Tools & Platforms
Blueprint for Tech Dominance or Policy Overreach?
Insider Brief
- The White House released a sweeping AI Action Plan aimed at securing U.S. leadership in artificial intelligence through accelerated innovation, deregulation, infrastructure upgrades, and international strategy.
- The plan promotes open-source models, reduced regulatory oversight, and expanded access to computing and workforce training, while linking AI development to energy policy and national security.
- Critics warn the strategy prioritizes industry growth over privacy and safety, and raises concerns about politicized funding, global trust, and the balance between unilateral dominance and allied cooperation.
The White House has released an expansive blueprint to secure American dominance in artificial intelligence, detailing a sweeping set of federal initiatives that aim to reshape innovation, infrastructure, and international policy. The plan — called America’s AI Action Plan — seeks to propel the U.S. into a new era of economic competitiveness and national security while countering rising global competition, especially from China.
Released in July 2025 and framed as a national imperative, the 23-page document outlines the administration’s three-pillar strategy: accelerate AI innovation, build AI infrastructure, and lead in global AI diplomacy and security. The plan positions artificial intelligence not only as a transformative tool for economic growth but as the centerpiece of 21st-century geopolitical power.
It’s overall message: Build, Baby, Build.
The report states: “We need to build and maintain vast AI infrastructure and the energy to power it. To do that, we will continue to reject radical climate dogma and bureaucratic red tape, as the Administration has done since Inauguration Day. Simply put, we need to ‘Build, Baby, Build!’”
Deregulation Overlays Innovation
A central theme in the plan is the rejection of regulatory barriers seen as hindering the development and deployment of AI. The White House has moved quickly to roll back regulations enacted under the previous administration, including revoking Biden-era executive orders on AI safety. Instead, the plan promotes a deregulatory agenda that favors open-source innovation, free speech protections in AI systems, and reduced scrutiny on companies building or deploying large models.
The administration directs agencies such as the Office of Management and Budget, the Department of Commerce, and the Federal Trade Commission to review and repeal rules that may slow AI development. New funding guidelines will penalize states with what are described as burdensome AI laws, aiming to concentrate federal resources in regions more favorable to private-sector growth.
The theme is not a surprise for the White House’s AI watchers — proponents and critics, alike.
Vice President JD Vance gave a speech shortly after Trump took officer outlining the administrations desire to pull back regulations. “
We believe that excessive regulation of the AI sector could kill a transformative industry just as it’s taking off, and we’ll make every effort to encourage pro-growth AI policies,” Vance said, as reported in Wired, adding, “we feel strongly that AI must remain free from ideological bias, and that American AI will not be co-opted into a tool for authoritarian censorship.”
Open Models, Strategic Value
The plan also gives strategic priority to open-source and open-weight AI models, which it argues offer innovation benefits and broader adoption across sensitive sectors like healthcare and national security. To address cost barriers, the government will help establish financial markets for compute — such as spot or forward contracts for access to advanced chips—paralleling commodities trading.
Academic and startup communities are expected to benefit from expanded access to computing resources through the National AI Research Resource pilot. These measures are designed to help U.S.-developed open models become de facto global standards, furthering both scientific collaboration and geopolitical influence.
AI-Enabled Workforce and Education
While automation often raises concerns about job displacement, the action plan frames AI as a net positive for American workers. A broad set of federal programs will target skill development, retraining, and early education in AI-relevant trades—from software engineering to electrical work supporting data centers.
The Department of Labor, Department of Education, and National Science Foundation are tasked with overhauling curriculum and apprenticeship programs to align with new infrastructure needs. Tax guidance will encourage employer investment in worker upskilling, while federal grants will incentivize industry to co-develop training programs tied to hiring pipelines.
Labor market impacts from AI adoption will be tracked through enhanced economic surveys, with a new AI Workforce Research Hub to analyze trends and guide policy responses.
Science, Security, and the Future of Discovery
The plan elevates AI as a driver of scientific progress, calling for new investments in AI-enabled laboratories, automated experimentation platforms, and research organizations using machine learning for hypothesis generation. Federal agencies are instructed to require public release of non-sensitive datasets generated during federally funded research, positioning data as a national strategic asset.
Agencies will also fund research into AI interpretability and robustness, identified as technical areas critical for ensuring that AI systems behave predictably in high-stakes domains such as defense, energy, and healthcare. The Department of Defense and National Science Foundation will lead efforts to evaluate vulnerabilities in large models and sponsor competitions to test AI transparency and control.
Infrastructure as a Foundation
One of the most striking claims in the plan is that AI’s future demands a fundamental upgrade of the nation’s power grid. Data centers, semiconductor fabrication plants, and AI-related energy needs are forecast to outpace existing capacity. In response, the administration will streamline permitting processes, open up federal lands for infrastructure, and prioritize dispatchable energy sources like nuclear and geothermal power.
The plan encourages federal agencies to fast-track approval of power-hungry AI projects by reducing regulatory complexity under laws such as the Clean Water Act and the National Environmental Policy Act. Additionally, it calls for the creation of high-security data centers specifically designed for sensitive government workloads, with input from military and intelligence agencies.
Global AI Diplomacy and Export Control
International alignment is a key feature of the third pillar. The administration seeks to export U.S.-developed AI technologies to partner nations while preventing adversaries from acquiring the same capabilities. It proposes full-stack AI export packages and more aggressive enforcement of chip export controls, with particular scrutiny on advanced computing systems.
China is specifically named as a strategic rival. The plan outlines efforts to counter Chinese influence in international standard-setting bodies and encourages allies to adopt U.S.-aligned frameworks for AI governance and intellectual property protection. New initiatives will coordinate technology diplomacy and align export controls across the AI supply chain.
In parallel, the plan outlines proposals to patch gaps in semiconductor export controls by targeting sub-systems, not just whole machines, and calls for stronger oversight of U.S. research institutions to prevent unauthorized knowledge transfer.
Responding to Deepfakes and Biosecurity Risks
The plan also acknowledges AI’s risks, including the spread of synthetic media and the potential misuse of AI in biological threats. Federal agencies are directed to develop standards for identifying and countering deepfakes in the legal system and to enhance forensic tools to authenticate audio and video.
In biosecurity, the plan mandates stricter controls over the use of AI in genetic synthesis, including required screening for synthetic DNA ordering and stronger data-sharing between providers to detect malicious actors.
Toward an AI-Empowered Government
Inside government, the action plan calls for AI adoption across agencies. It proposes new interagency councils, procurement platforms, and workforce exchanges to ensure the public sector keeps pace with private innovation. Frontier language models will be made available to civil servants whose roles could benefit from automation, and best practices will be codified in an AI Incident Response Playbook.
The Department of Defense is directed to automate workflows, develop test environments for autonomous systems, and codify access to commercial compute resources in the event of a national emergency.
Bold Vision, Real Challenges
Taken together, America’s AI Action Plan is a bold document — one that sets clear direction for maintaining U.S. leadership in a rapidly evolving domain. But many of its objectives, from reshaping permitting rules to expanding power grid capacity, will require coordination across federal, state, and private sectors.
The plan avoids discussion of potential tensions, such as conflicts between open-source promotion and export control, or between deregulation and risk mitigation. It also remains silent on privacy protections for individuals affected by AI systems, aside from a general pledge to respect civil liberties.
As Graham Brookie of the Atlantic Council said that the plan’s success will depend not just on leading in AI, but on building an ecosystem that can evolve quickly enough to stay competitive. He notes there are three unanswered questions that loom over the implementation of America’s AI Action Plan.
With budget and staffing cuts across federal agencies, it’s unclear whether the government has the resources or expertise to deliver on its sweeping goals, especially in areas like tech diplomacy and scientific research. The plan’s proposal to tie federal funding to state-level AI regulations also raises concerns about politicized enforcement. Also, while the strategy emphasizes exporting U.S. technology to allies, it offers little detail on how the U.S. will collaborate on shared AI norms or counter China’s influence in global governance bodies.
There’s also a question on how will this balance of unilateral dominance and alliance formation will be tricky, to say the least.
“The United States can lead the way—but not through dominance alone,” said Raul Brens Jr., the director of the GeoTech Center. “An alliance is built on the stabilizing forces of trust, not tech stack supply chains or destabilizing attempts to force partners to follow one country’s standards. Building this trust will require working together to respond to the ways that AI shapes our societies, not just unilaterally fixating on its growth.”
Other critics think the plan is just a ploy for big business expansion.
The co-executive directors of the AI Now Institute — Sarah Myers West and Amba Kak — said in a statement sent to Wired the plan as “written by Big Tech interests invested in advancing AI that’s used on us, not by us.”
Nonetheless, by linking economic policy, national security, scientific progress, and global diplomacy under a unified AI strategy, the plan marks a significant escalation in U.S. government involvement in the AI race—and underscores the view that technological superiority is no longer optional, but essential.
Tools & Platforms
NVIDIA Partners with Black Tech Street to Bring AI Revolution to Tulsa, Home of $10,000 Remote Worker Grants
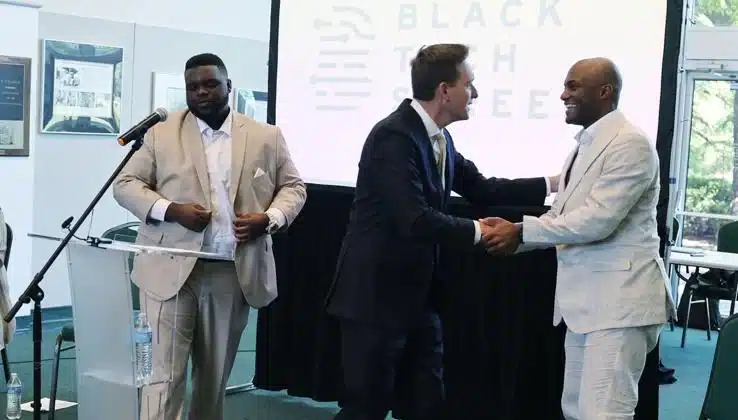

NVIDIA has formed a major partnership with Black Tech Street to develop Tulsa’s historic Greenwood District into a national artificial intelligence center, marking a significant economic development initiative for the area once known as Black Wall Street.
Partnership Overview and Goals
The collaboration, formalized through a Memorandum of Understanding, aims to train up to 10,000 people in AI technologies while supporting local startups and positioning Tulsa as a leader in artificial intelligence innovation. The initiative centers on creating the Greenwood AI Center of Excellence within the district that was devastated by the 1921 Tulsa Race Massacre.
“This is going to have an incredible impact on Tulsa,” said Terrance Billingsley II, CEO of Black Tech Street. “NVIDIA is the most valuable company in the world, leading the most important technological revolution in human history.”
The partnership leverages Tulsa’s recent designation as a federal Tech Hub, which awarded the city $51 million from the U.S. Economic Development Administration. Of that funding, $10.6 million will specifically support the AI center development.
Comprehensive Training and Education Program
The initiative’s training component will reach across multiple educational institutions and community organizations. Partners include Langston University, Tulsa Community College, and Oklahoma State University, creating a comprehensive educational ecosystem for AI development.
Educators will receive certification through the NVIDIA Deep Learning Institute University Ambassador Program, providing access to cloud-based tools powered by NVIDIA GPUs. This infrastructure aims to ensure high-quality, standardized training across participating institutions.
The 10,000-person training target represents an ambitious scale that could significantly impact Tulsa’s workforce development. The program plans to serve students, workers, and entrepreneurs throughout the region, creating multiple pathways for AI skill development.
Economic Development and Startup Support
Beyond education, the partnership includes substantial business development components. NVIDIA will provide local startups access to its Inception program, which offers early-stage companies technology support and networking opportunities crucial for growth in competitive tech markets.
The collaboration also includes access to advanced computing resources, including GPUs and cloud platforms essential for AI development projects. These resources typically require significant capital investment, making the partnership valuable for local entrepreneurs and researchers.
Billingsley emphasized the local economic focus: “The next step is getting NVIDIA integrated into the community, getting certain programs up and running for people to take advantage of, hosting different events, and trying to architect what the big play that is going to transform our local economy is going to be.”
Strategic Location and Historical Significance
The choice of Greenwood District for this initiative carries particular historical weight. The area was once known as Black Wall Street, representing one of the most prosperous Black communities in early 20th-century America before its destruction in the 1921 Tulsa Race Massacre.
This partnership positions AI development within a community that has symbolic importance for Black economic empowerment and entrepreneurship. The initiative aims to create high-paying tech jobs and drive entrepreneurship in an area working to rebuild its economic foundation.
Political and Community Support
The partnership has garnered support from political leaders across party lines. U.S. Senator James Lankford highlighted Oklahoma’s growing technology profile: “Oklahoma is fast becoming a national leader in next-generation innovation, from AI to aerospace and beyond. Whether it is in Tulsa or across the state, Oklahoma is proving that you do not have to be on the coasts to be on the cutting edge.”
Tulsa Mayor Monroe Nichols expressed enthusiasm for the economic opportunities: “NVIDIA and Black Tech Street are setting the stage for new jobs for Tulsans, and I am eager to see how this investment in innovation will open more doors of opportunity for our community.”
Building on Tulsa’s Remote Work Success
This AI initiative builds upon Tulsa’s proven track record in attracting talent through innovative programs. The city’s Tulsa Remote program, which offers $10,000 grants to remote workers who relocate to the city, has successfully attracted approximately 3,500 participants since 2018.
Recent economic analysis found that Tulsa Remote generates more than $4 in community benefits for every $1 spent, demonstrating the city’s ability to create successful workforce attraction programs. Participants have collectively generated $622 million in direct employment income, with 70% remaining in the city after completing the program.
Industry Partnership Framework
Louis Stewart, NVIDIA’s head of ecosystem development, emphasized the collaborative approach: “Our collaboration with Black Tech Street and the larger Tulsa ecosystem is helping prepare and equip all segments of the workforce to operate and sustain transformative technology that is building America’s future.”
The partnership extends beyond NVIDIA and Black Tech Street to include Tulsa Innovation Labs, Microsoft, Langston University, and the Tulsa Economic Development Corporation. This multi-stakeholder approach aims to create a comprehensive support system for AI development and adoption.
Future Expansion Potential
The agreement establishes a foundation for potential expansion across Oklahoma, suggesting the initiative could serve as a model for other communities seeking to develop AI capabilities. The collaborative framework developed in Tulsa could be replicated in other regions working to participate in the artificial intelligence economy.
The partnership represents a significant investment in both Tulsa’s economic future and the broader democratization of AI education and development opportunities beyond traditional tech centers.
Tools & Platforms
5-Week AI Mentorship for Startups in SF

OpenAI has unveiled a new initiative aimed at nurturing the next generation of artificial intelligence innovators, marking a strategic push into talent development amid intensifying competition in the AI sector. The program, dubbed OpenAI Grove, targets early-stage entrepreneurs who are either pre-idea or in the nascent phases of building AI-focused companies. According to details shared in a recent announcement, the five-week mentorship scheme will be hosted at OpenAI’s San Francisco headquarters, providing participants with hands-on guidance from industry experts and access to cutting-edge tools.
The program’s structure emphasizes practical support, including technical assistance, community building, and early exposure to unreleased OpenAI models. As reported by The Indian Express, participants will have opportunities to interact with new AI tools before their public release, fostering an environment where budding founders can experiment and iterate rapidly. This comes at a time when AI startups are proliferating, with OpenAI positioning itself as a hub for innovation rather than just a technology provider.
A Strategic Move in AI Talent Cultivation OpenAI’s launch of Grove reflects a broader effort to secure its influence in the rapidly evolving AI ecosystem, where retaining and attracting top talent is crucial. By offering mentorship to pre-seed founders, the company aims to create a pipeline of AI-driven ventures that could potentially integrate with or complement its own technologies. Recent posts on X highlight enthusiasm from the tech community, with users noting the program’s potential to accelerate startup growth through exclusive access to OpenAI’s resources.
Industry observers see this as OpenAI’s response to competitors like Anthropic and Grok, which have also been aggressive in talent acquisition. The first cohort, limited to about 15 participants, is set to run from October 20 to November 21, 2025, with applications closing on September 24. As detailed in coverage from CNBC, the initiative includes in-person sessions focused on co-building prototypes with OpenAI researchers, underscoring a hands-on approach that differentiates it from traditional accelerator programs.
Benefits and Broader Implications for Startups Participants in Grove stand to gain more than just technical know-how; the program promises a robust network of peers and mentors, which could be invaluable for fundraising and scaling. Early access to unreleased models, as mentioned in reports from NewsBytes, allows founders to test ideas with state-of-the-art AI capabilities, potentially giving them a competitive edge in a market where speed to innovation is key.
This mentorship model aligns with OpenAI’s history of fostering external ecosystems, similar to its past investments in startups through funds like the OpenAI Startup Fund. However, Grove appears more focused on individual founders, particularly those without formal teams or funding, addressing a gap in the startup support system. Insights from The Daily Jagran emphasize how the program could help participants raise capital or refine their business models, drawing on expert guidance to navigate challenges like ethical AI development and market fit.
Challenges and Future Outlook While the program has generated buzz, questions remain about its scalability and inclusivity. With only 15 spots in the initial cohort, selection will be highly competitive, potentially favoring founders with existing connections in the tech world. Recent news on X suggests mixed sentiments, with some praising the initiative for democratizing AI access, while others worry it might reinforce Silicon Valley’s dominance in the field.
Looking ahead, OpenAI plans to run Grove multiple times a year, potentially expanding its reach globally. As covered in TechStory, this could evolve into a cornerstone of OpenAI’s strategy to build a supportive community around its technologies, much like how Y Combinator has shaped the broader startup world. For industry insiders, Grove represents not just a mentorship opportunity but a signal of OpenAI’s commitment to shaping the future of AI entrepreneurship, ensuring that innovative ideas flourish under its umbrella.
Potential Impact on the AI Innovation Ecosystem The introduction of Grove could catalyze a wave of AI startups, particularly in areas like generative models and ethical AI applications, by providing resources that lower barriers to entry. Founders selected for the program will benefit from personalized feedback loops, helping them avoid common pitfalls in AI development such as data biases or scalability issues.
Moreover, this initiative underscores OpenAI’s evolution from a research lab to a multifaceted player in the tech industry. By mentoring early-stage talent, the company may indirectly fuel advancements that enhance its own ecosystem, creating a virtuous cycle of innovation. As the AI sector continues to mature, programs like Grove could play a pivotal role in distributing expertise more evenly, empowering a diverse array of entrepreneurs to contribute to technological progress.
Tools & Platforms
San Antonio Spa Unveils First AI-Powered Robot Massager

In the heart of San Antonio, a quiet revolution in wellness technology is unfolding at Float Wellness Spa on Fredericksburg Road. The spa has become the first in the city to introduce the Aescape AI-powered robot massager, a device that promises to blend cutting-edge artificial intelligence with the ancient art of massage therapy. Customers lie face-down on a specialized table, where robotic arms equipped with sensors scan their bodies to deliver personalized treatments, adjusting pressure and techniques in real time based on individual anatomy and preferences.
This innovation arrives amid a broader surge in AI applications within the health and wellness sector, where automation is increasingly tackling labor shortages and consistency issues in human-delivered services. According to a recent feature by Texas Public Radio, the Aescape system at Float Wellness Spa uses advanced algorithms to map muscle tension and provide targeted relief, marking a significant step for Texas in adopting such tech.
Technological Backbone and Operational Mechanics
At its core, the Aescape robot employs a combination of 3D body scanning, machine learning, and haptic feedback to simulate professional massage techniques. Users select from various programs via a touchscreen interface, and the system adapts on the fly, much like a therapist responding to subtle cues. This isn’t mere gimmickry; it’s backed by years of development, with the company raising substantial funds to refine its precision.
In a March 2025 report from Bloomberg, Aescape secured $83 million in funding from investors including Valor Equity Partners and NBA star Kevin Love, underscoring investor confidence in robotic wellness solutions. The technology draws from earlier prototypes showcased at events like CES 2024, where similar AI-driven massage robots demonstrated personalized adaptations to user needs.
Market Expansion and Local Adoption in San Antonio
The rollout in San Antonio follows successful debuts in cities like Los Angeles, as detailed in a December 2024 piece by the Los Angeles Times, which described the experience as precise yet impersonal. At Float Wellness Spa, appointments are now bookable, with sessions priced competitively to attract a mix of tech enthusiasts and those seeking convenient relief from daily stresses.
Posts on X, formerly Twitter, reflect growing public intrigue, with users like tech influencer Mario Nawfal highlighting the robot’s eight axes of motion for deep-tissue work without the awkwardness of human interaction. This sentiment aligns with San Antonio’s burgeoning tech scene, where AI innovations are intersecting with local industries, as noted in recent updates from the San Antonio Express-News.
User Experiences and Industry Implications
Early adopters in San Antonio report a mix of awe and adjustment. One reviewer in a Popular Science article from March 2024 praised the Aescape for its customized convenience, likening it to “the world’s most advanced massage” powered by AI that learns from each session. However, some note the absence of human warmth, a point echoed in an Audacy video report from August 2025, which captured the robot’s debut turning heads in the city.
For industry insiders, this represents a pivot toward scalable wellness tech. With labor costs rising and therapist shortages persistent, robots like Aescape could redefine spa economics, potentially expanding to chains like Equinox. Yet, challenges remain, including regulatory hurdles for AI in healthcare-adjacent fields and ensuring data privacy for body scans.
Future Prospects and Competitive Dynamics
Looking ahead, Aescape’s expansion signals broader trends in robotic automation. A Yahoo Finance piece from August 2025 introduced a competing system, RoboSculptor, which also leverages AI for massage, hinting at an emerging market rivalry. In San Antonio, this could spur further innovation, with local startups like those covered in Nucamp’s tech news roundup exploring AI tools in customer service and beyond.
As AI integrates deeper into personal care, ethical questions arise—will robots supplant human jobs, or augment them? For now, Float Wellness Spa’s offering provides a tangible glimpse into this future, blending Silicon Valley ingenuity with Texas hospitality. Industry watchers will be keen to monitor adoption rates, as success here could accelerate nationwide rollout, transforming how we unwind in an increasingly automated world.
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoThe Guardian view on Trump and the Fed: independence is no substitute for accountability | Editorial
-
Tools & Platforms1 month ago
Building Trust in Military AI Starts with Opening the Black Box – War on the Rocks
-

 Ethics & Policy2 months ago
Ethics & Policy2 months agoSDAIA Supports Saudi Arabia’s Leadership in Shaping Global AI Ethics, Policy, and Research – وكالة الأنباء السعودية
-

 Events & Conferences4 months ago
Events & Conferences4 months agoJourney to 1000 models: Scaling Instagram’s recommendation system
-

 Jobs & Careers2 months ago
Jobs & Careers2 months agoMumbai-based Perplexity Alternative Has 60k+ Users Without Funding
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoHappy 4th of July! 🎆 Made with Veo 3 in Gemini
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoVEX Robotics launches AI-powered classroom robotics system
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoMacron says UK and France have duty to tackle illegal migration ‘with humanity, solidarity and firmness’ – UK politics live | Politics
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoOpenAI 🤝 @teamganassi
-

 Funding & Business2 months ago
Funding & Business2 months agoKayak and Expedia race to build AI travel agents that turn social posts into itineraries

