Tools & Platforms
A National Breakthrough in AI Inference Chips — TradingView News

HONG KONG, Aug 8, 2025 – (ACN Newswire) – Currently, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) technology are driving the evolution of AI from iterative improvements in algorithms to significant breakthroughs in computational infrastructure. During this round of technological evolution, a massive demand for AI inference computing is emerging, setting new benchmarks for the architecture and cost-efficiency of computing power.
Compared with general-purpose GPU architectures, NPU chips designed specifically for AI inference scenarios have become the foundation supporting the large-scale commercialization of AI industries due to the advantages such as high cost-effectiveness, energy efficiency and customization. These chips are gradually becoming one of the mainstream development directions for AI chips, accelerating the industry’s transition from an era centered on GPUs for large model training to an era focused on NPUs for AI inference computing. In this race, the innovation capabilities at the foundational architecture level and extensive experience in large-scale application deployment are progressively contributing to a company’s overall competitiveness and sustainability.
Among these players, Shenzhen Intellifusion Technologies Co., Ltd. (“Intellifusion”) is the first company to commercialize domestic high computing power AI inference chips in China. As a pioneer in NPU research and design, Intellifusion integrates multiple generations of architectural technical knowledge with mature commercialization experience to create high-performance, cost-effective and highly versatile inference chips. Intellifusion has achieved large-scale deployments across enterprise, consumer and industry-grade scenarios, establishing a leading position in China’s AI inference chip-related products and services market in terms of revenue in 2024. On July 30, Intellifusion submitted its listing application to the Hong Kong Stock Exchange.
Led by a ‘Hardcore’ management team: providing strong traction for strategic implementation
In the deep tech sector of AI chips where technology, capital and talent concerntration converge, the management team serves not only as decision-maker for corporate strategy but also as “navigators” guiding Intellifusion through technological and industrial cycles. Intellifusion’s ability to gain a firm foothold in the highly complex and fiercely competitive AI inference chip market is inseparable from its core team, which boasts strategic foresight, technical prowess and hands-on industry experience.
Dr. Chen Ning, founder, executive director and general manager of Intellifusion, is a worldwide rare expert with deep experience in semiconductor and possesses both overseas and domestic industry experience. Standing at the forefront of technology, Dr. Chen deeply understands the path from theoretical breakthroughs to product transformation, and not only possesses visionary technical foresight, but also demonstrates strong execution capability in industrialization and commercialization, which enable him to grasp Intellifusion’s long-term strategic trajectory from the cutting edge of technological development with commercialization capability, and drive deep innovation along the “algorithm + chip” integration path, providing long-term traction for Intellifusion’s sustained growth.
As one of the key pioneers in China’s domestically-developed AI inference chips, Dr. Chen Ning has spearheaded the design and development of homegrown AI inference chips, achieving end-to-end innovation from algorithmic breakthroughs to chip-based implementation. He can rightly be considered one of the founding figures in the industrialization of China’s AI inference chips. His recognition as the prominent individuals in innovation and entrepreneurship and outstanding role models at the 40th Anniversary of Shenzhen Special Economic Zone, and in July of this year, he was selected alongside entrepreneurs such as Xingxing Wang, founder of Unitree Robotics, Weiliang Chen, founder of MetaX, and Peng Zhang, CEO of Zhipu AI, as one of CCTV’s ‘AI Leaders of the Year’,.further solidifies his strategic leadership position in China’s AI industry.
Under the leadership of Dr. Chen Ning, Intellifusion has assembled a elite Research & Development (‘R&D’) team with core members averaging over 25 years of experience in the AI industry. These veterans have long served at leading domestic technology companies, covering the entire critical technology chain from chip architecture design to algorithm development and optimization. As of the Latest Practicable Date, Intellifusion boasts 489 R&D personnel, including more than 50 engineers with over a decade of chip design experience and multiple national-level leading technical experts. This composition has established a synergistic system for chip design and algorithm development guided by seasoned industry specialists, providing robust support for rapid product innovations and continuous technological breakthroughs.
“Algorithm + chip” integrated strategy builds high technological barriers
Unlike traditional “algorithm companies” or “chip companies” that focus on singular breakthroughs, Intellifusion has consistently adhered to the advanced concept of co-designing algorithms and chips since its inception. This approach has forged an integrated software-hardware technical capability that creates a self-reinforcing virtuous cycle, where insights from real-world deployment continuously refine algorithms, algorithmic innovations drive chip architecture upgrades, and enhanced chip performance unlocks new application scenarios. This creates a compounding flywheel effect, progressively elevating R&D efficiency and commercial scalability.
At the foundational technology level, Intellifusion has established its proprietary “IFIC” platform through its algorithm-to-silicon integration capability. This end-to-end system encompasses the entire AI inference chip R&D process: algorithm analysis – instruction set definition – chip architecture design – toolchain optimization. This enables Intellifusion to develop successive generations of NPUs and AI inference chips, ensuring optimal efficiency and scenario-specific adaptability.
For architectural design, Intellifusion launched ‘AI Computing Blocks’ by employing fully home-grown advanced domestic manufacturing processes, secure supply chain with advanced semiconductor processes, featuring standardized compute units that can be stacked like building blocks to flexibly configure chips with variable computing power and enable multi-chip interconnect for scalable systems, realizing single tape-out enables multiple packaging variants, efficiently producing chips of diverse specifications while balancing flexibility and cost. To address the data transmission bottleneck of traditional computer chips, Intellifusion has pioneered an innovative Near-memory Hyper-converged Architecture, which realizes vertical integration by seamlessly combining memory and computing units in a stacked configuration, enabling direct data flow through the 3D structure, eliminating bandwidth limitations of traditional packaging interconnections, achieving on-chip bandwidth and sub-nanosecond latency, dramatically lowering the energy consumption of data transportation, and perfectly adapting to the needs of real-time loading of large-model parameters.
In the chip domain, Intellifusion has developed its DeepEdge Series of inference chips based on the “IFIC” Infrastructure, utilizing the innovative ” AI Computing Blocks” Architecture. Currently, DeepEdge10 Series covers a wide range from 8T to 128T of computing power per chip and supports Transformer-based models for efficient AI inference, which can realize balanced performance & efficiency, low power consumption, and flexible deployment.
In terms of technology update, Intellifusion has completed development of its 4th-generation NPU and is now advancing R&D for the next-generation high-performance NPU, Nova 500.
This integrated R&D system centered on “algorithms + chips” enables Intellifusion to not only ensure leading-edge performance and rapid iteration in chip design but also continuously strengthen its technological moat through product adaptability, deployment scalability, and ecosystem expansion. Notably, Intellifusion has been awarded the highest award for intelligent science and technology in China. – the “Wu Wenjun AI Science & Technology Award ” – three times, making it the only company in China to have won top prizes in all three categories: algorithms, chips, and applications. This recognition underscores its end-to-end innovation capability, from core technology development to industrial implementation.
Riding the Global Inference Wave: Securing Long-Term Value in AI Chips
As the proportion of inference computing in the total lifecycle cost of large models continues to rise, surging application demand will dramatically expand the scale of inference computing needs, creating a historic opportunity for the AI industry. According to the CIC Report, the market size of AI inference chip-related products and services industry in China is expected to reach RMB1,383.0 billion by 2029, at a CAGR of 53.4% from 2024 to 2029. In particular, the NPU-powered market size is projected to climb to RMB395.4 billion by 2029, at a CAGR of 72.3% from 2024 to 2029, significantly outpacing the overall market.
Under the guideline of the advanced algorithm-to-silicon chip design methodology, Intellifusion, a pioneer in the high-potential market, has established an integrated software-hardware technical capability that creates a self-reinforcing virtuous cycle. Its products and services have been validated across multiple critical application scenarios, positioning Intellifusion as an industry frontrunner. According to the CIC Report, Intellifusion is a global top-three leader in full-scenario AI inference chip-related products and services in China, based on the relevant revenue in 2024. Intellifusion is also a top-two provider of NPU-powered AI inference chip-related products and services in China, based on the relevant revenue in 2024.
Leveraging its IFIC Infrastructure, R&D capabilities in AI inference chips, and deep market insight, Intellifusion can respond quickly to changes in industrial demands and grasp the opportunity in the upcoming boom in AI inference chip-related products and services industry. Supported by policy tailwinds, growing application maturity, and semiconductor supply chain localization trends, Intellifusion is strategically positioned to capitalize on China’s golden window for domestic AI chips, emerging as both a key beneficiary and driver in the global recomposition of AI compute power.
In summary, Intellifusion has not only achieved full autonomy from self-developed architectures to ecosystem development but also made breakthroughs across market expansion, technological innovation, and product commercialization, establishing a difficult-to-replicate end-to-end advantage. Should its Hong Kong IPO proceed smoothly, at the time of listing, Intellifusion could potentially become China’s first and only artificial intelligence company with a dual A+H listing (Shanghai + Hong Kong). This milestone would fully unlock cross-border M&A opportunities, allowing Intellifusion to aggregate global resources, attract top-tier AI talent worldwide, and further solidify its leadership in China’s AI industry, particularly in the inference chip segment.
Copyright 2025 ACN Newswire . All rights reserved.
Tools & Platforms
Why Micron Technology (MU) Is Up 19.7% After AI-Driven Demand Boosts Analyst Optimism and Data Center Revenue
- In the past week, Micron Technology attracted widespread analyst upgrades and sector optimism due to robust demand for advanced memory chips powering artificial intelligence applications and data centers. Analysts highlighted Micron’s rapidly rising data center revenue and its strengthened position as an essential supplier for AI infrastructure solutions.
- A unique aspect is that Micron’s momentum has been reinforced by major enterprise customers’ commentary, especially Oracle’s, reflecting industry-wide confidence in continued AI-driven demand for memory products through at least 2026.
- We’ll explore how these positive demand signals from large AI customers impact Micron’s investment narrative and growth outlook.
Trump has pledged to “unleash” American oil and gas and these 22 US stocks have developments that are poised to benefit.
Micron Technology Investment Narrative Recap
To be a Micron Technology shareholder, you need to believe in ongoing strength in AI-driven data center demand that can offset the inherent volatility and competition of the memory chip industry. The latest surge in analyst upgrades and sector optimism has sharpened focus on Micron’s position in the AI supply chain, but it does not eliminate the cyclical risks still present in both DRAM and NAND markets that could impact earnings momentum if demand trends shift unexpectedly.
Among recent announcements, Micron’s raised Q4 2025 earnings guidance stands out as closely linked to the surge in AI-fueled memory demand, reinforcing confidence behind current analyst enthusiasm. The updated outlook, with expected revenue of US$11.2 billion and EPS of US$2.64, reflects tangible benefits from AI, making near-term results a primary market catalyst in the coming weeks.
Yet, despite this tailwind, investors should also consider how quickly competition from other memory giants could…
Read the full narrative on Micron Technology (it’s free!)
Micron Technology’s narrative projects $53.6 billion in revenue and $13.6 billion in earnings by 2028. This requires 16.6% yearly revenue growth and a $7.4 billion earnings increase from $6.2 billion today.
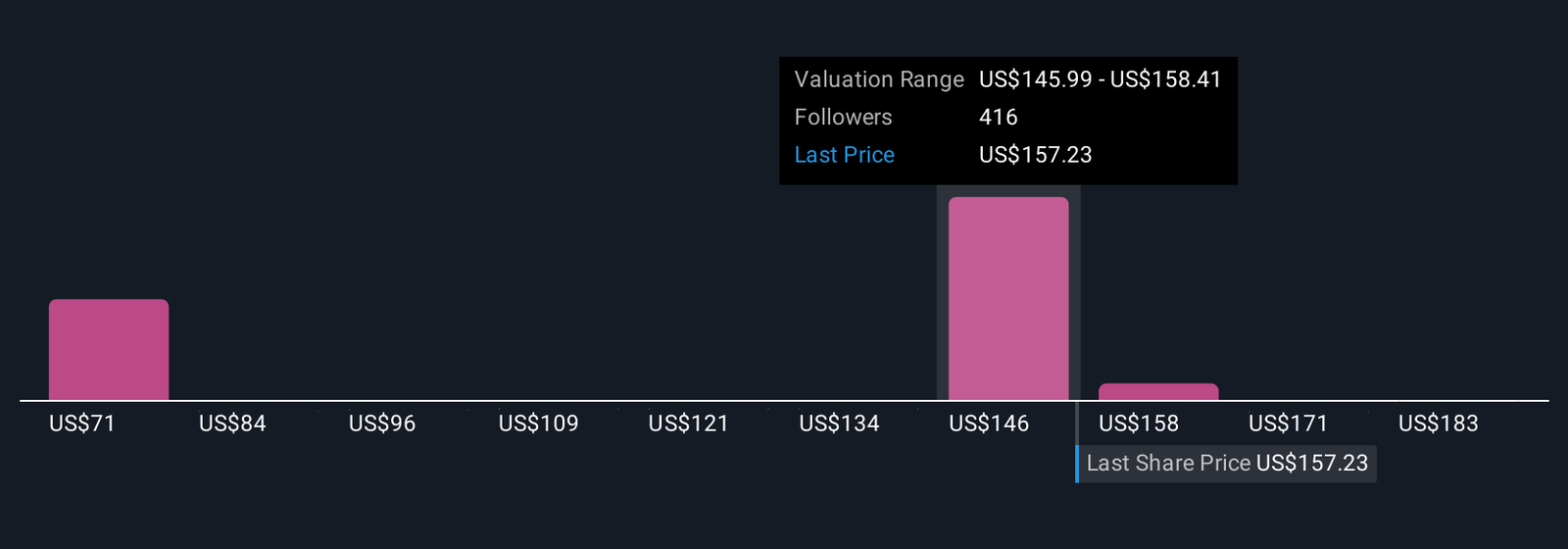
Uncover how Micron Technology’s forecasts yield a $150.57 fair value, a 4% downside to its current price.
Exploring Other Perspectives
Fifty members of the Simply Wall St Community estimate Micron’s fair value between US$71.48 and US$195.67 per share. However, continued robust demand for advanced DRAM and HBM in AI data centers could prove pivotal for future revenue and margin strength, so consider a range of market outlooks.
Explore 50 other fair value estimates on Micron Technology – why the stock might be worth as much as 24% more than the current price!
Build Your Own Micron Technology Narrative
Disagree with existing narratives? Create your own in under 3 minutes – extraordinary investment returns rarely come from following the herd.
Want Some Alternatives?
Every day counts. These free picks are already gaining attention. See them before the crowd does:
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data
and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your
financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data.
Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material.
Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
New: Manage All Your Stock Portfolios in One Place
We’ve created the ultimate portfolio companion for stock investors, and it’s free.
• Connect an unlimited number of Portfolios and see your total in one currency
• Be alerted to new Warning Signs or Risks via email or mobile
• Track the Fair Value of your stocks
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team@simplywallst.com
Tools & Platforms
California Finalizes 2025 CCPA Rules on Data & AI Oversight

If you’ve ever been rejected for a job by an algorithm, denied an apartment by a software program, or had your health coverage questioned by an automated system, California just voted to change the rules of the game. On July 24, 2025, the California Privacy Protection Agency (CPPA) voted to finalize one of the most consequential privacy rulemakings in U.S. history. The new regulations—covering cybersecurity audits, risk assessments, and automated decision-making technology (ADMT)—are the product of nearly a year of public comment, political pressure, and industry lobbying.
They represent the most ambitious expansion of U.S. privacy regulation since voters approved the California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA) in 2020 and its provisions took effect in 2023, adding for the first time binding obligations around automated decision-making, cybersecurity audits, and ongoing risk assessments.
How We Got Here: A Contentious Rulemaking
The CPPA formally launched the rulemaking process in November 2024. At stake was how California would regulate technologies often grouped under the “AI” umbrella-term. The CPPA opted to focus narrowly on automated decision-making technology (ADMT), rather than attempting to define AI in general. This move generated both relief and frustration among stakeholders. The groups weighing in ranged from Silicon Valley giants to labor unions and gig workers, reflecting the numerous corners of the economy that automated decision-making touches.
Early drafts had explicitly mentioned “artificial intelligence” and “behavioral advertising.” By the time the final rules were adopted, those references were stripped out. Regulators stated that they sought to avoid ambiguity and not encompass too many technologies. Critics said the changes weakened the rules.
The comment period drew over 575 pages of submissions from more than 70 organizations and individuals, including tech companies, civil society groups, labor advocates, and government officials. Gig workers described being arbitrarily deactivated by opaque algorithms. Labor unions argued the rules should have gone further to protect employees from automated monitoring. On the other side, banks, insurers, and tech firms warned that the regulations created duplicative obligations and legal uncertainty.
The CPPA staff defended the final draft as one that “strikes an appropriate balance,” while acknowledging the need to revisit these rules as technology and business practices evolve. After the July 24 vote, the agency formally submitted the package to the Office of Administrative Law, which has 30 business days to review it for procedural compliance before the rules take effect.
At today’s meeting, the CPPA Board unanimously voted to adopt a proposed rulemaking package on ADMT, cybersecurity audits, risk assessments, insurance, and CCPA updates. Now, the proposed regulations will be filed with the Office of Administrative Law. pic.twitter.com/A8IB38E66l
— California Privacy Protection Agency (@CalPrivacy) July 24, 2025
Scroll to continue reading
Automated Decision-Making Technology (ADMT): Redefining AI Oversight
The centerpiece of the regulations is the framework for ADMT. The rules define ADMT as “any technology that processes personal information and uses computation to replace human decisionmaking, or substantially replace human decisionmaking.”
The CPPA applies these standards to what it calls “significant decisions:” choices that determine whether someone gets a job or contract, qualifies for a loan, secures housing, is admitted to a school, or receives healthcare. In practice, that means résumé-screening algorithms, tenant-screening apps, loan approval software, and healthcare eligibility tools all fall within the law’s scope.
Companies deploying ADMT for significant decisions will face several new obligations. They must provide plain-language pre-use notices so consumers understand when and how automated systems are being applied. Individuals must also be given the right to opt out or, at minimum, appeal outcomes to a qualified human reviewer with real authority to reverse the decision. Businesses are further required to conduct detailed risk assessments, documenting the data inputs, system logic, safeguards, and potential impacts. In short, if an algorithm decides whether you get hired, approved for a loan, or accepted into housing, the company has to tell you up front, offer a meaningful appeal, and prove that the system isn’t doing more harm than good. Liability also cannot be outsourced: with the business itself, firms remain responsible even when they rely on third-party vendors.
Some tools are excluded—like firewalls, anti-malware, calculators, and spreadsheets—unless they are actually used to make the decision. Additionally, the CPPA tightened what counts as “meaningful human review.” Reviewers must be able to interpret the system’s output, weigh other relevant information, and have genuine authority to overturn the result.
Compliance begins on January 1, 2027.
Cybersecurity Audits: Scaling Expectations
Another pillar of the new rules is the requirement for annual cybersecurity audits. For the first time under state law, companies must undergo independent assessments of their security controls.
The audit requirement applies broadly to larger data-driven businesses. It covers companies with annual gross revenue exceeding $26.6 million that process the personal information of more than 250,000 Californians, as well as firms that derive half or more of their revenue from selling or sharing personal data.
Audits must be conducted by independent professionals who cannot report to a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) or other executives directly responsible for cybersecurity to ensure objectivity.
The audits cover a comprehensive list of controls, from encryption and multifactor authentication to patch management and employee training, and must be certified annually to the CPPA or Attorney General if requested.
Deadlines are staggered:
- April 1, 2028: $100M+ businesses
- April 1, 2029: $50–100M businesses
- April 1, 2030: <$50M businesses
By codifying this framework and embedding these requirements into law, California is effectively setting a de facto national cybersecurity baseline: one that may exceed federal NIST standards and ripple into vendor contracts nationwide. For businesses, these audits won’t just be about checking boxes: they could become the new cost of entry for doing business in California. Because companies can’t wall off California users from the rest of their customer base, these standards are likely to spread nationally through vendor contracts and compliance frameworks.
Privacy Risk Assessments: Accountability in High-Risk Processing
The regulations also introduce mandatory privacy risk assessments, required annually for companies engaged in high-risk processing.
Triggering activities include:
- Selling or sharing personal information
- Processing sensitive personal data (including neural data, newly classified as sensitive)
- Deploying ADMT for significant decisions
- Profiling workers or students
- Training ADMT on personal data
Each assessment must document categories of personal information processed, explain the purpose and benefits, identify potential harms and safeguards, and be submitted annually to the CPPA starting April 21, 2028, with attestations under penalty of perjury (a high-stakes accountability mechanism). This clause is designed to prevent “paper compliance.” By requiring executives to sign off under penalty of perjury, California is telling companies this isn’t paperwork. Leaders will be personally accountable if their systems mishandle sensitive data. Unlike voluntary risk assessments, California’s system ties accountability directly to the personal liability of signatories.
Other Notable Provisions
Beyond these headline rules, the CPPA also addressed sector-specific issues and tied in earlier reforms. For the insurance industry, the regulations clarify how the CCPA applies to companies that routinely handle sensitive personal and health data—an area where compliance expectations were often unclear. The rules also fold in California’s Delete Act, which takes effect on August 1, 2026. That law will give consumers a single, one-step mechanism to request deletion of their personal information across all registered data brokers, closing a major loophole in the data marketplace and complementing the broader CCPA framework. Together, these measures reinforce California’s role as a privacy trendsetter, creating tools that other states are likely to copy as consumers demand similar rights.
Implications for California
California has long served as the nation’s privacy laboratory, pioneering protections that often ripple across the country. This framework places California among the first U.S. jurisdictions to regulate algorithmic governance. With these rules, the state positions itself alongside the EU AI Act and the Colorado AI Act, creating one of the world’s most demanding compliance regimes.
However, the rules also set up potential conflict with the federal government. The America’s AI Action Plan, issued earlier this year, emphasizes innovation over regulation and warns that restrictive state-level rules could jeopardize federal AI funding decisions. This tension may play out in future policy disputes.
For California businesses, the impact is immediate. Companies must begin preparing governance frameworks, reviewing vendor contracts, and updating consumer-facing disclosures now. These compliance efforts build on earlier developments in California privacy law, including the creation of a dedicated Privacy Law Specialization for attorneys. This specialization will certify legal experts equipped to navigate the state’s intricate web of statutes and regulations, from ADMT disclosures to phased cybersecurity audits. Compliance will be expensive, but it will also drive demand for new privacy officers, auditors, and legal specialists. Mid-sized firms may struggle, while larger companies may gain an edge by showing early compliance. For businesses outside California, the ripple effects may be unavoidable because national companies will have to standardize around the state’s higher bar.
The CPPA’s finalized regulations mark a structural turning point in U.S. privacy and AI governance. Obligations begin as early as 2026 and accelerate through 2027–2030, giving businesses a narrow window to adapt. For consumers, the rules promise greater transparency and the right to challenge opaque algorithms. For businesses, they establish California as the toughest compliance environment in the country, forcing firms to rethink how they handle sensitive data, automate decisions, and manage cybersecurity. California is once again setting the tone for global debates on privacy, cybersecurity, and AI. Companies that fail to keep pace will not only face regulatory risk but could also lose consumer trust in the world’s fifth-largest economy. Just as California’s auto emissions standards reshaped national car design, its privacy rules are likely to shape national policy on data and AI. Other states will borrow from California, and Washington will eventually have to decide whether to match it or rein it in.
What starts in Sacramento rarely stays there. From Los Angeles to Silicon Valley, California just set the blueprint for America’s data and AI future.
Tools & Platforms
Rise of High-Paid Cleanup Engineers

In the rapidly evolving world of software development, a new breed of specialists is emerging to tackle the fallout from “vibe coding,” a trend where artificial intelligence tools generate code based on loose, natural-language prompts rather than rigorous engineering principles. This approach, popularized by figures like Andrej Karpathy, allows non-experts to churn out applications quickly, but it often results in tangled, inefficient codebases riddled with bugs and security flaws. As companies rush to adopt AI-driven coding to cut costs and speed up production, a shadow industry of cleanup experts has sprung up, commanding premium rates to salvage these digital disasters.
These “vibe code cleanup specialists,” as they’ve been dubbed on platforms like LinkedIn, are typically seasoned software engineers with deep expertise in debugging and refactoring. They step in after amateur or AI-assisted coders produce prototypes that work just well enough to impress stakeholders but fail under real-world scrutiny. According to a recent article in 404 Media, freelance developers and specialized firms are now making a lucrative business out of this, with some charging upwards of $200 per hour to untangle the messes left by tools like GitHub Copilot or Cursor.
The Rise of Vibe Coding and Its Hidden Costs
The term “vibe coding” gained traction earlier this year, building on Karpathy’s 2023 quip that English is the hottest new programming language, as detailed in a Wikipedia entry updated in August. It promises democratization: startups can prototype apps in days instead of months, empowering designers and entrepreneurs without formal coding training. However, critics argue it sacrifices maintainability for speed, leading to code that’s opaque even to its creators.
Posts on X, formerly Twitter, from users like software engineers and tech commentators highlight the frustration, with many sharing stories of prompts yielding conflicting results across AI models, turning simple tasks into endless tweaking sessions. This sentiment echoes in a Wired piece from June, which warned that engineering jobs, once stable, are now threatened by AI’s ability to “vibe” through code generation, though not without creating downstream chaos.
Case Studies from the Front Lines
Take the example of a mid-sized fintech startup that used vibe coding to build a payment processing app. The initial version, generated via natural-language descriptions to an AI, handled basic transactions but crumbled under high traffic, exposing vulnerabilities that could have led to data breaches. Enter the cleanup crew: engineers from firms specializing in AI code audits, who spent weeks dissecting the spaghetti-like structure, implementing proper error handling, and ensuring compliance with security standards.
Similar tales abound in industry forums. A Reddit thread on r/technology, discussing the 404 Media article, amassed hundreds of comments from developers venting about inheriting “vibe-coded messes” that lack documentation or logical flow. As one anonymous poster noted, these projects often require starting from scratch, inflating costs far beyond the initial savings promised by AI tools.
Economic Implications for the Tech Sector
The economic ripple effects are significant. A Ars Technica report from March explored how accepting AI-written code without full understanding is becoming commonplace, yet it burdens companies with technical debt. Cleanup specialists are filling this gap, with some reporting a 300% increase in demand over the past six months, per insights from X posts by tech recruiters.
This trend underscores a broader shift: while vibe coding accelerates innovation, it creates a two-tier system where elite engineers command higher premiums for remediation. A Verge analysis from September suggests that AI isn’t ending software engineering but evolving it, with humans essential for high-level comprehension and fixes.
Challenges and Solutions in Practice
Fixing vibe-coded software isn’t just about rewriting lines; it involves forensic analysis to trace bugs back to flawed prompts or model hallucinations. Engineers often employ tools like static analyzers and version control forensics to map out the chaos, as shared in a Medium post by a developer who likened the role to digital archaeology.
Solutions are emerging, too. Some companies are integrating “vibe coding hygiene” training, teaching teams to refine prompts and review AI outputs iteratively. X discussions from August reveal engineers experimenting with prompts that emphasize root-cause analysis, such as instructing AI to “trace the full user flow and identify origins,” which helps prevent messes from escalating.
The Future of AI-Assisted Development
Looking ahead, the cleanup boom may force a reckoning. Industry insiders, including those cited in a Index.dev blog from March, predict that as vibe coding matures, better AI models could reduce errors, but human oversight will remain crucial. Gary Marcus, in an X post from June, argued that prototypes still need professional rebuilding, a view supported by a ServiceNow community blog from early September noting that 95% of generative AI projects fail to reach production without engineering intervention.
Yet, optimism persists. A IT Munch overview from three weeks ago highlights vibe coding’s benefits for startups, like slashing development cycles to hours. The key, experts say, is hybrid approaches: use AI for speed, but pair it with engineers for polish.
Navigating the Cleanup Economy
For aspiring cleanup specialists, the field offers fertile ground. Freelance platforms are buzzing with gigs, and companies like those profiled in the 404 Media piece are scaling up. Rates reflect the expertise required—think $150,000-plus salaries for full-time roles, as per LinkedIn trends echoed on X.
Ultimately, this phenomenon reveals the double-edged sword of AI in tech: it empowers rapid creation but demands skilled humans to sustain it. As one engineer quipped in a recent X thread, “Vibe coding is the party; we’re the ones cleaning up the confetti—and getting paid handsomely for it.” With the current date marking mid-September 2025, the vibe coding cleanup wave shows no signs of slowing, positioning these specialists as the unsung guardians of reliable software in an AI-dominated era.
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoThe Guardian view on Trump and the Fed: independence is no substitute for accountability | Editorial
-
Tools & Platforms1 month ago
Building Trust in Military AI Starts with Opening the Black Box – War on the Rocks
-

 Ethics & Policy2 months ago
Ethics & Policy2 months agoSDAIA Supports Saudi Arabia’s Leadership in Shaping Global AI Ethics, Policy, and Research – وكالة الأنباء السعودية
-

 Events & Conferences4 months ago
Events & Conferences4 months agoJourney to 1000 models: Scaling Instagram’s recommendation system
-

 Jobs & Careers2 months ago
Jobs & Careers2 months agoMumbai-based Perplexity Alternative Has 60k+ Users Without Funding
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoHappy 4th of July! 🎆 Made with Veo 3 in Gemini
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoMacron says UK and France have duty to tackle illegal migration ‘with humanity, solidarity and firmness’ – UK politics live | Politics
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoVEX Robotics launches AI-powered classroom robotics system
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoOpenAI 🤝 @teamganassi
-

 Funding & Business2 months ago
Funding & Business2 months agoKayak and Expedia race to build AI travel agents that turn social posts into itineraries

