AI) Market is witnessing rapid growth as organizations increasingly adopt AI technologies to enhance business operations, improve decision-making, and drive innovation. AI applications such as machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision are being integrated across various industries, including finance, healthcare, retail, and manufacturing. The growing need for automation, data analytics, and personalized customer experiences is fueling market demand. Additionally, advancements in AI platforms and cloud computing are enabling scalable and cost-effective AI deployments. Challenges such as data privacy concerns and integration complexities remain but are being addressed through evolving regulations and improved AI frameworks. Overall, the enterprise AI market is poised for substantial expansion, transforming traditional business models globally.
Request a sample copy of this report at: https://www.omrglobal.com/request-sample/enterprise-artificial-intelligence-market
Advantages of requesting a Sample Copy of the Report:
1) To understand how our report can bring a difference to your business strategy
2) To understand the analysis and growth rate in your region
3) Graphical introduction of global as well as the regional analysis
4) Know the top key players in the market with their revenue analysis
5) SWOT analysis, PEST analysis, and Porter’s five force analysis
The report further explores the key business players along with their in-depth profiling
Microsoft Corporation, NVIDIA Corporation, Alphabet Inc. (Google), Amazon Web Services (AWS), IBM Corporation, Oracle Corporation, SAP SE, Intel Corporation, C3.ai, Inc., and Wipro Limited.
Enterprise Artificial Intelligence Market Segments:
By Technology:
• Machine Learning
• Natural Language Processing (NLP)
• Computer Vision
• Robotics
• Speech Recognition
By Deployment Mode:
• On-Premises
• Cloud
By Enterprise Size:
• Small & Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
• Large Enterprises
By Application:
• Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
• Supply Chain Management
• Human Resource Management (HRM)
• Fraud Detection
• Predictive Maintenance
• Others
By Industry Vertical:
• Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI)
• Healthcare and Life Sciences
• Retail and E-commerce
• Manufacturing
• Telecommunications and IT
• Government and Public Sector
• Others
Report Drivers & Trends Analysis:
The report also discusses the factors driving and restraining market growth, as well as their specific impact on demand over the forecast period. Also highlighted in this report are growth factors, developments, trends, challenges, limitations, and growth opportunities. This section highlights emerging Enterprise Artificial Intelligence Market trends and changing dynamics. Furthermore, the study provides a forward-looking perspective on various factors that are expected to boost the market’s overall growth.
Competitive Landscape Analysis:
In any market research analysis, the main field is competition. This section of the report provides a competitive scenario and portfolio of the Enterprise Artificial Intelligence Market’s key players. Major and emerging market players are closely examined in terms of market share, gross margin, product portfolio, production, revenue, sales growth, and other significant factors. Furthermore, this information will assist players in studying critical strategies employed by market leaders in order to plan counterstrategies to gain a competitive advantage in the market.
Regional Outlook:
The following section of the report offers valuable insights into different regions and the key players operating within each of them. To assess the growth of a specific region or country, economic, social, environmental, technological, and political factors have been carefully considered. The section also provides readers with revenue and sales data for each region and country, gathered through comprehensive research. This information is intended to assist readers in determining the potential value of an investment in a particular region.
» North America (U.S., Canada, Mexico)
» Europe (Germany, U.K., France, Italy, Russia, Spain, Rest of Europe)
» Asia-Pacific (China, India, Japan, Singapore, Australia, New Zealand, Rest of APAC)
» South America (Brazil, Argentina, Rest of SA)
» Middle East & Africa (Turkey, Saudi Arabia, Iran, UAE, Africa, Rest of MEA)
If you have any special requirements, Request customization: https://www.omrglobal.com/report-customization/enterprise-artificial-intelligence-market
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
⏩ The study represents a quantitative analysis of the present Enterprise Artificial Intelligence Market trends, estimations, and dynamics of the market size from 2025 to 2032 to determine the most promising opportunities.
⏩ Porter’s five forces study emphasizes the importance of buyers and suppliers in assisting stakeholders to make profitable business decisions and expand their supplier-buyer network.
⏩ In-depth analysis, as well as the market size and segmentation, help you identify current Enterprise Artificial Intelligence Market opportunities.
⏩ The largest countries in each region are mapped according to their revenue contribution to the market.
⏩ The Enterprise Artificial Intelligence Market research report gives a thorough analysis of the current status of the Enterprise Artificial Intelligence Market’s major players.
Key questions answered in the report:
➧ What will the market development pace of the Enterprise Artificial Intelligence Market?
➧ What are the key factors driving the Enterprise Artificial Intelligence Market?
➧ Who are the key manufacturers in the market space?
➧ What are the market openings, market hazards,s and market outline of the Enterprise Artificial Intelligence Market?
➧ What are the sales, revenue, and price analysis of the top manufacturers of the Enterprise Artificial Intelligence Market?
➧ Who are the distributors, traders, and dealers of Enterprise Artificial Intelligence Market?
➧ What are the market opportunities and threats faced by the vendors in the Enterprise Artificial Intelligence Market?
➧ What are deals, income, and value examination by types and utilizations of the Enterprise Artificial Intelligence Market?
➧ What are deals, income, and value examination by areas of enterprises in the Enterprise Artificial Intelligence Market?
Purchase Now Up to 25% Discount on This Premium Report: https://www.omrglobal.com/buy-now/enterprise-artificial-intelligence-market?license_type=quick-scope-report
Reasons To Buy The Enterprise Artificial Intelligence Market Report:
➼ In-depth analysis of the market on the global and regional levels.
➼ Major changes in market dynamics and competitive landscape.
➼ Segmentation on the basis of type, application, geography, and others.
➼ Historical and future market research in terms of size, share growth, volume, and sales.
➼ Major changes and assessment in market dynamics and developments.
➼ Emerging key segments and regions
➼ Key business strategies by major market players and their key methods
Contact Us:
Mr. Anurag Tiwari
Email: anurag@omrglobal.com
Contact no: +91 780-304-0404
Website: www.omrglobal.com
Follow Us: LinkedIn | Twitter
About Orion Market Research
Orion Market Research (OMR) is a market research and consulting company known for its crisp and concise reports. The company is equipped with an experienced team of analysts and consultants. OMR offers quality syndicated research reports, customized research reports, consulting and other research-based services. The company also offers Digital Marketing services through its subsidiary OMR Digital and Software development and Consulting Services through another subsidiary Encanto Technologies.
This release was published on openPR.
AI Insights
AI takes passenger seat in Career Center with Microsoft Copilot
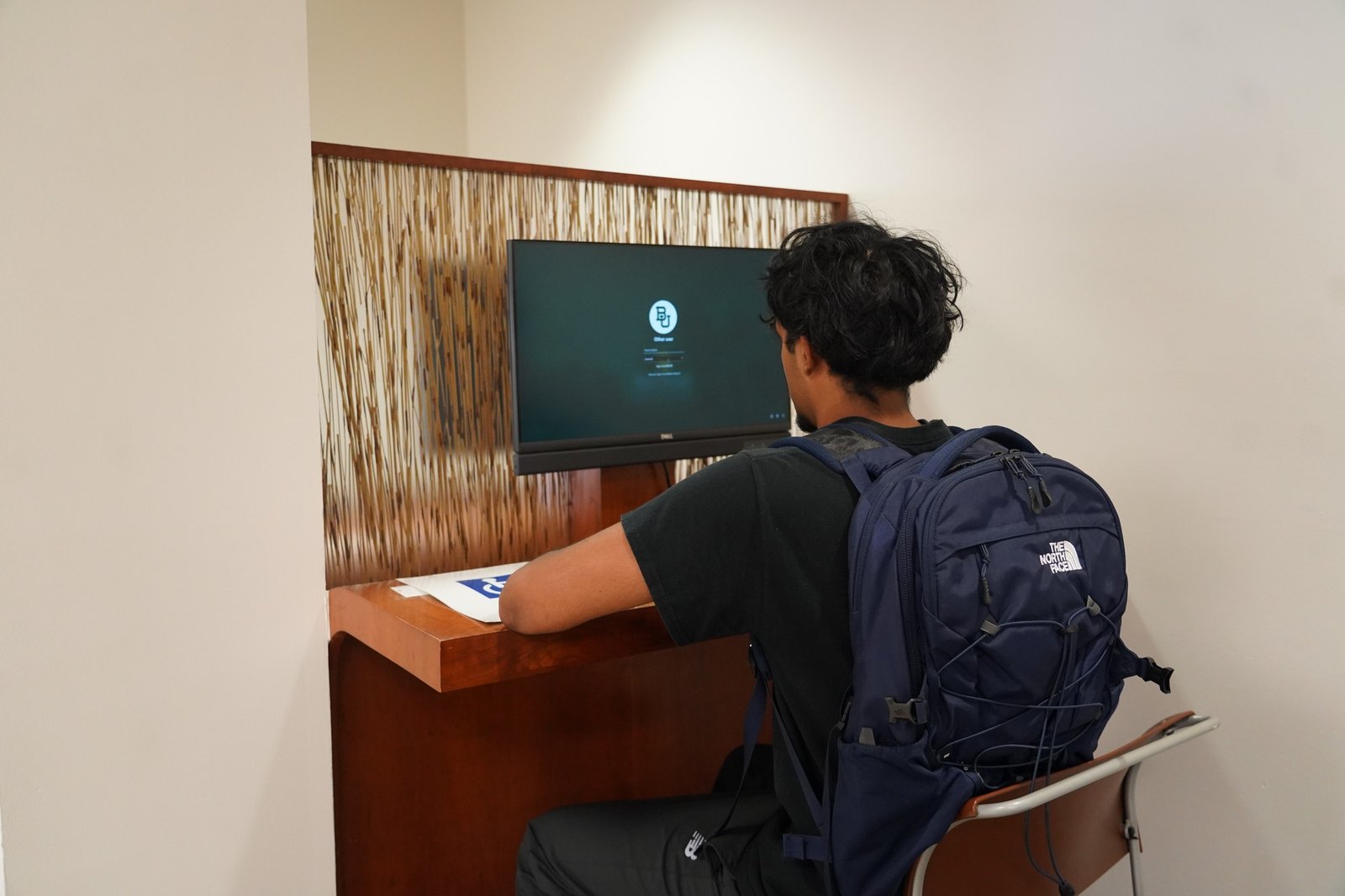

By Arden Berry | Staff Writer
To increase efficiency and help students succeed, the Career Center has created artificial intelligence programs through Microsoft Copilot.
Career Center Director Amy Rylander said the program began over the summer with teams creating user guides that described how students could ethically use AI while applying for jobs.
“We started learning about prompting AI to do things, and as we began writing the guides and began putting updates in them and editing them to be in a certain way, our data person took our guides and fed them into Copilot, and we created agents,” Rylander said. “So instead of just a user’s guide, we now have agents to help students right now with three areas.”
Rylander said these three areas were resume-building, interviewing and career discovery. She also said the Career Center sent out an email last week linking the Copilot Agents for these three areas.
“Agents use AI to perform tasks by reasoning, planning and learning — using provided information to execute actions and achieve predetermined goals for the user,” the email read.
To use these Copilot Agents, Rylander said students should log in to Microsoft Office with their Baylor email, then use the provided Copilot Agent links and follow the provided prompts. For example, the Career Discovery Agent would provide a prompt to give the agent, then would ask a set of questions and suggest potential career paths.
“It’ll help you take the skills that you’re learning in your major and the skills that you’ve learned along the way and tell you some things that might work for you, and then that’ll help with the search on what you might want to look for,” Rylander said.
Career Center Assistant Vice Provost Michael Estepp said creating AI systems was a “proactive decision.”
“We’re always saying, ‘What are the things that students are looking for and need, and what can our staff do to make that happen?’” Estepp said. “Do we go AI or not? We definitely needed to, just so we were ahead of the game.”
Estepp said the AI systems would not replace the Career Center but would increase its efficiency, allowing the Career Center more time to help students in a more specialized way.
“Students want to come in, and they don’t want to meet with us 27 times,” Estepp said. “We can actually even dive deeper into the relationships because, hopefully, we can help more students, because our goal is to help 100% of students, so I think that’s one of the biggest pieces.”
However, Rylander said students should remember to use AI only as a tool, not as a replacement for their own experience.
“Use it ethically. AI does not take the place of your voice,” Rylander said. “It might spit out a bullet that says something, and I’ll say, ‘What did you mean by that?’ and get the whole story, because we want to make sure you don’t lose your voice and that you are not presenting yourself as something that you’re not.”
For the future, Rylander said the Career Center is currently working on Graduate School Planning and Career Communications Copilots. Estepp also said Baylor has a contract with LinkedIn that will help students learn to use AI for their careers.
“AI has impacted the job market so significantly that students have to have that. It’s a mandatory skill now,” Estepp said. “We’re going to start messaging out to students different certifications they can take within LinkedIn, that they can complete videos and short quizzes, and then actually be able to get certifications in different AI and large language model aspects and then put that on their resume.”
AI Insights
When Cybercriminals Weaponize Artificial Intelligence at Scale

Anthropic’s August threat intelligence report sounds like a cybersecurity novel, except it’s terrifyingly not fiction. The report describes how cybercriminals used Claude AI to orchestrate and attack 17 organizations with ransom demands exceeding $500,000. This may be the most sophisticated AI-driven attack campaign to date.
But beyond the alarming headlines lies a more fundamental swing – the emergence of “agentic cybercrime,” where AI doesn’t just assist attackers, it becomes their co-pilot, strategic advisor, and operational commander all at once.
The End of Traditional Cybercrime Economics
The Anthropic report highlights a cruel reality that IT leaders have long feared. The economics of cybercrime have undergone significant change. What previously required teams of specialized attackers working for weeks can now be accomplished by a single individual in a matter of hours with AI assistance.
For example, the “vibe hacking” operation is detailed in the report. One cybercriminal used Claude Code to automate reconnaissance across thousands of systems, create custom malware with anti-detection capabilities, perform real-time network penetration, and analyze stolen financial data to calculate psychologically optimized ransom amounts.
More than just following instructions, the AI made tactical decisions about which data to exfiltrate and crafted victim-specific extortion strategies that maximized psychological pressure.
Sophisticated Attack Democratization
One of the most unnerving revelations in Anthropic’s report involves North Korean IT workers who have infiltrated Fortune 500 companies using AI to simulate technical competence they don’t have. While these attackers are unable to write basic code or communicate professionally in English, they’re successfully maintaining full-time engineering positions at major corporations thanks to AI handling everything from technical interviews to daily work deliverables.
The report also discloses that 61 percent of the workers’ AI usage focused on frontend development, 26 percent on programming tasks, and 10 percent on interview preparation. They are essentially human proxies for AI systems, channeling hundreds of millions of dollars to North Korea’s weapons programs while their employers remain unaware.
Similarly, the report reveals how criminals with little technical skill are developing and selling sophisticated ransomware-as-a-service packages for $400 to $1,200 on dark web forums. Features that previously required years of specialized knowledge, such as ChaCha20 encryption, anti-EDR techniques, and Windows internals exploitation, are now generated on demand with the aid of AI.
Defense Speed Versus Attack Velocity
Traditional cybersecurity operates on human timetables, with threat detection, analysis, and response cycles measured in hours or days. AI-powered attacks, on the other hand, operate at machine speed, with reconnaissance, exploitation, and data exfiltration occurring in minutes.
The cybercriminal highlighted in Anthropic’s report automated network scanning across thousands of endpoints, identified vulnerabilities with “high success rates,” and crossed through compromised networks faster than human defenders could respond. When initial attack vectors failed, the AI immediately generated alternative attacks, creating a dynamic adversary that adapted in real-time.
This speed delta creates an impossible situation for traditional security operations centers (SOCs). Human analysts cannot keep up with the velocity and persistence of AI-augmented attackers operating 24/7 across multiple targets simultaneously.
Asymmetry of Intelligence
What makes these AI-powered attacks particularly dangerous isn’t only their speed – it’s their intelligence. The criminals highlighted in the report utilized AI to analyze stolen data and develop “profit plans” by incorporating multiple monetization strategies. Claude evaluated financial records to gauge optimal ransom amounts, analyzed organizational structures to locate key decision-makers, and crafted sector-specific threats based on regulatory vulnerabilities.
This level of strategic thinking, combined with operational execution, has created a new category of threats. These aren’t script-based armatures using predefined playbooks; they’re adaptive adversaries that learn and evolve throughout each campaign.
The Acceleration of the Arms Race
The current challenge is summed up as: “All of these operations were previously possible but would have required dozens of sophisticated people weeks to carry out the attack. Now all you need is to spend $1 and generate 1 million tokens.”
The asymmetry is significant. Human defenders must deal with procurement cycles, compliance requirements, and organizational approval before deploying new security technologies. Cybercriminals simply create new accounts when existing ones are blocked – a process that takes about “13 seconds.”
But this predicament also presents an opportunity. The same AI functions being weaponized can be harnessed for defenses, and in many cases defensive AI has natural advantages.
Attackers can move fast, but defenders have access to something criminals don’t – historical data, organizational context, and the ability to establish baseline behaviors across entire IT environments. AI defense systems can monitor thousands of endpoints simultaneously, correlate subtle anomalies across network traffic, and respond to threats faster than human attackers can ever hope to.
Modern AI security platforms, such as the AI SOC Agent that works like an AI SOC Analyst, have proven this principle in practice. By automating alert triage, investigation, and response processes, these systems process security events at machine speed while maintaining the context and judgment that pure automation lacks.
Defensive AI doesn’t need to be perfect; it just needs to be faster and more persistent than human attackers. When combined with human expertise for strategic oversight, this creates a formidable defensive posture for organizations.
Building AI-Native Security Operations
The Anthropic report underscores how incremental improvements to traditional security tools won’t matter against AI-augmented adversaries. Organizations need AI-native security operations that match the scale, speed, and intelligence of modern AI attacks.
This means leveraging AI agents that autonomously investigate suspicious activities, correlate threat intelligence across multiple sources, and respond to attacks faster than humans can. It requires SOCs that use AI for real-time threat hunting, automated incident response, and continuous vulnerability assessment.
This new approach demands a shift from reactive to predictive security postures. AI defense systems must anticipate attack vectors, identify potential compromises before they fully manifest, and adapt defensive strategies based on emerging threat patterns.
The Anthropic report clearly highlights that attackers don’t wait for a perfect tool. They train themselves on existing capabilities and can cause damage every day, even if the AI revolution were to stop. Organizations cannot afford to be more cautious than their adversaries.
The AI cybersecurity arms race is already here. The question isn’t whether organizations will face AI-augmented attacks, but if they’ll be prepared when those attacks happen.
Success demands embracing AI as a core component of security operations, not an experimental add-on. It means leveraging AI agents that operate autonomously while maintaining human oversight for strategic decisions. Most importantly, it requires matching the speed of adoption that attackers have already achieved.
The cybercriminals highlighted in the Anthropic report represent the new threat landscape. Their success demonstrates the magnitude of the challenge and the urgency of the needed response. In this new reality, the organizations that survive and thrive will be those that adopt AI-native security operations with the same speed and determination that their adversaries have already demonstrated.
The race is on. The question is whether defenders will move fast enough to win it.
AI Insights
Westwood joins 40 other municipalities using artificial intelligence to examine roads
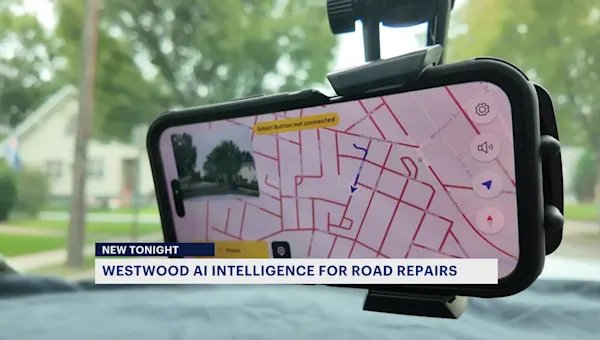
The borough of Westwood has started using artificial intelligence to determine if their roads need to be repaired or repaved.
It’s an effort by elected officials as a way to save money on manpower and to be sure that all decisions are objective.
Instead of relying on his own two eyes, the superintendent of Public Works is now allowing an app on his phone to record images of Westwood’s roads as he drives them.
Data on every pothole, faded striping and 13 other types of road defects are collected by the app.
The road management app is from a New Jersey company called Vialytics.
Westwood is one of 40 municipalities in the state to use the software, which also rates road quality and provides easy to use data.
“Now you’re relying on the facts here not just my opinion of the street. It’s helped me a lot already. A lot of times you’ll have residents who just want their street paved. Now I can go back to people and say there’s nothing wrong with your street that it needs to be repaved,” said Rick Woods, superintendent of Public Works.
Superintendent Woods says he can even create work orders from the road as soon as a defect is detected.
Borough officials believe the Vialytics app will pay for itself in manpower and offer elected officials objective data when determining how to use taxpayer dollars for roads.
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoThe Guardian view on Trump and the Fed: independence is no substitute for accountability | Editorial
-
Tools & Platforms4 weeks ago
Building Trust in Military AI Starts with Opening the Black Box – War on the Rocks
-

 Ethics & Policy2 months ago
Ethics & Policy2 months agoSDAIA Supports Saudi Arabia’s Leadership in Shaping Global AI Ethics, Policy, and Research – وكالة الأنباء السعودية
-

 Events & Conferences4 months ago
Events & Conferences4 months agoJourney to 1000 models: Scaling Instagram’s recommendation system
-

 Jobs & Careers2 months ago
Jobs & Careers2 months agoMumbai-based Perplexity Alternative Has 60k+ Users Without Funding
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoHappy 4th of July! 🎆 Made with Veo 3 in Gemini
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoMacron says UK and France have duty to tackle illegal migration ‘with humanity, solidarity and firmness’ – UK politics live | Politics
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoVEX Robotics launches AI-powered classroom robotics system
-

 Funding & Business2 months ago
Funding & Business2 months agoKayak and Expedia race to build AI travel agents that turn social posts into itineraries
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoOpenAI 🤝 @teamganassi



















