AI Insights
Better Artificial Intelligence Stock: Nvidia vs. Meta Platforms

Artificial intelligence (AI) stocks have proven to be big winners for investors lately — particularly last year, when some leading players in the space delivered double- and even triple-digit percentage gains. Though these high-growth companies’ share prices tumbled earlier this year due to concerns about President Donald Trump’s tariff plans, investors have recently returned to this compelling story.
Trump’s trade talks and tentative agreements on the frameworks of deals with the U.K. and China have boosted optimism that his tariffs won’t result in drastically higher costs for U.S. consumers or major earnings pressure on U.S. companies — in contrast to the worst-case scenario that many had feared. As a result, investors feel more comfortable investing in companies that rely on a strong economic environment to thrive — such as AI sector players.
This means that many investors are once again asking themselves which AI players look like the best buys today. Nvidia (NVDA 1.33%) and Meta Platforms (META 0.73%) are both aiming to reshape the future with their aggressive AI plans. If you could only buy one, which would be the better AI bet now?
Image source: Getty Images.
The case for Nvidia
Nvidia already has scored many AI victories. The company has built an empire of hardware and services that make it the go-to provider for any organization creating an AI platform or program. But the crown jewels of its portfolio are its graphics processing units (GPUs). It offers the top-performing parallel processors, and thanks to both its ecosystem and manufacturing lead, they’re also by far the best-sellers in their class. With demand from cloud infrastructure giants and other tech sector players still outstripping supply, Nvidia has been growing its sales at double- and triple-digit percentage rates, and setting new revenue records quarter after quarter.
In its fiscal 2025, which ended Jan. 26, Nvidia booked a 114% revenue gain to a record level of $130 billion. And the company isn’t just growing its top line — its net income surged by 145% to almost $73 billion as it continued to generate high levels of profitability on those sales.
Nvidia’s clients today rely heavily on its hardware to power their projects, as its GPUs are some of the best chips available for the training of large language models (LLMs), as well as for inferencing — the technical term for when those trained models are used to process real data to solve actual problems or make predictions. And Nvidia is helping customers with so much more — from the design of AI agents to the powering of autonomous vehicle systems and drug-discovery platforms.
Nvidia also is innovating steadily to stay ahead of rivals. It recently shifted to an accelerated schedule that will have it releasing chips based on new and improved architectures every year; previously, it rolled out new architectures about once every two years. So this company is likely to keep playing a major role in the evolution of AI throughout its next chapters.
The case for Meta Platforms
You will know Meta best as an owner of social media apps, some of which you probably use every day — its core “family of apps” includes Facebook, Messenger, WhatsApp, and Instagram. And the sales of advertising space across those platforms have provided billions of dollars in revenue and profits for the company.
But today, Meta’s big focus is on AI. The company has built its own LLM, Llama, and made it open source so that anyone can contribute to its development. The open-source model can result in the faster creation of a better-quality product — and in this case, it could help Meta emerge as a leader in the field. The company has put its money where its mouth is: It plans as much as $72 billion in capital spending this year to boost its AI presence. And just recently, Meta has been hiring up a storm in its efforts to staff its newly launched Meta Superintelligence Labs. That business unit will work on foundation models like Llama as well as other AI research projects.
In a memo to employees regarding the new AI unit, Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg highlighted why it’s well positioned to lead in AI development: “We have a strong business that supports building out significantly more compute than smaller labs. We have deeper experience building and growing products that reach billions of people,” he said.
Those points are true, and they could help Meta reach its goals — and deliver big wins to investors over time.
Which stock is the better buy?
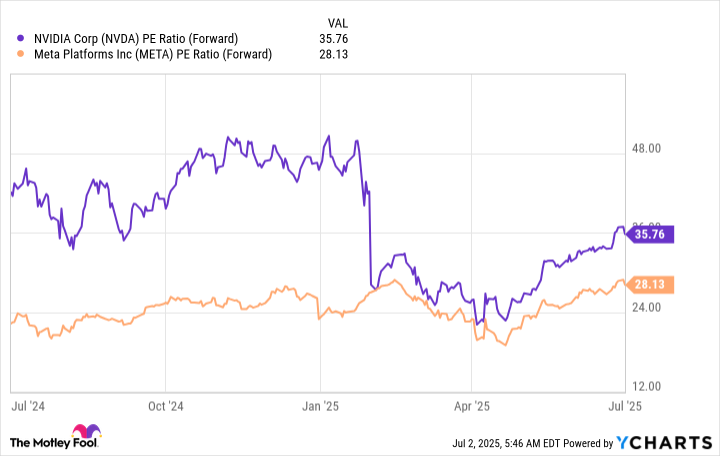
From a valuation perspective, you might choose Meta, as the stock is cheaper in relation to forward earnings estimates than Nvidia — a condition that has generally been the case.
NVDA PE Ratio (Forward) data by YCharts.
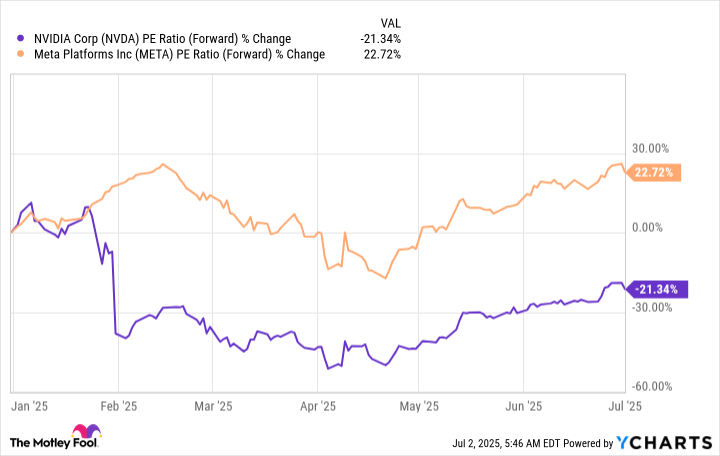
But a closer look shows that while Nvidia’s valuation is down since the start of the year, Meta’s actually has climbed.
NVDA PE Ratio (Forward) data by YCharts.
With that in mind, Nvidia looks like a more appealing buying opportunity, especially considering the company’s ongoing strong growth and its involvement in every area of AI development and application in real-world situations. Meta also could emerge as a major AI winner down the road, and the stock is still reasonably priced today in spite of its gains in valuation. But Nvidia remains the key player in this space — and at today’s valuation, it’s the better buy.
Randi Zuckerberg, a former director of market development and spokeswoman for Facebook and sister to Meta Platforms CEO Mark Zuckerberg, is a member of The Motley Fool’s board of directors. Adria Cimino has no position in any of the stocks mentioned. The Motley Fool has positions in and recommends Meta Platforms and Nvidia. The Motley Fool has a disclosure policy.
AI Insights
Vikings vs. Falcons props, bets, SportsLine Machine Learning Model AI predictions: Robinson over 68.5 rushing

Week 2 of Sunday Night Football will see the Minnesota Vikings (1-0) hosting the Atlanta Falcons (0-1). J.J. McCarthy and Michael Penix Jr. will be popular in NFL props, as the two will face off for the first time since squaring off in the 2023 CFP National Title Game. The cast of characters around them has changed since McCarthy and Michigan prevailed over Washington, as the likes of Justin Jefferson, Kyle Pitts, T.J. Hockenson, and Drake London now flank the quarterbacks. There are several NFL player props one could target for these star players, or you may find value in going after under-the-radar options.
Tyler Allgeier had 10 carries in Week 1, which were just two fewer than Bijan Robinson, with the latter being more involved in the passing game with six receptions. If Allgeier has a similar type of volume going forward, then the over for his rushing yards NFL prop may be one to consider. A strong run game would certainly help out a young quarterback like Penix, so both Allgeier and Robinson have intriguing Sunday Night Football props. Before betting any Falcons vs. Vikings props for Sunday Night Football, you need to see the Vikings vs. Falcons prop predictions powered by SportsLine’s Machine Learning Model AI.
Built using cutting-edge artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques by SportsLine’s Data Science team, AI Predictions and AI Ratings are generated for each player prop.
For Falcons vs. Vikings NFL betting on Sunday Night Football, the Machine Learning Model has evaluated the NFL player prop odds and provided Vikings vs. Falcons prop picks. You can only see the Machine Learning Model player prop predictions for Atlanta vs. Minnesota here.
Top NFL player prop bets for Falcons vs. Vikings
After analyzing the Vikings vs. Falcons props and examining the dozens of NFL player prop markets, the SportsLine’s Machine Learning Model says Falcons RB Bijan Robinson goes Over 68.5 rushing yards (-114 at FanDuel). Robinson ran for 92 yards and a touchdown in Week 14 of last season versus Minnesota, despite the Vikings having the league’s No. 2 run defense a year ago. After replacing their entire starting defensive line in the offseason, it doesn’t appear the Vikings are as stout on the ground. They allowed 119 rushing yards in Week 1, which is more than they gave up in all but four games a year ago.
Robinson is coming off a season with 1,454 rushing yards, which ranked third in the NFL. He averaged 85.6 yards per game, and not only has he eclipsed 65.5 yards in six of his last seven games, but he’s had at least 90 yards on the ground in those six games. Over Minnesota’s last eight games, including the postseason, six different running backs have gone over 65.5 rushing yards, as the SportsLine Machine Learning Model projects Robinson to have 85.6 yards in a 4.5-star prop pick. See more NFL props here, and new users can also target the FanDuel promo code, which offers new users $300 in bonus bets if their first $5 bet wins:
How to make NFL player prop bets for Minnesota vs. Atlanta
In addition, the SportsLine Machine Learning Model says another star sails past his total and has five additional NFL props that are rated four stars or better. You need to see the Machine Learning Model analysis before making any Falcons vs. Vikings prop bets for Sunday Night Football.
Which Vikings vs. Falcons prop bets should you target for Sunday Night Football? Visit SportsLine now to see the top Falcons vs. Vikings props, all from the SportsLine Machine Learning Model.
AI Insights
Prediction: These AI Stocks Could Outperform the “Magnificent Seven” Over the Next Decade

The “Magnificent Seven” stocks, which drove indexes higher over the past couple of years, continued that job in recent months. And for good reason. Most of these tech giants are playing key roles in the high-growth industry of artificial intelligence (AI), a market forecast to reach into the trillions of dollars by the early 2030s. Investors, wanting to benefit from this growth, have piled into these current and potential AI winners.
But the Magnificent Seven stocks aren’t the only ones that may be set to excel in AI and deliver growth to investors. As the AI story progresses, the need for infrastructure capacity and certain equipment could result in surging sales for other companies too. That’s why my prediction is the following three stocks are on track for major strength in AI and may even outperform the Magnificent Seven over the coming decade. Let’s check them out.
Image source: Getty Images.
1. Oracle
Oracle (ORCL -5.05%) started out as a database management specialist, and it still is a giant in this area, but in recent times it’s put the focus on growing its cloud infrastructure business — and this has supercharged the company’s revenue.
AI customers are rushing to Oracle for capacity to run training and inferencing workloads, and this movement helped the company report a 55% increase in infrastructure revenue in the recent quarter. And Oracle predicts this may be just the beginning. The company expects this business to deliver $18 billion in revenue this year — and grow that to $144 billion four years from now.
Investors were so excited about Oracle’s forecasts that the stock surged about 35% in one trading session, adding more than $200 billion in market value. Customers are seeing the value of Oracle’s database technology paired with AI — a combination that allows them to securely apply AI to their businesses — and this may keep the demand for Oracle’s services going strong and the stock price heading higher as the AI story enters its next chapters.
2. CoreWeave
CoreWeave (CRWV -0.65%) has designed its cloud platform specifically for AI workloads, and the company works closely with chip leader Nvidia. So far, this has resulted in CoreWeave’s being the first to make Nvidia’s latest platforms generally available to customers. This is a big plus as companies scramble to gain access to Nvidia’s innovations as soon as possible.
Nvidia also is a believer in CoreWeave’s potential as the chip giant holds shares in the company. As of the second quarter, CoreWeave makes up 91% of Nvidia’s investment portfolio. Considering Nvidia’s knowledge of the AI landscape, this investment is particularly meaningful.
Customers may also like the flexibility of CoreWeave’s services, allowing them to rent graphics processing units (GPUs) by the hour or for the long term. All of this has led to explosive revenue growth for the company. In the latest quarter, revenue tripled to more than $1.2 billion.
The growing need for AI infrastructure should translate into ongoing explosive growth for CoreWeave, and that may make it a stronger stock market performer than long-established players — such as the Magnificent Seven.
3. Broadcom
Broadcom (AVGO 0.19%) is a networking leader, with its products present in a variety of places from your smartphone to data centers. And in recent times, demand from AI customers — for items such as customized chips and networking equipment — has helped revenue soar.
In the recent quarter, Broadcom said AI revenue jumped 63% year over year to $5.2 billion, and the company forecast AI revenue of $6.2 billion in the next quarter. The company already is working on custom chips for three major customers, and demand from them is growing — on top of this, Broadcom just announced a $10 billion order from another customer, one that analysts and press reports say may be OpenAI.
Meanwhile, Broadcom’s expertise in networking is paying off as high-performance systems are needed to connect customers’ growing numbers of compute nodes. As AI customers scale up their platforms, they need to share data between more and more of these nodes — and Broadcom has what it takes to do the job.
We’re still in the early phases of this AI buildout — as mentioned, the AI market may be heading for the trillion-dollar mark — and Broadcom clearly will benefit. And that may help this top tech stock to outperform the Magnificent Seven over the next decade.
Adria Cimino has positions in Oracle. The Motley Fool has positions in and recommends Nvidia and Oracle. The Motley Fool recommends Broadcom. The Motley Fool has a disclosure policy.
AI Insights
Zheng Yongnian on why China must look beyond the West to build a better AI

For many years, you have called for the rebuilding of China’s own knowledge system. Recently, you have also voiced concerns about “intellectual colonialism” in the artificial intelligence era. Can you elaborate?
The concerns mainly refer to challenges in China’s social sciences which originated from the West.
Religions, ideology, values – as Samuel Huntington explained in his book The Clash of Civilisations – are important for any nation. And the meaning of society and technology is determined by the humanities and social sciences.
Chinese researchers learned and adopted theories of Western social sciences, but these are based on Western methods that summarise Western practices and experiences, and are then used to explain Western society.
Those theories have failed to explain Confucian civilisation, the Islamic world and Indian society. We should fully embrace our secular civilisation, and thereby play a proper role in the international order.
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoThe Guardian view on Trump and the Fed: independence is no substitute for accountability | Editorial
-
Tools & Platforms1 month ago
Building Trust in Military AI Starts with Opening the Black Box – War on the Rocks
-

 Ethics & Policy2 months ago
Ethics & Policy2 months agoSDAIA Supports Saudi Arabia’s Leadership in Shaping Global AI Ethics, Policy, and Research – وكالة الأنباء السعودية
-

 Events & Conferences4 months ago
Events & Conferences4 months agoJourney to 1000 models: Scaling Instagram’s recommendation system
-

 Jobs & Careers3 months ago
Jobs & Careers3 months agoMumbai-based Perplexity Alternative Has 60k+ Users Without Funding
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoHappy 4th of July! 🎆 Made with Veo 3 in Gemini
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoVEX Robotics launches AI-powered classroom robotics system
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoMacron says UK and France have duty to tackle illegal migration ‘with humanity, solidarity and firmness’ – UK politics live | Politics
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoOpenAI 🤝 @teamganassi
-

 Funding & Business3 months ago
Funding & Business3 months agoKayak and Expedia race to build AI travel agents that turn social posts into itineraries