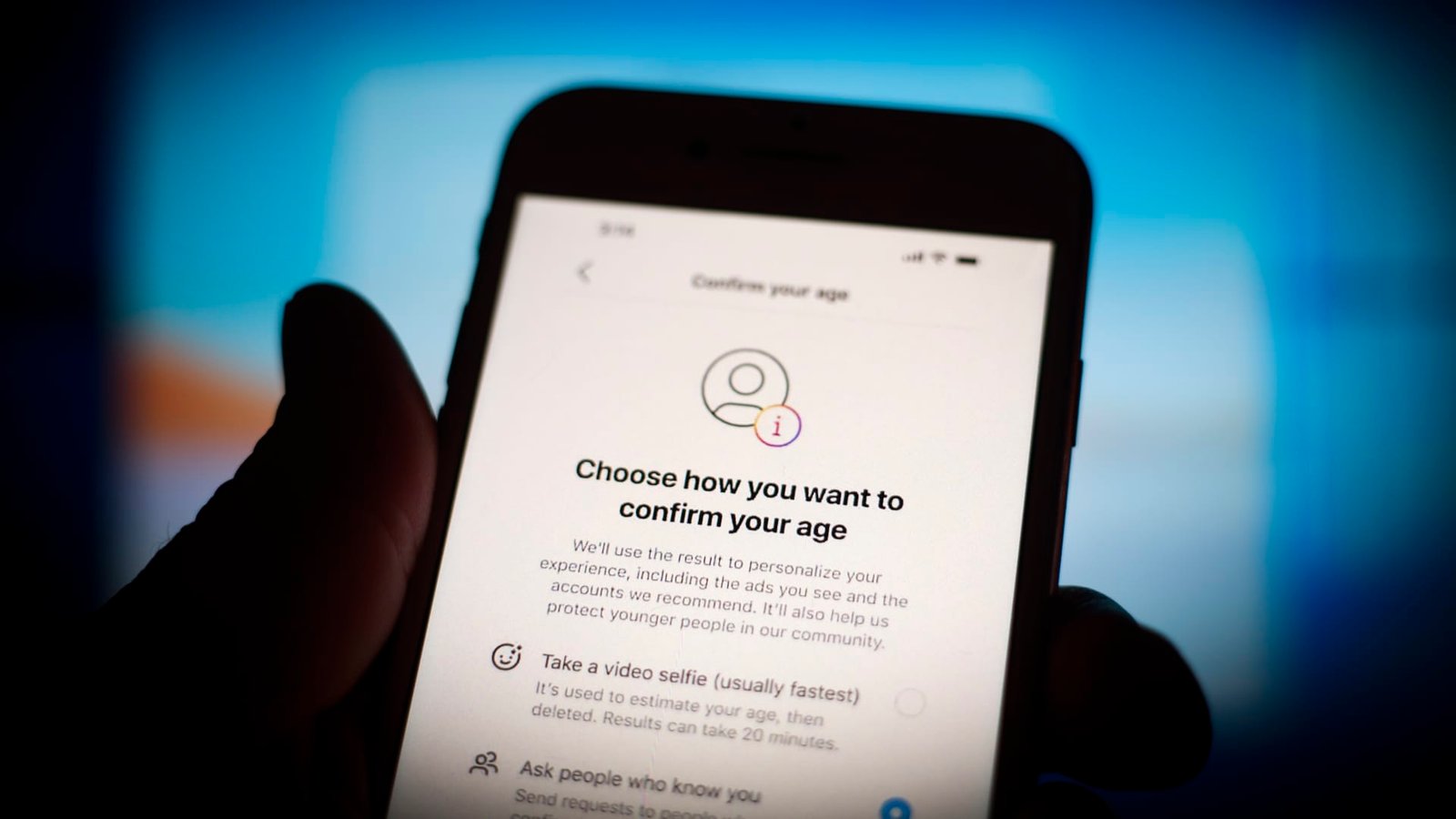
Spotify, Reddit and X have all implemented age assurance systems to prevent children from being exposed to inappropriate content.
STR | Nurphoto via Getty Images
The global online safety movement has paved the way for a number of artificial intelligence-powered products designed to keep kids away from potentially harmful things on the internet.
In the U.K., a new piece of legislation called the Online Safety Act imposes a duty of care on tech companies to protect children from age-inappropriate material, hate speech, bullying, fraud, and child sexual abuse material (CSAM). Companies can face fines as high as 10% of their global annual revenue for breaches.
Further afield, landmark regulations aimed at keeping kids safer online are swiftly making their way through the U.S. Congress. One bill, known as the Kids Online Safety Act, would make social media platforms liable for preventing their products from harming children — similar to the Online Safety Act in the U.K.
This push from regulators is increasingly causing something of a rethink at several major tech players. Pornhub and other online pornography giants are blocking all users from accessing their sites unless they go through an age verification system.
Porn sites haven’t been alone in taking action to verify users ages, though. Spotify, Reddit and X have all implemented age assurance systems to prevent children from being exposed to sexually explicit or inappropriate materials.
Such regulatory measures have been met with criticisms from the tech industry — not least due to concerns that they may infringe internet users’ privacy.
Digital ID tech flourishing
At the heart of all these age verification measures is one company: Yoti.
Yoti produces technology that captures selfies and uses artificial intelligence to verify someone’s age based on their facial features. The firm says its AI algorithm, which has been trained on millions of faces, can estimate the age of 13 to 24-year-olds within two years of accuracy.
The firm has previously partnered with the U.K.’s Post Office and is hoping to capitalize on the broader push for government-issued digital ID cards in the U.K. Yoti is not alone in the identity verification software space — other players include Entrust, Persona and iProov. However, the company has been the most prominent provider of age assurance services under the new U.K. regime.
“There is a race on for child safety technology and service providers to earn trust and confidence,” Pete Kenyon, a partner at law firm Cripps, told CNBC. “The new requirements have undoubtedly created a new marketplace and providers are scrambling to make their mark.”
Yet the rise of digital identification methods has also led to concerns over privacy infringements and possible data breaches.
“Substantial privacy issues arise with this technology being used,” said Kenyon. “Trust is key and will only be earned by the use of stringent and effective technical and governance procedures adopted in order to keep personal data safe.”
Rani Govender, policy manager for child safety online at British child protection charity NSPCC, said that the technology “already exists” to authenticate users without compromising their privacy.
“Tech companies must make deliberate, ethical choices by choosing solutions that protect children from harm without compromising the privacy of users,” she told CNBC. “The best technology doesn’t just tick boxes; it builds trust.”
Child-safe smartphones
The wave of new tech emerging to prevent children from being exposed to online harms isn’t just limited to software.
Earlier this month, Finnish phone maker HMD Global launched a new smartphone called the Fusion X1, which uses AI to stop kids from filming or sharing nude content or viewing sexually explicit images from the camera, screen and across all apps.
The phone uses technology developed by SafeToNet, a British cybersecurity firm focused on child safety.
Finnish phone maker HMD Global’s new smartphone uses AI to prevent children from being exposed nude or sexually explicit images.
HMD Global
“We believe more needs to be done in this space,” James Robinson, vice president of family vertical at HMD, told CNBC. He stressed that HMD came up with the concept for children’s devices prior to the Online Safety Act entering into force, but noted it was “great to see the government taking greater steps.”
The release of HMD’s child-friendly phone follows heightened momentum in the “smartphone-free” movement, which encourages parents to avoid letting their children own a smartphone.
Going forward, the NSPCC’s Govender says that child safety will become a significant priority for digital behemoths such as Google and Meta.
The tech giants have for years been accused of worsening mental health in children and teens due to the rise of online bullying and social media addiction. They in return argue they’ve taken steps to address these issues through increased parental controls and privacy features.
“For years, tech giants have stood by while harmful and illegal content spread across their platforms, leaving young people exposed and vulnerable,” she told CNBC. “That era of neglect must end.”