Events & Conferences
Differential privacy for deep learning at GPT scale

Deep-learning models are data driven, and that data may contain sensitive information that requires privacy protection. Differential privacy (DP) is a formal framework for ensuring the privacy of individuals in datasets, so that adversarial users can’t learn whether any given data sample was or was not used to train a machine learning model. Employing DP in deep learning typically means capping the contribution that each training sample makes to the model’s parameter adjustments, an approach known as per-sample gradient clipping.
Per-sample gradient clipping, however, makes deep learning much more time consuming than it would be otherwise, impeding the development of large DP models — for instance, at the level of the GPT language models, with billions of parameters.
In 2022, in workshops at the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML) and the Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), we presented two papers that advance DP for deep learning. In the first paper, “Automatic clipping: Differentially private deep learning made easier and stronger“, we described an automatic method that improves the efficiency of tuning the gradient-clipping process by an order of magnitude (say, 5-10 times).
Typically, gradient clipping involves an expensive ablation study to select a clipping threshold above which a data sample’s contribution to the model’s parameter adjustments is cut off, or clipped. Our approach instead uses normalization, completely eliminating the tuning of the clipping threshold.
In the second paper, “Differentially private bias-term only fine-tuning of foundation models” (DP-BiTFiT), which won the Best Paper Award at the NeurIPS Workshop on Trustworthy and Socially Responsible Machine Learning (TSRML), we introduced BiTFiT, a parameter-efficient method for doing fine-tuning during DP learning.
Generally speaking, a neural network has two types of parameters: the weights, which constitute more than 99% of the parameters and capture most of the information from the training data, and the biases, which shift (offset) the model output. We show that privately fine-tuning the bias terms alone is enough to achieve high accuracy under DP constraints, make DP learning 2 to 30 times faster, reduce memory use by 50% to 88%, and incur only 1/1000 the communication cost in the distributed environment.
Together, these two techniques have made fine-tuning a DP-GPT-2 as efficient as fine-tuning a standard GPT-2 in a parameter-efficient manner. We have made both methods publicly available, to encourage researchers to experiment with and benefit from faster DP deep learning.
Automatic clipping
The deep-learning process includes a tunable hyperparameter called the learning rate, which determines the degree to which the model weights can change during updates. The per-sample gradient clipping threshold is similar, but it imposes a limit on a per-sample basis. The existing approach to DP training requires an ablation study to simultaneously tune the clipping threshold and the learning rate. As such, if K (say, five, in practice) different clipping thresholds are evaluated, this makes the model’s hyperparameter tuning stage K times more expensive.
To solve this problem, we introduced automatic clipping, using gradient normalization instead of per-sample gradient clipping. This (1) eliminates the clipping threshold, (2) enlarges the small gradients that were not clipped, and (3) provably optimizes performance. Equipped with our automatic clipping, the DP stochastic-gradient-descent-optimization algorithm (DP-SGD) has the same asymptotic convergence rate as the standard (non-DP) SGD, even in the nonconvex-optimization setting, where the deep learning optimization lies.
Our experiments across several computer vision and language tasks show that automatic clipping can achieve state-of-the-art DP accuracy, on par with per-sample clipping methods, without sacrificing the training efficiency or the privacy guarantee.
DP-BiTFiT
The first advantage of differentially private bias-term fine-tuning (DP-BiTFiT) is that it’s model agnostic; we can apply it to any model by simply freezing all weights during fine-tuning, updating only the bias terms. In sharp contrast, prior alternatives such as low-rank adaption (LoRA) and adapters are applicable exclusively to transformers and involve extra tuning of the adaption ranks.
The second advantage of DP-BiTFiT is its parameter efficiency. In a study that spanned a range of foundation models, we found that the bias terms constitute only around 0.1% of model parameters. This means that DP-BiTFiT provides large efficiency improvements in terms of training time, memory footprint, and communication cost in the distributed-learning setting.
The third advantage of DP-BiTFiT is its computational advantage over other parameter-efficient approaches, such as DP-LoRA. Even if both approaches fine-tune roughly the same number of parameters, DP-BiTFiT still enjoys a great advantage in memory saving, as it does not need to store and access expensive activation tensors when computing the bias gradients; that’s unavoidable when computing weight gradients. We verify this rigorously through the chain rules of the back-propagation, where DP-BiTFiT has a much simpler computation graph because the activation tensors are not used.
Empirically, we have observed a substantial boost in efficiency when switching from DP full fine-tuning to DP-BiTFiT, while still maintaining state-of-the-art accuracy on large foundation models such as GPT-2-large, ResNet 152, RoBERTa-large, and Vision Transformers. For instance, we compare DP-BiTFiT to DP full fine-tuning and observe a four- to tenfold speedup and a two- to tenfold memory saving on GPT-2.
Acknowledgements: We would like to acknowledge our coauthors on the papers for their contributions: Sheng Zha and George Karypis. We thank Huzefa Rangwala for reviewing this post.
Events & Conferences
A New Ranking Framework for Better Notification Quality on Instagram

- We’re sharing how Meta is applying machine learning (ML) and diversity algorithms to improve notification quality and user experience.
- We’ve introduced a diversity-aware notification ranking framework to reduce uniformity and deliver a more varied and engaging mix of notifications.
- This new framework reduces the volume of notifications and drives higher engagement rates through more diverse outreach.
Notifications are one of the most powerful tools for bringing people back to Instagram and enhancing engagement. Whether it’s a friend liking your photo, another close friend posting a story, or a suggestion for a reel you might enjoy, notifications help surface moments that matter in real time.
Instagram leverages machine learning (ML) models to decide who should get a notification, when to send it, and what content to include. These models are trained to optimize for user positive engagement such as click-through-rate (CTR) – the probability of a user clicking a notification – as well as other metrics like time spent.
However, while engagement-optimized models are effective at driving interactions, there’s a risk that they might overprioritize the product types and authors someone has previously engaged with. This can lead to overexposure to the same creators or the same product types while overlooking other valuable and diverse experiences.
This means people could miss out on content that would give them a more balanced, satisfying, and enriched experience. Over time, this can make notifications feel spammy and increase the likelihood that people will disable them altogether.
The real challenge lies in finding the right balance: How can we introduce meaningful diversity into the notification experience without sacrificing the personalization and relevance people on Instagram have come to expect?
To tackle this, we’ve introduced a diversity-aware notification ranking framework that helps deliver more diverse, better curated, and less repetitive notifications. This framework has significantly reduced daily notification volume while improving CTR. It also introduces several benefits:
- The extensibility of incorporating customized soft penalty (demotion) logic for each dimension, enabling more adaptive and sophisticated diversity strategies.
- The flexibility of tuning demotion strength across dimensions like content, author, and product type via adjustable weights.
- The integration of balancing personalization and diversity, ensuring notifications remain both relevant and varied.
The Risks of Notifications without Diversity
The issue of overexposure in notifications often shows up in two major ways:
Overexposure to the same author: People might receive notifications that are mostly about the same friend. For example, if someone often interacts with content from a particular friend, the system may continue surfacing notifications from that person alone – ignoring other friends they also engage with. This can feel repetitive and one-dimensional, reducing the overall value of notifications.
Overexposure to the same product surface: People might mostly receive notifications from the same product surface such as Stories, even when Feed or Reels could provide value. For example, someone may be interested in both reel and story notifications but has recently interacted more often with stories. Because the system heavily prioritizes past engagement, it sends only story notifications, overlooking the person’s broader interests.
Introducing Instagram’s Diversity-Aware Notification Ranking Framework
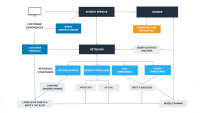
Instagram’s diversity-aware notification ranking framework is designed to enhance the notification experience by balancing the predicted potential for user engagement with the need for content diversity. This framework introduces a diversity layer on top of the existing engagement ML models, applying multiplicative penalties to the candidate scores generated by these models, as figure1, below, shows.
The diversity layer evaluates each notification candidate’s similarity to recently sent notifications across multiple dimensions such as content, author, notification type, and product surface. It then applies carefully calibrated penalties—expressed as multiplicative demotion factors—to downrank candidates that are too similar or repetitive. The adjusted scores are used to re-rank the candidates, enabling the system to select notifications that maintain high engagement potential while introducing meaningful diversity. In the end, the quality bar selects the top-ranked candidate that passes both the ranking and diversity criteria.
Mathematical Formulation
Within the diversity layer, we apply a multiplicative demotion factor to the base relevance score of each candidate. Given a notification candidate 𝑐, we compute its final score as the product of its base ranking score and a diversity demotion multiplier:
where R(c) represents the candidate’s base relevance score, and D(c) ∈ [0,1] is a penalty factor that reduces the score based on similarity to recently sent notifications. We define a set of semantic dimensions (e.g., author, product type) along which we want to promote diversity. For each dimension i, we compute a similarity signal pi(c) between candidate c and the set of historical notifications H, using a maximal marginal relevance (MMR) approach:
where simi(·,·) is a predefined similarity function for dimension i. In our baseline implementation, pi(c) is binary: it equals 1 if the similarity exceeds a threshold 𝜏i and 0 otherwise.
The final demotion multiplier is defined as:
where each wi ∈ [0,1] controls the strength of demotion for its respective dimension. This formulation ensures that candidates similar to previously delivered notifications along one or more dimensions are proportionally down-weighted, reducing redundancy and promoting content variation. The use of a multiplicative penalty allows for flexible control across multiple dimensions, while still preserving high-relevance candidates.
The Future of Diversity-Aware Ranking
As we continue evolving our notification diversity-aware ranking system, a next step is to introduce more adaptive, dynamic demotion strategies. Instead of relying on static rules, we plan to make demotion strength responsive to notification volume and delivery timing. For example, as a user receives more notifications—especially of similar type or in rapid succession—the system progressively applies stronger penalties to new notification candidates, effectively mitigating overwhelming experiences caused by high notification volume or tightly spaced deliveries.
Longer term, we see an opportunity to bring large language models (LLMs) into the diversity pipeline. LLMs can help us go beyond surface-level rules by understanding semantic similarity between messages and rephrasing content in more varied, user-friendly ways. This would allow us to personalize notification experiences with richer language and improved relevance while maintaining diversity across topics, tone, and timing.
Events & Conferences
Simplifying book discovery with ML-powered visual autocomplete suggestions

Every day, millions of customers search for books in various formats (audiobooks, e-books, and physical books) across Amazon and Audible. Traditional keyword autocomplete suggestions, while helpful, usually require several steps before customers find their desired content. Audible took on the challenge of making book discovery more intuitive and personalized while reducing the number of steps to purchase.
We developed an instant visual autocomplete system that enhances the search experience across Amazon and Audible. As the user begins typing a query, our solution provides visual previews with book covers, enabling direct navigation to relevant landing pages instead of the search result page. It also delivers real-time personalized format recommendations and incorporates multiple searchable entities, such as book pages, author pages, and series pages.
Our system needed to understand user intent from just a few keystrokes and determine the most relevant books to display, all while maintaining low latency for millions of queries. Using historical search data, we match keystrokes to products, transforming partial inputs into meaningful search suggestions. To ensure quality, we implemented confidence-based filtering mechanisms, which are particularly important for distinguishing between general queries like “mystery” and specific title searches. To reflect customers’ most recent interests, the system applies time-decay functions to long historical user interaction data.
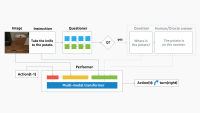
To meet the unique requirements of each use case, we developed two distinct technical approaches. On Audible, we deployed a deep pairwise-learning-to-rank (DeepPLTR) model. The DeepPLTR model considers pairs of books and learns to assign a higher score to the one that better matches the customer query.
The DeepPLTR model’s architecture consists of three specialized towers. The left tower factors in contextual features and recent search patterns using a long-short-term-memory model, which processes data sequentially and considers its prior decisions when issuing a new term in the sequence. The middle tower handles keyword and item engagement history. The right tower factors in customer taste preferences and product descriptions to enable personalization. The model learns from paired examples, but at runtime, it relies on books’ absolute scores to assemble a ranked list.
For Amazon, we implemented a two-stage modeling approach involving a probabilistic information-retrieval model to determine the book title that best matches each keyword and a second model that personalizes the book format (audiobooks, e-books, and physical books). This dual-strategy approach maintains low latency while still enabling personalization.
In practice, a customer who types “dungeon craw” in the search bar now sees a visual recommendation for the book Dungeon Crawler Carl, complete with book cover, reducing friction by bypassing a search results page and sending the customer directly to the product detail page. On Audible, the system also personalizes autocomplete results and enriches the discovery experience with relevant connections. These include links to the author’s complete works (Matt Dinniman’s author page) and, for titles that belong to a series, links to the full collection (such as the Dungeon Crawler Carl series).
On Amazon, when the customer clicks on the title, the model personalizes the right book-format (audiobooks, e-books, physical books) recommendation and directs the customer to the right product detail page.
In both cases, after the customer has entered a certain number of keystrokes, the system employs a model to detect customer intent (e.g., book title intent for Amazon or author intent for Audible) and determine which visual widget should be displayed.
Audible and Amazon books’ visual autocomplete provides customers with more relevant content more rapidly than traditional autocomplete, and its direct navigation reduces the number of steps to find and access desired books — all while handling millions of queries at low latency.
This technology is not just about making book discovery easier; it is laying the foundation for future improvements in search personalization and visual discovery across Amazon’s ecosystem.
Acknowledgements: Jiun Kim, Sumit Khetan, Armen Stepanyan, Jack Xuan, Nathan Brothers, Eddie Chen, Vincent Lee, Soumy Ladha, Justine Luo, Yuchen Zeng, David Torres, Gali Deutsch, Chaitra Ramdas, Christopher Gomez, Sharmila Tamby, Melissa Ma, Cheng Luo, Jeffrey Jiang, Pavel Fedorov, Ronald Denaux, Aishwarya Vasanth, Azad Bajaj, Mary Heer, Adam Lowe, Jenny Wang, Cameron Cramer, Emmanuel Ankrah, Lydia Diaz, Suzette Islam, Fei Gu, Phil Weaver, Huan Xue, Kimmy Dai, Evangeline Yang, Chao Zhu, Anvy Tran, Jessica Wu, Xiaoxiong Huang, Jiushan Yang
Events & Conferences
Revolutionizing warehouse automation with scientific simulation

Modern warehouses rely on complex networks of sensors to enable safe and efficient operations. These sensors must detect everything from packages and containers to robots and vehicles, often in changing environments with varying lighting conditions. More important for Amazon, we need to be able to detect barcodes in an efficient way.
The Amazon Robotics ID (ARID) team focuses on solving this problem. When we first started working on it, we faced a significant bottleneck: optimizing sensor placement required weeks or months of physical prototyping and real-world testing, severely limiting our ability to explore innovative solutions.
To transform this process, we developed Sensor Workbench (SWB), a sensor simulation platform built on NVIDIA’s Isaac Sim that combines parallel processing, physics-based sensor modeling, and high-fidelity 3-D environments. By providing virtual testing environments that mirror real-world conditions with unprecedented accuracy, SWB allows our teams to explore hundreds of configurations in the same amount of time it previously took to test just a few physical setups.
Camera and target selection/positioning
Sensor Workbench users can select different cameras and targets and position them in 3-D space to receive real-time feedback on barcode decodability.
Three key innovations enabled SWB: a specialized parallel-computing architecture that performs simulation tasks across the GPU; a custom CAD-to-OpenUSD (Universal Scene Description) pipeline; and the use of OpenUSD as the ground truth throughout the simulation process.
Parallel-computing architecture
Our parallel-processing pipeline leverages NVIDIA’s Warp library with custom computation kernels to maximize GPU utilization. By maintaining 3-D objects persistently in GPU memory and updating transforms only when objects move, we eliminate redundant data transfers. We also perform computations only when needed — when, for instance, a sensor parameter changes, or something moves. By these means, we achieve real-time performance.
Visualization methods
Sensor Workbench users can pick sphere- or plane-based visualizations, to see how the positions and rotations of individual barcodes affect performance.
This architecture allows us to perform complex calculations for multiple sensors simultaneously, enabling instant feedback in the form of immersive 3-D visuals. Those visuals represent metrics that barcode-detection machine-learning models need to work, as teams adjust sensor positions and parameters in the environment.
CAD to USD
Our second innovation involved developing a custom CAD-to-OpenUSD pipeline that automatically converts detailed warehouse models into optimized 3-D assets. Our CAD-to-USD conversion pipeline replicates the structure and content of models created in the modeling program SolidWorks with a 1:1 mapping. We start by extracting essential data — including world transforms, mesh geometry, material properties, and joint information — from the CAD file. The full assembly-and-part hierarchy is preserved so that the resulting USD stage mirrors the CAD tree structure exactly.
To ensure modularity and maintainability, we organize the data into separate USD layers covering mesh, materials, joints, and transforms. This layered approach ensures that the converted USD file faithfully retains the asset structure, geometry, and visual fidelity of the original CAD model, enabling accurate and scalable integration for real-time visualization, simulation, and collaboration.
OpenUSD as ground truth
The third important factor was our novel approach to using OpenUSD as the ground truth throughout the entire simulation process. We developed custom schemas that extend beyond basic 3-D-asset information to include enriched environment descriptions and simulation parameters. Our system continuously records all scene activities — from sensor positions and orientations to object movements and parameter changes — directly into the USD stage in real time. We even maintain user interface elements and their states within USD, enabling us to restore not just the simulation configuration but the complete user interface state as well.
This architecture ensures that when USD initial configurations change, the simulation automatically adapts without requiring modifications to the core software. By maintaining this live synchronization between the simulation state and the USD representation, we create a reliable source of truth that captures the complete state of the simulation environment, allowing users to save and re-create simulation configurations exactly as needed. The interfaces simply reflect the state of the world, creating a flexible and maintainable system that can evolve with our needs.
Application
With SWB, our teams can now rapidly evaluate sensor mounting positions and verify overall concepts in a fraction of the time previously required. More importantly, SWB has become a powerful platform for cross-functional collaboration, allowing engineers, scientists, and operational teams to work together in real time, visualizing and adjusting sensor configurations while immediately seeing the impact of their changes and sharing their results with each other.
New perspectives
In projection mode, an explicit target is not needed. Instead, Sensor Workbench uses the whole environment as a target, projecting rays from the camera to identify locations for barcode placement. Users can also switch between a comprehensive three-quarters view and the perspectives of individual cameras.
Due to the initial success in simulating barcode-reading scenarios, we have expanded SWB’s capabilities to incorporate high-fidelity lighting simulations. This allows teams to iterate on new baffle and light designs, further optimizing the conditions for reliable barcode detection, while ensuring that lighting conditions are safe for human eyes, too. Teams can now explore various lighting conditions, target positions, and sensor configurations simultaneously, gleaning insights that would take months to accumulate through traditional testing methods.
Looking ahead, we are working on several exciting enhancements to the system. Our current focus is on integrating more-advanced sensor simulations that combine analytical models with real-world measurement feedback from the ARID team, further increasing the system’s accuracy and practical utility. We are also exploring the use of AI to suggest optimal sensor placements for new station designs, which could potentially identify novel configurations that users of the tool might not consider.
Additionally, we are looking to expand the system to serve as a comprehensive synthetic-data generation platform. This will go beyond just simulating barcode-detection scenarios, providing a full digital environment for testing sensors and algorithms. This capability will let teams validate and train their systems using diverse, automatically generated datasets that capture the full range of conditions they might encounter in real-world operations.
By combining advanced scientific computing with practical industrial applications, SWB represents a significant step forward in warehouse automation development. The platform demonstrates how sophisticated simulation tools can dramatically accelerate innovation in complex industrial systems. As we continue to enhance the system with new capabilities, we are excited about its potential to further transform and set new standards for warehouse automation.
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoThe Guardian view on Trump and the Fed: independence is no substitute for accountability | Editorial
-
Tools & Platforms3 weeks ago
Building Trust in Military AI Starts with Opening the Black Box – War on the Rocks
-

 Ethics & Policy1 month ago
Ethics & Policy1 month agoSDAIA Supports Saudi Arabia’s Leadership in Shaping Global AI Ethics, Policy, and Research – وكالة الأنباء السعودية
-

 Events & Conferences4 months ago
Events & Conferences4 months agoJourney to 1000 models: Scaling Instagram’s recommendation system
-

 Jobs & Careers2 months ago
Jobs & Careers2 months agoMumbai-based Perplexity Alternative Has 60k+ Users Without Funding
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoVEX Robotics launches AI-powered classroom robotics system
-

 Funding & Business2 months ago
Funding & Business2 months agoKayak and Expedia race to build AI travel agents that turn social posts into itineraries
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoHappy 4th of July! 🎆 Made with Veo 3 in Gemini
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoOpenAI 🤝 @teamganassi
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoAERDF highlights the latest PreK-12 discoveries and inventions