AI Research
AI Data Centers Market Size to Hit USD 165.73 Billion by 2034
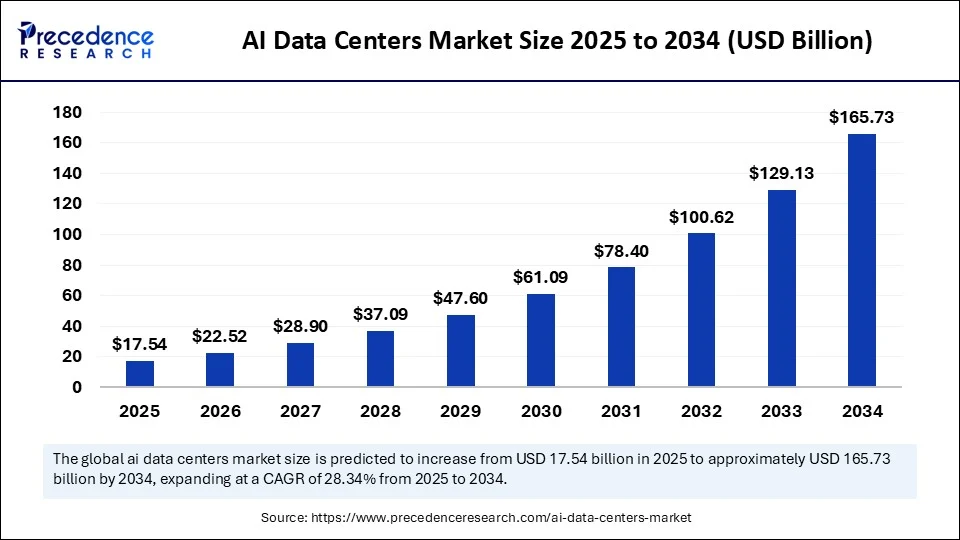
AI Data Centers Market Size and Forecast 2025 to 2034
The global AI data centers market size was calculated at USD 13.67 billion in 2024 and is predicted to increase from USD 17.54 billion in 2025 to approximately USD 165.73 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 28.34% from 2025 to 2034. The rising adoption of AI technologies to streamline data transmission drives the growth of the AI data centers market. The demand for high-performance computing power has increased, further contributing to market growth.
AI Data Centers Market Key Takeaways
- In terms of revenue, the global AI data centers market was valued at USD 13.67 billion in 2024.
- It is projected to reach USD 165.73 billion by 2034.
- The market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 28.34% from 2025 to 2034.
- North America dominated the AI data centers market with the largest share of 39% in 2024.
- Asia Pacific is expected to grow at a significant CAGR from 2025 to 2034.
- By component, the hardware segment contributed the biggest market share of 58% in 2024.
- By component, the services segment will expand at a significant CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- By data center type, the hyperscale AI data centers segment captured the highest market share of 64% in 2024.
- By data center type, the edge AI data centers segment will grow at a notable CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- By AI workload type, the training workloads segment held the largest market share of 45% in 2024.
- By AI workload type, the generative AI segment will expand at a significant CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- By cooling infrastructure, the air cooling segment contributed the biggest market share of 62% in 2024.
- By cooling infrastructure, the liquid cooling segment will expand at a significant CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- By power capacity, the 20–50 MW segment led the market generated the major market share of 36% in 2024.
- By power capacity, the above 50 MW segment will grow at a CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- By deployment mode, the cloud-based segment accounted for a significant market share of 52% in 2024.
- By deployment mode, the hybrid cloud segment will expand to a remarkable CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- By end-user industry, the technology & cloud providers segment held the major market share of 48% in 2024.
- By end-user industry, the healthcare & life sciences segment will expand at a significant CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
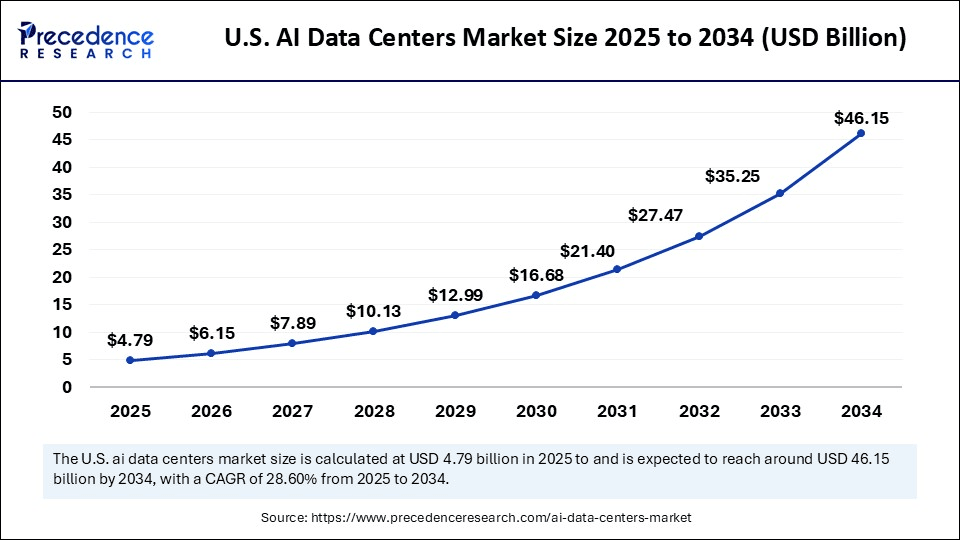
U.S. AI Data Centers Market Size and Growth 2025 to 2034
The U.S. AI data centers market size was evaluated at USD 3.73 billion in 2024 and is projected to be worth around USD 46.15 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 28.60% from 2025 to 2034.
What Made North America the Dominant Region in the AI Data Centers Market in 2024?
North America dominated the AI data centers market with a major revenue share in 2024 due to its robust, technologically advanced infrastructure, strong investors in AI-ready data center infrastructures, and rapid AI adoption in various industries, aligning with government support and initiatives. The rising demand for AI technologies across various industries and the growing focus on green AI data centers are boosting the regional market growth. Additionally, the strong existence of key market players like Microsoft. IBM and NVIDIA are driving innovative approaches in AI data centers.
The U.S. is a major player in the regional market. The U.S. has an advanced technological infrastructure with the presence of key market player and their investments in AI capabilities. The U.S.-based companies are increasing their AI-ready data center infrastructure investments to support emerging technologies like big data analytics, machine learning, and generative AI. The rapid adoption of AI across the country is fostering market growth.
- In July 2025, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) announced a new step on the Donald Trump administration’s plan for accelerating the development of AI infrastructure by siting on DOE lands. The DOE has selected its four sites, such as Idaho National Laboratory, Oak Ridge Reservation, Paducah Gaseous Diffusion Plant, and Savannah River Site, while inviting private sector partners for the development of advanced AI data centers and energy generation projects. (Source: https://www.energy.gov)
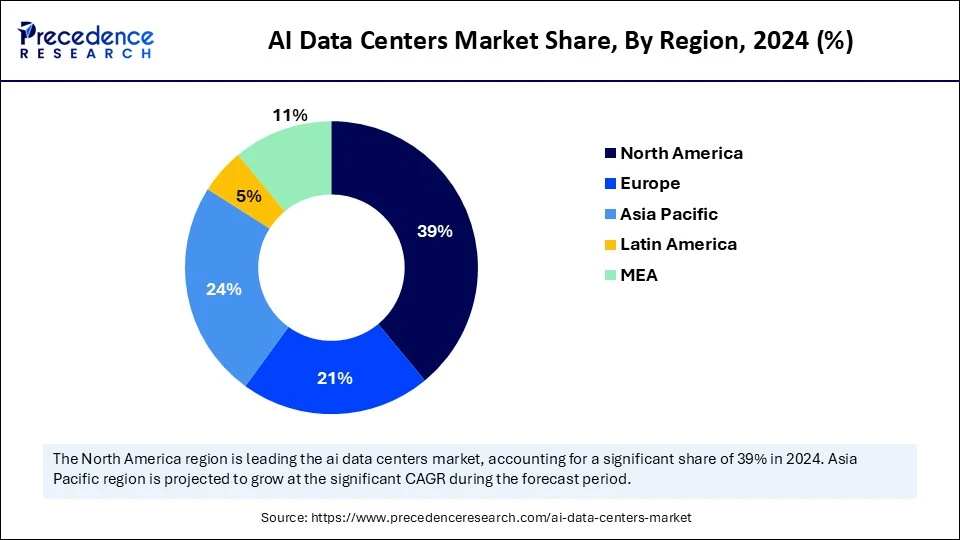
Asia Pacific AI Data Centers Market Trends
Asia Pacific is expected to grow at the fastest rate in the coming years, driven by the increasing adoption of AI services and adoption of cutting-edge computer infrastructure. The government of Asia is implementing several regulations and policies to promote the use of digital technologies and cloud services. The government-led AI initiatives are boosting the adoption of AI-enabled analytics and edge technologies. Additionally, the smart city projects are further contributing to the need for robust AI-ready data centers in Asia. Cities like Singapore, Tokyo, and Sydney are the major hubs for AI-driven data centers in Asia.
China is a major player in the regional market, contributing to growth due to the expanding digital economy and government investments in AI infrastructure. The government initiatives in promoting AI adoption, developments, and data center constructions are fostering this growth. Additionally, country investments in innovations, including underwater cooling technology for data centers, further add to market growth.
India is a significant player in the regional market. This is mainly due to rapid AI adoption, expanding IT infrastructures, and government promotion for digitalization across various industries. The Government of India is investing heavily in advancing data center infrastructure, leveraging AI in its practices, and fueling the market.
- The cutting-edge data centers in India, including Yotta NM1, Reliance Jio’s AI data centers, AdaniConneX data centers, CtrlS AI Mega Campus, and ST Telemedia Global Data Centers (STT GDC India), are driving significant innovations and investments in data center infrastructure.
Europe AI Data Centers Market Trends
Europe is expected to grow at a notable rate during the projection period due to rapid digitalization and demand for IoT technologies in the region. The adoption of cloud computing has increased. Europe is a hub for sustainable initiatives, emphasizes renewable energy sources and energy designs, and has a significant focus on AI data centers. The hyperscalers are taking the largest portion of data center capacity in Europe, which is expected to bring out significant and novel data center capabilities by 2025.
Countries like the UK, Germany, and France are leading the regional market, driven by the UK’s national AI strategy, Germany’s larger data center abilities, the digital transformation and sustainability, and France’s AI for Humanity strategies.
- In January 2025, the European government released its AI Opportunities Action Plan, which includes a large number of policies and actions for the government to take part in its overarching aspiration to enhance economic growth.
- In February 2025, France invests €109 billion in its AI sector, with a €30 billion and a €50 billion commitment from the UAE to finance a 1-gigawatt data center, which is four times the power capacity of the UK’s largest operational facility. (Source: https://www.pillsburylaw.com)
Market Overview
AI data centers are specialized computing facilities designed and optimized to handle the massive data processing and compute-intensive workloads associated with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) applications. Unlike traditional data centers, AI data centers integrate high-performance hardware (e.g., GPUs, TPUs), advanced cooling systems, and AI-specific infrastructure software to train and infer AI models at scale. They support workloads like generative AI, deep learning, NLP, computer vision, and real-time analytics. Companies are investing heavily in hardware like AI-optimized chips and services, leading to improved data center performance. The rising need for cutting-edge data centers in industries like BFSI is fueling the market expansion.
What are the Key Trends in the AI Data Centers Market?
- Expanding Cloud Computing: The expanding cloud computing is driving the need for cutting-edge data center infrastructure with AI integration.
- Demand for High-Performance Computing Power: The demand for high-performance computing power has increased to handle complex AI models and large datasets, driving innovations in AI data centers.
- Adoption of AI Applications: AI applications have increased in industries like data analytics, machine learning, and generative AI, driving the need for strong data center infrastructures.
- Technological Advancements: Advancements in technologies like 5G networks, AI-driven analytics, and IoT devices prompt the urgent need for robust data center infrastructure.
- Sustainability Concerns: The growing emphasis on building data centers with less environmental impact, the implementation of energy-efficient cooling systems, the use of renewable energy sources, and the utilization of eco-friendly materials in construction are driving focus on AI data centers.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 165.73 Billion |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 17.54 Billion |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 13.67 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 28.34% |
| Dominating Region | Asia Pacific |
| Fastest Growing Region | North America |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Component, Data Center Type, AI Workload Type, Cooling Infrastructure, Power Capacity, Deployment Mode, End-User Industry, and Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Drivers
Digital Transformation
The rapid digital transformation is boosting the need for AI-driven data centers globally. The demand for AI-powered applications has increased. Data centers support these demanding applications, including infrastructures for deep learning, generative AI, and machine learning. The growth of cloud computing is driving the need for AI data centers, driven by the requirement for scalable and flexible cloud services. Additionally, the growing adoption of edge computing and low-latency processing contributes to digital transformation accelerations. The government initiatives in promoting the use of digital technologies in various industries like healthcare, banking, automotives, and others, with growing emphasis on sustainability and energy efficiency, are fostering this transformation. These promotions are mitigating high-energy consumption and reducing greenhouse gas emissions, making a significant step toward AI-powered data centers.
Restraint
Concerns Over Data Privacy and Cybersecurity
Data privacy and cybersecurity concerns are the major challenges for the global AI data centers market. Data centers have a high risk of data breaches, making them challenging ecosystems for regulatory damage, regulatory analyses, and overall financial loss. AI data centers are vulnerable to cybersecurity attacks, like ransomware attacks, hacking, and malware, which hampers data integrity and availability. The Government has implemented several strict data protection regulations, including GDPR and CCPA, making it essential for AI data centers to implement security measures, which leads to increased cost and complexity. AI data centers can mitigate such barriers by implementing strong security measures, conducting regular security audits, and investing in cybersecurity talents.
Opportunity
Government Investments and Regulations
Government initiatives in promoting the use of digital technologies and investments in digital infrastructure, like data centers, are fostering innovations and advancements in AI-driven data centers. Governments worldwide have implemented several regulations for data protection and privacy, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which contributes to the increasing need for secure data storage solutions. Government funding for AI research and development, and support for adoption of cloud computing and data centers policies, are bringing significant opportunities for the AI data centers. Additionally, green initiatives and support for sustainability plans are further leveraging initiatives in AI data center infrastructure.
- On July 23, 2025, President Donald Trump signed three AI-related Executive Orders for implementing the recently released White House’s Artificial Intelligence (AI) Action Plan. (Source: https://www.workforcebulletin.com)
Component Insights
Which Component Segment Dominate the AI Data Centers Market in 2024?
The hardware segment dominated the market with the largest share in 2024. This is mainly due to its ability to enhance the performance and power efficiency of AI workloads. Hardware is playing a crucial role in enhancing sustainability and energy efficiency in data centers. The demand for specialized hardware like GPUs and ASICs has increased for AI computer capacity. Additionally, the growing adoption of liquid cooling and advancements in chip designs are driving the importance of hardware to enhance the efficiency and power of AI data centers.
The services segment is expected to grow at the fastest rate during the projection period, driven by increased AI deployment complexity and the requirement for expert supporting services in infrastructure management. The adoption of hybrid and multi-cloud ecosystems has increased, driving demand for services to handle both on-premises and cloud-based systems. Services like consulting, implementation, integration, managed, and maintenance services are highly in demand.
Data Center Type Insights
What Made Hyperscale AI Data Centers the Dominant Segment in the AI Data Centers Market in 2024?
The hyperscale AI data centers segment dominated the market in 2024. This is mainly due to their ability to offer scalable, flexible, high computing power, and networking required for meeting growing demands. The hyperscale AI data centers can handle large-scale AI workloads. The advanced architecture of hyperscale AI data centers helps to support high-density services and AI accelerators, including TPUs and GPUs.
The edge AI data centers segment is expected to expand a the fastest CAGR over the forecast period, due to increased demand for real-time data processing and low-latency applications. The edge AI data centers enable quick decision making through their real-time data processing and reduce bandwidth constraints. The increasing adoption of IoT devices and 5G networking has increased the need for AI decentralization in industries like smart manufacturing, healthcare, and automotives to reduce latency and process data closer to the source.
AI Workload Type Insights
Why Did the Training Workloads Segment Dominate the AI Data Centers Market in 2024?
The training workloads segment dominated the market in 2024 due to high computational requirements and specialized facilities. The training workloads are crucial in high-performance computing. The increased adoption of AI and ML into applications ike pattern recognition, data analysis, and predictive modelling is driving the need for training workloads.
The generative AI segment is expected to expand at the highest CAGR in the upcoming period, driven by the increased demand for strong infrastructure to support large amounts of data processing and complex computations. Generative AI streamlines the data centers’ workflow. The expanding generative AI movements have contributed to increased demand for data center GPUs, CPUs, DPU, AI ASICs, and networking ASICs.
Cooling Infrastructure Insights
Which Cooling Infrastructure Segment Dominate the AI Data Centers Market in 2024?
The air cooling segment dominated the market with the largest share in 2024, due to its ability to maintain an optimal temperature level. The expanding data centers drive the need for efficient cooling solutions like air cooling. Air-cooling solutions like room-based cooling and air handling units are essential in maintaining optimal airflow, temperature, and humidity levels. Ongoing advancements in air cooling, like enhanced efficiency and reduced energy consumption, further contribute to the segment’s growth.
The liquid cooling segment is likely to grow at the fastest CAGR in the upcoming period. The growth of the segment is driven by increased demand for energy-efficient cooling solutions. High-performance computing and AI-related workloads require liquid cooling solutions. The Direct-to-Chip Liquid Cooling sub-segment is leading the charge, driven by increased demand for thermal efficiency in high computational environments.
Power Capacity Insights
What Made 20-50 MW the Dominant Segment in the AI Data Centers Market in 2024?
The 20–50 MW segment dominated the market in 2024, due to its wide use in enterprises running AI workloads along with traditional applications. The small to medium data centers typically range between 20–50 MW. The 20–50 MW segment power capacity enables a balance between power capacity and scalability.
The above 50 MW segment is expected to grow at the fastest rate over the forecast period, driven by its utilization in large-scale facilities with higher power capacity demands. The AI data centers with above 50 MW power capacity offer hyperscale applications, high-performance computing, and support large AI workloads. The increased use of digital technologies has driven the need for large-scale AI data centers with more than 50 MW power capacity.
Deployment Mode Insights
How Does the Cloud-Based Segment Leads the AI Data Centers Market?
The cloud-based segment led the market in 2024 due to increased adoption of AI and cloud computing. The cloud-based AI data centers are flexible, scalable, cost-effective, and speed to setup. These data centers offer pre-configured AI tools, helping to reduce costs and enhance efficiency. The growing popularity of AI-as-a-service has contributed to the need for cloud-based AI data centers.
The hybrid cloud segment is likely to grow at the fastest rate in the coming years due to its scalability, flexibility, and affordability. The hybrid cloud-based data centers combine both on-premises and cloud infrastructures. The deployment of hybrid cloud has increased for more security & compliance, growing demand for edge computing, and AI integration for enabling cutting-edge data analysis and automations.
End-Use Industry Insights
Why Did the Technology & Cloud Service Providers Segment Dominate the AI Data Centers Market in 2024?
The technology & cloud service providers segment dominated the market in 2024, due to increased demand for cloud computing services. The technology giants and cloud service providers are becoming more visible due to increased adoption of cloud services and the need for data centers. Additionally, the adoption of multi-cloud strategies and hybrid strategies is driving the need for hybrid cloud management solutions, interconnection platforms, and services. The technology & cloud providers play a crucial role in increased AI and ML integration.
The healthcare & life sciences segment is expected to expand at the highest CAGR during the forecast period due to increased adoption of AI in the healthcare & life sciences industry. The utilization of AI for personalized medicine and genomics areas is contributing to the market growth. Personalized medicine and genomics require a large amount of data storage and analysis, driving demand for AI data centers. Additionally, the rapid digital transformation in the healthcare industry is fostering this growth.
AI Data Centers Market Companies

- NVIDIA Corporation
- AMD (Advanced Micro Devices)
- Intel Corporation
- Broadcom Inc.
- Micron Technology
- Marvell Technology
- Samsung Electronics
- SK hynix Inc.
- TSMC (Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company)
- Supermicro (Super Micro Computer, Inc.)
- Dell Technologies
- Hewlett-Packard Enterprise (HPE)
- Lenovo Group Ltd.
- Inspur Group
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- Arista Networks
- Equinix, Inc. (data center infrastructure & interconnection)
- Vertiv Holdings Co. (power & cooling systems)
- Eaton Corporation
- Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Recent Developments
- In July 2025, Google announced investments of $25 billion in data centers and artificial intelligence infrastructure, more than the next two years, in states across the biggest electric grid in the U.S. (Source: https://www.cnbc.com)
- In April 2025, Nvidia announced $500 billion for building AI infrastructure in the U.S. over the next four years, under the collaboration of TSM, the latest American tech firm backing the Trump administration’s push for local manufacturing giants.
(Source: https://cio.economictimes.indiatimes.com) - In January 2025, Microsoft announced investments of $80 billion in FY25 for the construction of data centers to handle artificial intelligence workloads. Over half of the expected AI infrastructure spending took place in the U.S.
(Source: https://www.cnbc.com) - In July 2025, a global leader in hyperscale digital infrastructure, Khazna Data Centers, partnered with Eni, a global integrated energy company, under a Heads of Terms (HOT) agreement set up as a joint venture for the development of an “AI Data Center Campus” with a total IT capacity of 500 MW in Ferrera Erbognone, Lombarly. (Source: https://www.eni.com)
- In April 2025, a leading AI-ready data center provider in India, ST Telemedia Global Data Centers, announced enhancing its data center landscape in Eastern India by launching its state-of-the-art facility in New Town, Kolkata. This next-generation campus is established on 5.59 acres and engineered to support the rising demands of AI computing with high-density rack configurations, cutting-edge cooling systems, and a modular and scalable design. (Source: https://www.sttelemediagdc.com)
Segment Covered in the Report
By Component
- Hardware
- Compute (GPUs, CPUs, TPUs, ASICs)
- Memory (HBM, DRAM, Flash)
- Storage (NVMe SSD, HDD, Object Storage)
- Networking (Switches, Routers, Interconnects)
- Software
- AI Workload Management Platforms
- Orchestration Tools (e.g., Kubernetes for AI)
- Virtualization & Containerization Software
- AI Model Training/Inference Frameworks
- Services
- Deployment & Integration
- Managed Services
- Consulting & Support
By Data Center Type
- Hyperscale AI Data Centers
- Colocation AI Data Centers
- Edge AI Data Centers
- Enterprise (Private) AI Data Centers
By AI Workload Type
- Training Workloads
- Inference Workloads
- Real-Time Analytics
- Generative AI
- Reinforcement Learning
By Cooling Infrastructure
- Liquid Cooling
- Immersion Cooling
- Direct-to-Chip Liquid Cooling
- Air Cooling
- CRAH/CRAC Units
- Chilled Water Systems
- Hybrid Cooling Systems
By Power Capacity
- Below 5 MW
- 5–20 MW
- 20–50 MW
- Above 50 MW
By Deployment Mode
- On-Premise
- Cloud-Based
- Hybrid Cloud
By End-User Industry
- Technology & Cloud Service Providers
- BFSI
- Healthcare & Life Sciences
- Automotive (Autonomous Driving)
- Retail & E-commerce
- Government & Defense
- Telecom
- Energy & Utilities
- Education & Research
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
AI Research
Prediction: This Artificial Intelligence (AI) Semiconductor Stock Will Join Nvidia, Microsoft, Apple, Alphabet, and Amazon in the $2 Trillion Club by 2028. (Hint: Not Broadcom)

This company is growing quickly, and its stock is a bargain at the current price.
Big tech companies are set to spend $375 billion on artificial intelligence (AI) infrastructure this year, according to estimates from analysts at UBS. That number will climb to $500 billion next year.
The biggest expense item in building out AI data centers is semiconductors. Nvidia (NVDA -3.38%) has been by far the biggest beneficiary of that spend so far. Its GPUs offer best-in-class capabilities for general AI training and inference. Other AI accelerator chipmakers have also seen strong sales growth, including Broadcom (AVGO -3.70%), which makes custom AI chips as well as networking chips, which ensure data moves efficiently from one server to another, keeping downtime to a minimum.
Broadcom’s stock price has increased more than fivefold since the start of 2023, and the company now sports a market cap of $1.4 trillion. Another year of spectacular growth could easily place it in the $2 trillion club. But another semiconductor stock looks like a more likely candidate to reach that vaunted level, joining Nvidia and the four other members of the club by 2028.
Image source: Getty Images.
Is Broadcom a $2 trillion company?
Broadcom is a massive company with operations spanning hardware and software, but its AI chips business is currently steering the ship.
To that end, AI revenue climbed 46% year over year last quarter to reach $4.4 billion. Management expects the current quarter to produce $5.1 billion in AI semiconductor revenue, accelerating growth to roughly 60%. AI-related revenue now accounts for roughly 30% of Broadcom’s sales, and that’s set to keep climbing over the next few years.
Broadcom’s acquisition of VMware last year is another growth driver. The software company is now fully integrated into Broadcom’s larger operations, and it’s seen strong success in upselling customers to the VMware Cloud Foundation, enabling enterprises to run their own private clouds. Over 87% of its customers have transitioned to the new subscription, resulting in double-digit growth in annual recurring revenue.
But Broadcom shares are extremely expensive. The stock garners a forward P/E ratio of 45. While its AI chip sales are growing quickly and it’s seeing strong margin improvement from VMware, it’s important not to lose sight of how broad a company Broadcom is. Despite the stellar growth in those two businesses, the company is still only growing its top line at about 20% year over year. Investors should expect only incremental margin improvements going forward as it scales the AI accelerator business. That means the business is set up for strong earnings growth, but not enough to justify its 45 times earnings multiple.
Another semiconductor stock trades at a much more reasonable multiple, and is growing just as fast.
The semiconductor giant poised to join the $2 trillion club by 2028
Both Broadcom and Nvidia rely on another company to ensure they can create the most advanced semiconductors in the world for AI training and inference. That company is Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing (TSM -3.05%), which actually prints and packages both companies’ designs. Almost every company designing leading-edge chips relies on TSMC for its technological capabilities. As a result, its market share of semiconductor manufacturing has climbed to more than two-thirds.
TSMC benefits from a virtuous cycle, ensuring it maintains and grows its massive market share. Its technology lead helps it win big contracts from companies like Nvidia and Broadcom. That gives it the capital to invest in expanding capacity and research and development for its next-generation process. As a result, it maintains its technology lead while offering enough capacity to meet the growing demand for manufacturing.
TSMC’s leading-edge process node, dubbed N2, will reportedly charge a 66% premium per silicon wafer over the previous generation (N3). That’s a much bigger step-up in price than it’s historically managed, but the demand for the process is strong as companies are willing to spend whatever it takes to access the next bump in power and energy efficiency. While TSMC typically experiences a significant drop off in gross margin as it ramps up a new expensive node with lower initial yields, its current pricing should help it maintain its margins for years to come as it eventually transitions to an even more advanced process next year.
Management expects AI-related revenue to average mid-40% growth per year from 2024 through 2029. While AI chips are still a relatively small part of TSMC’s business, that should produce overall revenue growth of about 20% for the business. Its ability to maintain a strong gross margin as it ramps up the next two manufacturing processes should allow it to produce operating earnings growth exceeding that 20% mark.
TSMC’s stock trades at a much more reasonable earnings multiple of 24 times expectations. Considering the business could generate earnings growth in the low 20% range, that’s a great price for the stock. If it can maintain that earnings multiple through 2028 while growing earnings at about 20% per year, the stock will be worth well over $2 trillion at that point.
Adam Levy has positions in Alphabet, Amazon, Apple, Microsoft, and Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing. The Motley Fool has positions in and recommends Alphabet, Amazon, Apple, Microsoft, Nvidia, and Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing. The Motley Fool recommends Broadcom and recommends the following options: long January 2026 $395 calls on Microsoft and short January 2026 $405 calls on Microsoft. The Motley Fool has a disclosure policy.
AI Research
Physicians Lose Cancer Detection Skills After Using Artificial Intelligence

Artificial intelligence shows great promise in helping physicians improve both their diagnostic accuracy of important patient conditions. In the realm of gastroenterology, AI has been shown to help human physicians better detect small polyps (adenomas) during colonoscopy. Although adenomas are not yet cancerous, they are at risk for turning into cancer. Thus, early detection and removal of adenomas during routine colonoscopy can reduce patient risk of developing future colon cancers.
But as physicians become more accustomed to AI assistance, what happens when they no longer have access to AI support? A recent European study has shown that physicians’ skills in detecting adenomas can deteriorate significantly after they become reliant on AI.
The European researchers tracked the results of over 1400 colonoscopies performed in four different medical centers. They measured the adenoma detection rate (ADR) for physicians working normally without AI vs. those who used AI to help them detect adenomas during the procedure. In addition, they also tracked the ADR of the physicians who had used AI regularly for three months, then resumed performing colonoscopies without AI assistance.
The researchers found that the ADR before AI assistance was 28% and with AI assistance was 28.4%. (This was a slight increase, but not statistically significant.) However, when physicians accustomed to AI assistance ceased using AI, their ADR fell significantly to 22.4%. Assuming the patients in the various study groups were medically similar, that suggests that physicians accustomed to AI support might miss over a fifth of adenomas without computer assistance!
This is the first published example of so-called medical “deskilling” caused by routine use of AI. The study authors summarized their findings as follows: “We assume that continuous exposure to decision support systems such as AI might lead to the natural human tendency to over-rely on their recommendations, leading to clinicians becoming less motivated, less focused, and less responsible when making cognitive decisions without AI assistance.”
Consider the following non-medical analogy: Suppose self-driving car technology advanced to the point that cars could safely decide when to accelerate, brake, turn, change lanes, and avoid sudden unexpected obstacles. If you relied on self-driving technology for several months, then suddenly had to drive without AI assistance, would you lose some of your driving skills?
Although this particular study took place in the field of gastroenterology, I would not be surprised if we eventually learn of similar AI-related deskilling in other branches of medicine, such as radiology. At present, radiologists do not routinely use AI while reading mammograms to detect early breast cancers. But when AI becomes approved for routine use, I can imagine that human radiologists could succumb to a similar performance loss if they were suddenly required to work without AI support.
I anticipate more studies will be performed to investigate the issue of deskilling across multiple medical specialties. Physicians, policymakers, and the general public will want to ask the following questions:
1) As AI becomes more routinely adopted, how are we tracking patient outcomes (and physician error rates) before AI, after routine AI use, and whenever AI is discontinued?
2) How long does the deskilling effect last? What methods can help physicians minimize deskilling, and/or recover lost skills most quickly?
3) Can AI be implemented in medical practice in a way that augments physician capabilities without deskilling?
Deskilling is not always bad. My 6th grade schoolteacher kept telling us that we needed to learn long division because we wouldn’t always have a calculator with us. But because of the ubiquity of smartphones and spreadsheets, I haven’t done long division with pencil and paper in decades!
I do not see AI completely replacing human physicians, at least not for several years. Thus, it will be incumbent on the technology and medical communities to discover and develop best practices that optimize patient outcomes without endangering patients through deskilling. This will be one of the many interesting and important challenges facing physicians in the era of AI.
AI Research
AI exposes 1,000+ fake science journals

A team of computer scientists led by the University of Colorado Boulder has developed a new artificial intelligence platform that automatically seeks out “questionable” scientific journals.
The study, published Aug. 27 in the journal “Science Advances,” tackles an alarming trend in the world of research.
Daniel Acuña, lead author of the study and associate professor in the Department of Computer Science, gets a reminder of that several times a week in his email inbox: These spam messages come from people who purport to be editors at scientific journals, usually ones Acuña has never heard of, and offer to publish his papers — for a hefty fee.
Such publications are sometimes referred to as “predatory” journals. They target scientists, convincing them to pay hundreds or even thousands of dollars to publish their research without proper vetting.
“There has been a growing effort among scientists and organizations to vet these journals,” Acuña said. “But it’s like whack-a-mole. You catch one, and then another appears, usually from the same company. They just create a new website and come up with a new name.”
His group’s new AI tool automatically screens scientific journals, evaluating their websites and other online data for certain criteria: Do the journals have an editorial board featuring established researchers? Do their websites contain a lot of grammatical errors?
Acuña emphasizes that the tool isn’t perfect. Ultimately, he thinks human experts, not machines, should make the final call on whether a journal is reputable.
But in an era when prominent figures are questioning the legitimacy of science, stopping the spread of questionable publications has become more important than ever before, he said.
“In science, you don’t start from scratch. You build on top of the research of others,” Acuña said. “So if the foundation of that tower crumbles, then the entire thing collapses.”
The shake down
When scientists submit a new study to a reputable publication, that study usually undergoes a practice called peer review. Outside experts read the study and evaluate it for quality — or, at least, that’s the goal.
A growing number of companies have sought to circumvent that process to turn a profit. In 2009, Jeffrey Beall, a librarian at CU Denver, coined the phrase “predatory” journals to describe these publications.
Often, they target researchers outside of the United States and Europe, such as in China, India and Iran — countries where scientific institutions may be young, and the pressure and incentives for researchers to publish are high.
“They will say, ‘If you pay $500 or $1,000, we will review your paper,'” Acuña said. “In reality, they don’t provide any service. They just take the PDF and post it on their website.”
A few different groups have sought to curb the practice. Among them is a nonprofit organization called the Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ). Since 2003, volunteers at the DOAJ have flagged thousands of journals as suspicious based on six criteria. (Reputable publications, for example, tend to include a detailed description of their peer review policies on their websites.)
But keeping pace with the spread of those publications has been daunting for humans.
To speed up the process, Acuña and his colleagues turned to AI. The team trained its system using the DOAJ’s data, then asked the AI to sift through a list of nearly 15,200 open-access journals on the internet.
Among those journals, the AI initially flagged more than 1,400 as potentially problematic.
Acuña and his colleagues asked human experts to review a subset of the suspicious journals. The AI made mistakes, according to the humans, flagging an estimated 350 publications as questionable when they were likely legitimate. That still left more than 1,000 journals that the researchers identified as questionable.
“I think this should be used as a helper to prescreen large numbers of journals,” he said. “But human professionals should do the final analysis.”
A firewall for science
Acuña added that the researchers didn’t want their system to be a “black box” like some other AI platforms.
“With ChatGPT, for example, you often don’t understand why it’s suggesting something,” Acuña said. “We tried to make ours as interpretable as possible.”
The team discovered, for example, that questionable journals published an unusually high number of articles. They also included authors with a larger number of affiliations than more legitimate journals, and authors who cited their own research, rather than the research of other scientists, to an unusually high level.
The new AI system isn’t publicly accessible, but the researchers hope to make it available to universities and publishing companies soon. Acuña sees the tool as one way that researchers can protect their fields from bad data — what he calls a “firewall for science.”
“As a computer scientist, I often give the example of when a new smartphone comes out,” he said. “We know the phone’s software will have flaws, and we expect bug fixes to come in the future. We should probably do the same with science.”
Co-authors on the study included Han Zhuang at the Eastern Institute of Technology in China and Lizheng Liang at Syracuse University in the United States.
-
Tools & Platforms3 weeks ago
Building Trust in Military AI Starts with Opening the Black Box – War on the Rocks
-

 Ethics & Policy1 month ago
Ethics & Policy1 month agoSDAIA Supports Saudi Arabia’s Leadership in Shaping Global AI Ethics, Policy, and Research – وكالة الأنباء السعودية
-

 Events & Conferences3 months ago
Events & Conferences3 months agoJourney to 1000 models: Scaling Instagram’s recommendation system
-

 Jobs & Careers2 months ago
Jobs & Careers2 months agoMumbai-based Perplexity Alternative Has 60k+ Users Without Funding
-

 Funding & Business2 months ago
Funding & Business2 months agoKayak and Expedia race to build AI travel agents that turn social posts into itineraries
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoVEX Robotics launches AI-powered classroom robotics system
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoHappy 4th of July! 🎆 Made with Veo 3 in Gemini
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoOpenAI 🤝 @teamganassi
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoThe Guardian view on Trump and the Fed: independence is no substitute for accountability | Editorial
-

 Jobs & Careers2 months ago
Jobs & Careers2 months agoAstrophel Aerospace Raises ₹6.84 Crore to Build Reusable Launch Vehicle

