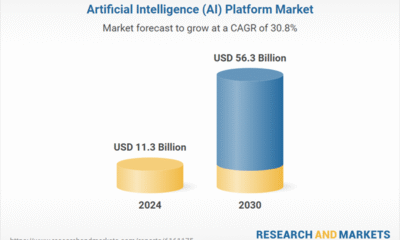
When businesses first started using artificial intelligence (AI) for business operations, they were often siloed into performing specific tasks— one model for inventory management, another for pricing, and several for customer service.
But today’s AI models differ significantly from those of years past. With generative AI and open-weight AI, businesses can use best-of-breed specialized AI to streamline across their business operations.
There are three factors for moving toward more efficient AI models:
- With open-weight AI, companies will have the ability to fine-tune already-powerful models across various industries.
- Recently, companies have been working on developing smaller, more efficient AI models, which will enable faster and more cost-effective data processing.
- The increased availability of cloud computing resources allows companies to deploy and scale AI systems without extensive infrastructure costs.
The result is a new generation of AI that can seamlessly integrate into business operations, optimizing processes and scaling with organizational needs through an evolution that is transforming the business world. Companies are already leveraging these advancements to streamline operations, enhance decision-making, and reduce operational costs.
As AI efficiency continues to improve, adopting these solutions is no longer a matter of speculation. It’s actively reshaping the way businesses function.
Shift to Smaller, More Efficient AI Models
Over the years, AI models have become increasingly powerful, but they have required significant infrastructure to support them as well. Today, the trend is shifting toward smaller, more efficient AI models that provide near-state-of-the-art results while consuming fewer resources. Within the right agentic framework, these compact models are capable of performing complex tasks such as decision-making and delivering insights with remarkable speed.
The move to smaller models is driven by the need for businesses to optimize costs while improving performance. By reducing the size of AI models without compromising their capabilities, companies can run advanced systems on more affordable hardware. This shift also has the added benefit of reducing latency, which is particularly important in industries such as retail, finance, and hospitality, where real-time data processing is particularly crucial.
For businesses, the implications are clear: smaller, more efficient AI models not only reduce the need for extensive computing power but also make AI more accessible, enabling faster implementation and scaling without the high costs traditionally associated with large-scale AI systems.
A Shift Toward Customization
As AI technology matures, businesses are increasingly moving toward customized solutions tailored to their specific needs. While off-the-shelf AI tools can be effective for general tasks, they often lack the depth and specificity required to tackle industry-specific challenges.
More companies are focused on developing AI models trained on their unique datasets, optimizing them for the specific nuances of their operations. This industry-specific approach has led to faster deployments and more relevant AI systems that deliver precise, actionable insights. Whether it’s refining customer segmentation models in retail, improving predictive maintenance in manufacturing, or enhancing personalized guest experiences in hospitality, customized AI models are proving more effective in meeting the specific needs of these sectors.
For businesses, the key takeaway is that AI isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. Developing tailored AI models allows companies to gain a competitive edge by addressing their unique operational challenges with precision. This move toward customization is not only accelerating the deployment of AI but also increasing its relevance and impact across different industries.
Open-Weight Models
The introduction of open-weight AI models has further accelerated the efficiency of AI applications. Unlike closed systems, which are controlled by a single vendor and often require significant licensing fees, open-weight models allow businesses to access, modify, and deploy AI systems that are customized for their needs.
One of the primary advantages of open-weight AI is the level of control it gives businesses over their systems. Companies can adapt these models to fit their specific operational needs, fine-tuning them to process proprietary data more effectively. Additionally, companies can host open-weight AI models on their own infrastructure, keeping sensitive data in-house while still benefiting from cutting-edge AI capabilities.
The shift to open-weight models has not only reduced the costs associated with proprietary AI solutions but also made AI more accessible to smaller businesses. With the ability to scale AI models more easily and make adjustments as needed, companies can innovate without being dependent on third-party vendors.
Financial, Operational Benefits of AI Efficiency
The increased efficiency of AI models directly impacts a company’s bottom line. Smaller, more efficient models reduce the need for costly hardware and cloud services, enabling businesses to lower their operational costs. Furthermore, the ability to build custom models tailored to specific business functions means AI can deliver more precise results, thereby enhancing decision-making and overall performance.
The impact of AI efficiency isn’t limited to cost savings. By streamlining business processes, AI enables companies to automate routine tasks, minimize human errors, and expedite the time-to-market (TTM) for new products and services. Whether it’s optimizing supply chains, refining marketing strategies, or improving customer support, the financial and operational benefits of AI efficiency are clear.
For organizations already using AI, adopting more efficient models offers an opportunity to further optimize operations, refine existing AI systems, and ensure that AI investments deliver maximum return. As AI continues to evolve, businesses that embrace these advancements will be better positioned to meet the demands of a competitive marketplace.
Key Competitive Advantage
The shift toward more efficient AI models is changing the landscape of business operations. Smaller, more efficient models, customized AI solutions, and open-weight systems are making it possible for businesses to harness the full potential of AI while reducing costs and improving performance. This new generation of AI is not only more accessible but also more adaptable to the specific needs of different industries.
For businesses, integrating these advanced AI systems into operations represents a significant opportunity. As AI continues to evolve, the companies that leverage these advancements will be better equipped to stay ahead of the competition, improve efficiency, and achieve long-term success.
AI efficiency is no longer a future goal but a present reality. Embracing these technologies today is the key to thriving in an increasingly data-driven and competitive market.