Tools & Platforms
AI agents reshape advertising landscape
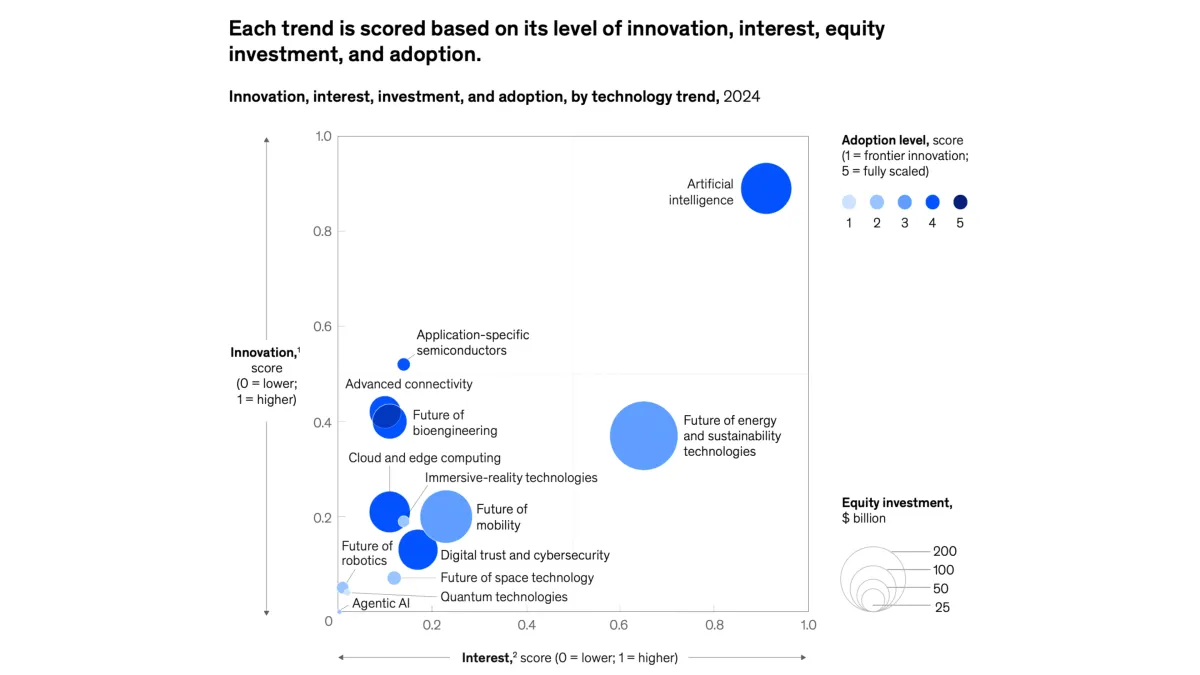
McKinsey’s Technology Trends Outlook 2025 report, published in July 2025, identifies 13 frontier technologies that could fundamentally reshape marketing strategies and advertising operations. The analysis shows the marketing industry moving toward autonomous systems and human-AI collaboration models that promise to transform everything from campaign management to customer targeting.
The report positions agentic AI – artificial intelligence systems capable of autonomous planning and execution – as the most significant emerging trend for marketing organizations. According to McKinsey’s analysis, agentic AI represents a shift from chatbot interactions to virtual coworkers that can independently manage complex workflows.
Subscribe the PPC Land newsletter ✉️ for similar stories like this one. Receive the news every day in your inbox. Free of ads. 10 USD per year.
“Agentic AI moves AI from a passive tool to an active collaborator with enterprise workflows,” states Delphine Nain Zurkiya, senior partner at McKinsey Boston. The technology enables marketing teams to automate tasks like campaign optimization, audience targeting, and performance analysis without constant human oversight.
McKinsey data indicates $1.1 billion in equity investment flowed into agentic AI in 2024, with job postings related to this technology increasing 985 percent from 2023 to 2024. The report notes that while interest levels remain relatively low compared to established AI technologies, growth rates exceed all other technology trends.
Investment patterns reveal scaling challenges
The Technology Trends Outlook documents significant investment fluctuations across marketing-relevant technologies. Artificial intelligence attracted $124.3 billion in equity investment during 2024, representing the highest funding levels among the 13 analyzed trends. Digital trust and cybersecurity technologies received $77.8 billion, while cloud and edge computing secured $80.8 billion.
These investment patterns highlight the complex relationship between technology maturity and market adoption. According to the report, organizations face scaling challenges due to surging demand for compute-intensive workloads, particularly from generative AI applications and robotics systems.
“The surging demand for compute-intensive workloads, especially from gen AI, robotics, and immersive environments, is creating new demands on global infrastructure,” the report states. Data center power constraints and supply chain delays are slowing technology deployments across marketing organizations.
Human-machine collaboration reshapes marketing operations
McKinsey identifies new human-machine collaboration models as a defining characteristic of 2025 technology trends. The report describes a shift toward “more natural interfaces, multimodal inputs, and adaptive intelligence” that enables more productive collaboration between marketing professionals and intelligent systems.
This evolution affects multiple aspects of marketing operations. Advanced connectivity technologies, including 5G networks and low-Earth-orbit satellites, enable real-time optimization of campaigns across diverse channels. Application-specific semiconductors designed for AI workloads improve the speed and efficiency of data processing for marketing analytics.
The future of robotics also impacts marketing operations, particularly in customer service and support functions. McKinsey notes that robots are expanding beyond manufacturing into service sectors, where they work alongside human employees in collaborative environments.
Regional competition intensifies technology adoption
The report documents increasing regional and national competition over critical technologies that affect marketing infrastructure. Countries and corporations are establishing sovereign infrastructure and localized technology capabilities to reduce dependence on external providers.
“Global competition over critical technologies has intensified. Countries and corporations have doubled down on sovereign infrastructure, localized chip fabrication, and funding technology initiatives,” according to the analysis. This trend affects marketing organizations’ access to technology tools and platforms, particularly for companies operating across multiple jurisdictions.
The development of sovereign cloud solutions creates new considerations for marketing data management and campaign deployment. Organizations must navigate evolving regulatory requirements while maintaining campaign effectiveness across different regions.
Subscribe the PPC Land newsletter ✉️ for similar stories like this one. Receive the news every day in your inbox. Free of ads. 10 USD per year.
Responsible innovation becomes strategic requirement
McKinsey emphasizes responsible innovation as a critical factor in technology adoption success. The report states that “trust is increasingly the gatekeeper to adoption” as technologies become more powerful and integrated into marketing workflows.
Marketing organizations face growing pressure to demonstrate transparency, fairness, and accountability in their use of AI models, data collection practices, and customer targeting systems. The report notes that “companies face growing pressure to demonstrate transparency, fairness, and accountability, whether in AI models, gene editing pipelines, or immersive platforms.”
This emphasis on responsible innovation affects how marketing teams implement new technologies. Organizations must balance the efficiency gains from automation with the need to maintain customer trust and regulatory compliance.
Quantum technologies prepare for future disruption
While still in early development stages, quantum technologies represent potential long-term disruption for marketing analytics and customer data processing. The report assigns quantum technologies an adoption score of 1 on McKinsey’s 5-point scale, indicating frontier innovation status with limited organizational investment.
However, recent advances in error correction and scalability suggest accelerating development timelines. Companies including Amazon Web Services, Google, IBM, and Microsoft announced quantum computing breakthroughs throughout 2024 and early 2025, addressing key technical challenges.
For marketing organizations, quantum technologies could eventually enable more sophisticated customer behavior modeling and predictive analytics capabilities beyond current classical computing limitations.
Space technologies expand marketing data capabilities
The future of space technologies creates new opportunities for marketing data collection and audience targeting. McKinsey notes that low-Earth-orbit satellite constellations and direct-to-device connectivity expand coverage for marketing campaigns in previously underserved areas.
“Space technologies are rapidly reshaping our world, unlocking new levels of connectivity and data-driven insights,” the report states. Earth observation systems enable more precise location-based marketing and real-time campaign optimization based on geographic and environmental factors.
The integration of space-based data with terrestrial marketing systems supports enhanced environmental monitoring for sustainable marketing initiatives and improved disaster response for crisis communications.
Bioengineering influences personalized marketing
McKinsey identifies bioengineering as a scaling technology with implications for personalized marketing and customer experience design. The report notes that bioengineering applications are moving “beyond limited deployments” toward broader commercial implementation.
Advances in precision medicine and personalized treatments create opportunities for pharmaceutical and healthcare marketing organizations to develop more targeted campaigns. The integration of AI with bioengineering accelerates research and development cycles, enabling faster iteration of marketing strategies for health-related products.
The report emphasizes that successful bioengineering adoption depends on addressing public acceptance and regulatory frameworks, factors that also affect marketing strategies for companies in related industries.
Energy sustainability drives marketing transformation
The future of energy and sustainability technologies affects marketing operations through both direct environmental impact and customer expectations. McKinsey notes that “the transformation of energy production, storage, and distribution systems is one of the most consequential challenges and opportunities of our time.”
Marketing organizations increasingly incorporate sustainability messaging and environmental impact considerations into campaign development. The report documents significant investment in clean energy technologies, with $223.2 billion in equity funding during 2024.
The growing demand for electricity from data centers creates pressure on marketing technology infrastructure. Organizations must balance increasing computational needs for AI-powered marketing tools with sustainability commitments and energy efficiency requirements.
Subscribe the PPC Land newsletter ✉️ for similar stories like this one. Receive the news every day in your inbox. Free of ads. 10 USD per year.
Timeline
Key terminology explained
Agentic AI
Agentic AI represents artificial intelligence systems that operate autonomously to plan and execute complex workflows without constant human supervision. Unlike traditional AI that responds to specific prompts, agentic AI creates virtual coworkers capable of managing entire marketing campaigns, from audience analysis to budget optimization. This technology marks a fundamental shift from passive AI tools to active collaborators that can adapt strategies based on real-time performance data and market conditions.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence encompasses computer systems designed to perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence, including pattern recognition, decision-making, and learning from experience. In marketing contexts, AI powers everything from predictive analytics and customer segmentation to automated content creation and bid management. The technology has evolved from experimental applications to essential infrastructure for competitive marketing operations.
Technology Trends
Technology trends refer to the directional patterns of innovation and adoption that shape business strategies and operational capabilities. McKinsey’s analysis identifies trends based on quantitative measures including patent filings, research publications, investment flows, and talent demand. Understanding these trends enables marketing organizations to anticipate infrastructure requirements, skill development needs, and competitive advantages in rapidly evolving digital landscapes.
Marketing Organizations
Marketing organizations encompass the departments, agencies, and teams responsible for customer acquisition, brand management, and revenue generation through digital and traditional channels. These entities are experiencing fundamental transformation as AI and automation technologies reshape campaign management, audience targeting, and performance measurement. Modern marketing organizations must balance human creativity with technological efficiency to maintain competitive positioning.
Investment Patterns
Investment patterns describe the flow of capital into specific technology sectors, indicating market confidence and development momentum. McKinsey’s data reveals significant funding fluctuations across marketing-relevant technologies, with artificial intelligence attracting $124.3 billion in 2024 while emerging areas like quantum technologies received substantially less. These patterns help marketing leaders understand which technologies are approaching commercial viability versus remaining experimental.
Human-Machine Collaboration
Human-machine collaboration represents the evolving partnership between marketing professionals and intelligent systems, emphasizing augmentation rather than replacement of human capabilities. This collaboration model enables more natural interfaces, multimodal inputs, and adaptive intelligence that responds to both data patterns and human intuition. Successful implementation requires redesigning workflows to leverage machine efficiency while preserving human strategic thinking and creative problem-solving.
Campaign Management
Campaign management involves the planning, execution, monitoring, and optimization of marketing initiatives across multiple channels and touchpoints. Modern campaign management increasingly relies on AI-powered automation for tasks like bid adjustments, audience targeting, and performance tracking. The evolution toward autonomous campaign management systems requires new skill sets focused on strategy development, goal setting, and result interpretation rather than manual execution.
Data Processing
Data processing encompasses the collection, analysis, and transformation of marketing information into actionable insights for decision-making. Advanced data processing capabilities enable real-time optimization, predictive analytics, and personalized customer experiences at scale. The exponential growth in data volume from digital interactions requires specialized infrastructure including application-specific semiconductors and cloud computing resources to maintain processing speed and accuracy.
Customer Targeting
Customer targeting involves identifying and reaching specific audience segments most likely to respond to marketing messages and convert to desired actions. AI-enhanced targeting systems analyze vast datasets including search history, behavioral patterns, and demographic information to predict customer preferences and optimize message delivery. The evolution of targeting capabilities must balance personalization effectiveness with privacy regulations and consumer trust considerations.
Infrastructure Requirements
Infrastructure requirements define the technological foundation necessary to support modern marketing operations, including computing power, data storage, networking capabilities, and security systems. The shift toward AI-powered marketing tools creates unprecedented demands on infrastructure, particularly for real-time processing and analysis of customer interactions. Organizations must invest in scalable infrastructure that can accommodate growing computational needs while maintaining performance and reliability standards.
Summary
Who: McKinsey & Company analysts and technology experts researching frontier technologies affecting business operations and marketing strategies.
What: Publication of Technology Trends Outlook 2025 identifying 13 key technologies including agentic AI, application-specific semiconductors, advanced connectivity, and sustainable energy systems that will reshape marketing operations.
When: July 2025 publication date covering technology developments through 2024 and projections for 2025-2030 timeframe.
Where: Global analysis covering technology adoption patterns across United States, Europe, China, and other major markets, with particular focus on regional competition and sovereign technology development.
Why: Organizations need strategic guidance for navigating technological transformation affecting marketing infrastructure, campaign management, customer targeting, and regulatory compliance in an increasingly AI-powered business environment.
Tools & Platforms
New Faculty Member Shiyan Jiang on Bringing AI to Every Classroom
Newswise — As one of Penn GSE’s newest faculty members, Shiyan Jiang is helping expand what AI education can look like—and who it’s for. She doesn’t believe AI should be confined to computer science classes or taught only by tech experts. Instead, she’s designing curriculum and professional learning that help educators across all subjects bring AI into their classrooms in ways that are accessible, meaningful, and rooted in identity. In this Q&A, Jiang shares her vision for inclusive AI education, what drew her to Penn GSE, and why she believes every teacher can be an AI educator.
Q: What first sparked your interest in education and technology?
A: What sparked my interest wasn’t just the excitement of building software or exploring new technologies—it was the realization that technology can transform how we experience learning.
As an undergraduate, I was deeply engaged in developing augmented reality tools that made textbooks come alive—books that didn’t just sit on a desk, but responded to the reader, invited interaction, and sparked curiosity. That experience taught me something powerful: when students can see, touch, and engage with ideas in dynamic ways, learning becomes more meaningful. It showed me that technology, when thoughtfully designed, can be a bridge between what students know and what they could imagine.
Q: Can you share a project or area of research you’re especially excited about right now?
A: I’m especially excited about our work on integrating AI across the curriculum in ways that are accessible, meaningful, and sustainable. We started with a simple but powerful idea: AI should be for all students—not just those in computer science classes. So, we created an AI curriculum for high school English Language Arts. But we soon realized that no single subject can capture the full range of what it means to understand AI. That led us to design short, discipline-specific modules—AI for ELA, AI for math, and AI for history—where each teacher contributes just 3–5 hours from their own subject lens, while students gain exposure to AI from multiple perspectives.
What excites me most now is shifting the narrative: AI doesn’t need to be a separate, specialized topic. It can show up in everyday teaching—through a 5-minute classroom discussion or a full 15-hour unit.
Every teacher has the potential to be an AI educator. So now, my work is focused on supporting teachers in building their AI educator identity, while also studying how students develop their AI learner identities. Because if we want AI education to be truly inclusive, we need to empower every teacher—not just a few—to bring AI into their classrooms.
Q: What drew you to Penn GSE?
A: What drew me to Penn GSE is its bold vision for what education can be. The school’s commitment to interdisciplinary research and leadership in educational innovation aligns perfectly with how I approach my own work—blending AI, data science, and learning sciences to reimagine what’s possible in classrooms.
I’ve long admired the translational work happening at Penn GSE. It’s a place where big ideas are not only welcomed but also supported and scaled. I see tremendous potential to partner with faculty, students, and practitioners at Penn GSE to keep pushing the boundaries of how we think about AI and the future of learning.
Q: How do you hope your work will make a difference for educators or students?
A: I want every student—not just those in computer science classes—to have the opportunity to understand, question, and shape the role of AI in their lives. My work is about making AI education more inclusive and relevant, so that students from all backgrounds can see themselves in AI careers and feel empowered to use data and technology to tackle the issues they care about.
For educators, I hope to remove the barriers that make AI feel intimidating or “not for them.” I design tools, curricula, and professional learning experiences that support teachers in confidently bringing AI into their classrooms—regardless of their subject area or technical background. Because ultimately, if we want AI education to reach all students, we need to equip all teachers to be part of that journey.
Q: What’s something about your research that you wish more people understood?
A: I wish more people understood that education—whether we’re teaching AI, data science, or any other subject—is not just about delivering knowledge. At its core, my research is about creating spaces where students can reflect on who they want to become. When we design learning experiences or build educational tools, the goal isn’t just to teach technical skills—it’s to help students see themselves as capable, curious, and powerful contributors to their communities and the world. Whether they end up working in AI or not, I want students to leave the classroom with a stronger sense of identity, agency, and purpose.
Q: Outside of work, what’s something you’re passionate about or enjoy doing?
A: Outside of work, I love creating creative data visualizations. For me, it’s not just about charts and graphs, but about finding beauty in patterns and helping people see information in new ways.
I’m also a passionate traveler—especially a food traveler. Wherever I go, the first place I want to visit is the local market. I love experiencing a culture through its food: the ingredients, the smells, the way people gather and cook. It’s a joyful and delicious way to connect with people and places.
Q: When you think about the growing role of AI in education, are you more hopeful or concerned—and why?
A: Honestly, my feelings have evolved over time—just like many others navigating this space. There have been moments when I’ve felt incredibly hopeful, seeing all the new possibilities AI opens up for teaching and learning. And there have been moments of concern, especially when I see issues of bias and over-reliance surface.
But I’ve come to realize that this kind of fluctuation is part of the exploration process—it’s normal when we’re working with something so new and transformative. Overall, I consider myself an AI optimist. I believe in engaging with these technologies thoughtfully, trying things out, and learning through doing. For me, it’s not about waiting for perfect solutions—it’s about building better ones through reflection, iteration, and inclusive design.
Tools & Platforms
AI drives medtech investment in 2025
Artificial intelligence companies have been a focus of investment in the medical technology sector so far in 2025. Although the number of funding rounds decreased in the first half of the year, AI startups were favored by investors, according to a recent report by PitchBook. For example, earlier this month, Aidoc received $150 million in funding for an AI foundation model.
AI devices have also been the subject of recent acquisitions. In August, Tempus agreed to buy Paige, a company making digital pathology software, for $81 million. More recently, GE Healthcare built out its AI portfolio with the planned acquisition of brain MRI software firm Icometrix.
Read on for recent deals involving AI-enabled medical devices covered by MedTech Dive:
Tools & Platforms
This country is first in the world to make AI a minister, and its duties are fighting corruption

Albania is making an artificial intelligence-powered digital assistant named Diella its minister, the world’s first artificial intelligence system to serve as a government minister, tasked with overseeing public procurement to eliminate corruption. Albanian Prime Minister Edi Rama announced the appointment this week, promising the AI minister will make Albania “a country where public tenders are 100% free of corruption.Diella, meaning “sun” in Albanian, will manage all government contract decisions previously handled by human officials, ensuring complete transparency in public spending. The AI minister represents a radical shift from traditional governance, with Rama describing her as “the first cabinet member who isn’t physically present, but is virtually created by AI.”
Digital assistant becomes government decision-maker
Diella originally launched in January as an AI-powered virtual assistant on Albania’s e-Albania platform, helping citizens obtain government documents and services. Dressed in traditional Albanian attire, she has already processed 36,600 digital documents and provided nearly 1,000 services to users through voice commands and electronic stamps.The AI minister will now assume responsibility for evaluating and awarding all public tenders, with decisions transferred from human government officials in a “step-by-step” process. This represents a major shift in how governments worldwide might leverage artificial intelligence for governance.
Albanian public skeptical about AI minister’s success
Public procurement has long been plagued by corruption scandals in Albania, a Balkan nation experts describe as a hub for international money laundering from drug and weapons trafficking. Graft has reportedly reached the highest levels of government, complicating the country’s European Union accession goals.Rama aims to lead Albania into the EU by 2030, making anti-corruption efforts crucial for membership eligibility. However, the government provided no details about human oversight mechanisms or safeguards against potential AI manipulation. Public reaction remains mixed, with skeptical Facebook users commenting “Even Diella will be corrupted in Albania” and “Stealing will continue and Diella will be blamed.“The parliament is expected to vote on Rama’s fourth-term cabinet, including the AI minister, when it convenes Friday. Rama won his fourth consecutive term in May elections and has previously advocated for AI as an anti-corruption tool that eliminates bribes, threats, and conflicts of interest in government decision-making.
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoThe Guardian view on Trump and the Fed: independence is no substitute for accountability | Editorial
-
Tools & Platforms1 month ago
Building Trust in Military AI Starts with Opening the Black Box – War on the Rocks
-

 Ethics & Policy2 months ago
Ethics & Policy2 months agoSDAIA Supports Saudi Arabia’s Leadership in Shaping Global AI Ethics, Policy, and Research – وكالة الأنباء السعودية
-

 Events & Conferences4 months ago
Events & Conferences4 months agoJourney to 1000 models: Scaling Instagram’s recommendation system
-

 Jobs & Careers2 months ago
Jobs & Careers2 months agoMumbai-based Perplexity Alternative Has 60k+ Users Without Funding
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoHappy 4th of July! 🎆 Made with Veo 3 in Gemini
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoVEX Robotics launches AI-powered classroom robotics system
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoMacron says UK and France have duty to tackle illegal migration ‘with humanity, solidarity and firmness’ – UK politics live | Politics
-

 Funding & Business2 months ago
Funding & Business2 months agoKayak and Expedia race to build AI travel agents that turn social posts into itineraries
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoOpenAI 🤝 @teamganassi

