AI Research
Faster, Smarter, Cheaper: AI Is Reinventing Market Research

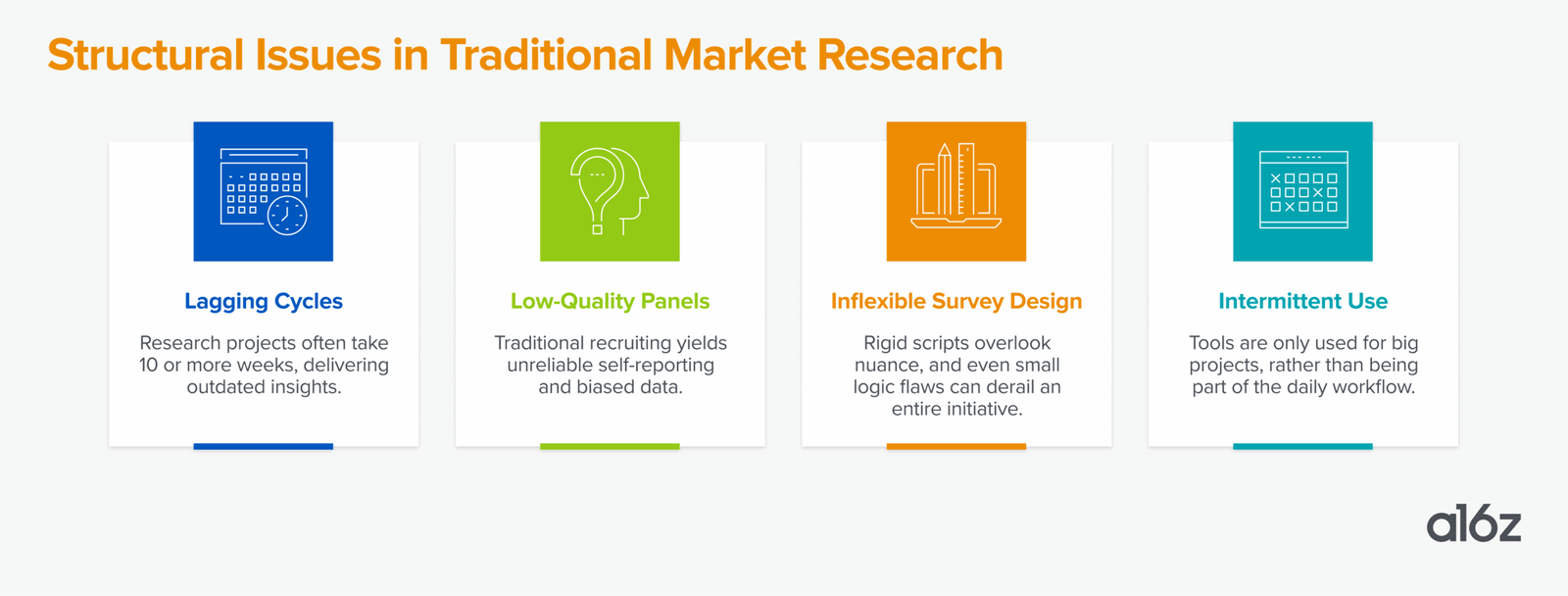
For decades, companies have poured billions of dollars into market research to better understand their customers, only to be constrained by slow surveys, biased panels, and lagging insights. Despite the $140 billion spent each year on market research, software is little more than a rounding error. Case in point: Traditional human-driven consulting firms Gartner and McKinsey are each valued at $40 billion, while software platforms Qualtrics and Medallia are worth $12.5 billion and $6.4 billion, respectively. And that’s just accounting for external spend.
With AI, we’re seeing yet another case of a market ready to shift labor spend into software. Early AI players are already leveraging speech-to-text and text-to-speech models to build AI-native survey platforms that conduct autonomous video interviews with people, then use LLMs to analyze results and create presentations. Those early movers are growing quickly, signing large deals, and co-opting budget that traditionally went to market research and consulting firms.
In doing so, these AI-enabled startups are reshaping how organizations derive insights from customers, make decisions, and execute at scale. However, most of these startups still rely on panel providers to source humans for surveys.
Now we’re seeing a crop of AI research companies replace the expensive human survey and analysis process entirely. Instead of recruiting a panel of people and asking them what they think, these companies can go as far as simulating entire societies of generative AI agents that can be queried, observed, and experimented with, modeling real human behavior. This turns market research from a lagging, one-time input into a continuous, dynamic advantage.
Where market research is today
The field of customer research has slowly incorporated software over time. In the 1990s, research was primarily conducted manually, with pen and paper data collection and analysis. Qualtrics and Medallia, among others, introduced online surveys in the early 2000s, followed by real-time analytics and mobile-based survey collection. Both companies used surveys to build deeper experience management tools around customers and employees. In parallel, the rise of bottom-up, self-serve tools like SurveyMonkey enabled individual teams to run quick, lightweight surveys — broadening access to research, but often resulting in fragmented efforts, inconsistent methodologies, and limited organizational visibility. These tools lacked the governance, scale, and integration required to support enterprise-wide research operations.
Consulting firms, McKinsey included, built entire divisions dedicated to deploying software-based research tools for customer segmentation and consumer insights at scale. These engagements often took months, cost millions, and relied on expensive and biased panels. The process of research often takes weeks to recruit a panel of participants, run the survey, analyze the results, then create reporting. And then the survey results are usually delivered to the buyer in packaged form, without much opportunity to revisit the process or dive deeper into the findings.
Most enterprises still rely on quarterly research to guide major launches, but that doesn’t provide the ongoing insights needed for fast, everyday decisions. Because traditional research is expensive, small bets and early ideas often go untested. Even companies eager to modernize find themselves stuck with outdated tools and slow processes.
In the late 2010s, a new wave of UX research tools emerged that was built directly for product teams, not consultants or survey ops. Instead of outsourcing user research, companies began embedding it into their development loops. Through unmoderated usability tests, in-product surveys, and prototype feedback, tools like Sprig, Maze, and Dovetail enabled faster, customer-informed decisions. These research tools demonstrated just how important integrated research is in modern businesses. But while such tools provided real-time value for software-driven teams, they were less oriented toward non-software companies and were primarily optimized for team-level use, rather than cross-functional use. AI-native research companies build on the advances of UX research: insights are immediate and applicable across teams, products, and industries, whether software-native or not.
AI + market research: a natural fit
AI has already increased the pace and decreased the cost of surveying. AI makes it easy to generate surveys quickly and adapt questions in real time based on how people respond. Analysis that once took weeks now happens in hours. Insight libraries learn over time, spotting patterns across projects and extrapolating early signals. This shift doesn’t just make research accessible to smaller companies; it also expands the set of decisions that can be informed by data, from early product concepts to nuanced positioning questions that were previously too expensive to investigate. Now AI-powered research tools are being used by many more users across a company’s marketing, product, sales, and customer success teams, as well as leadership.
These improvements matter. But even AI-powered surveys are still limited by the variability and accessibility of human panels and often depend on third-party recruiting to access respondents, limiting pricing control and differentiation.
Generative agents: Simulated societies move beyond human panels
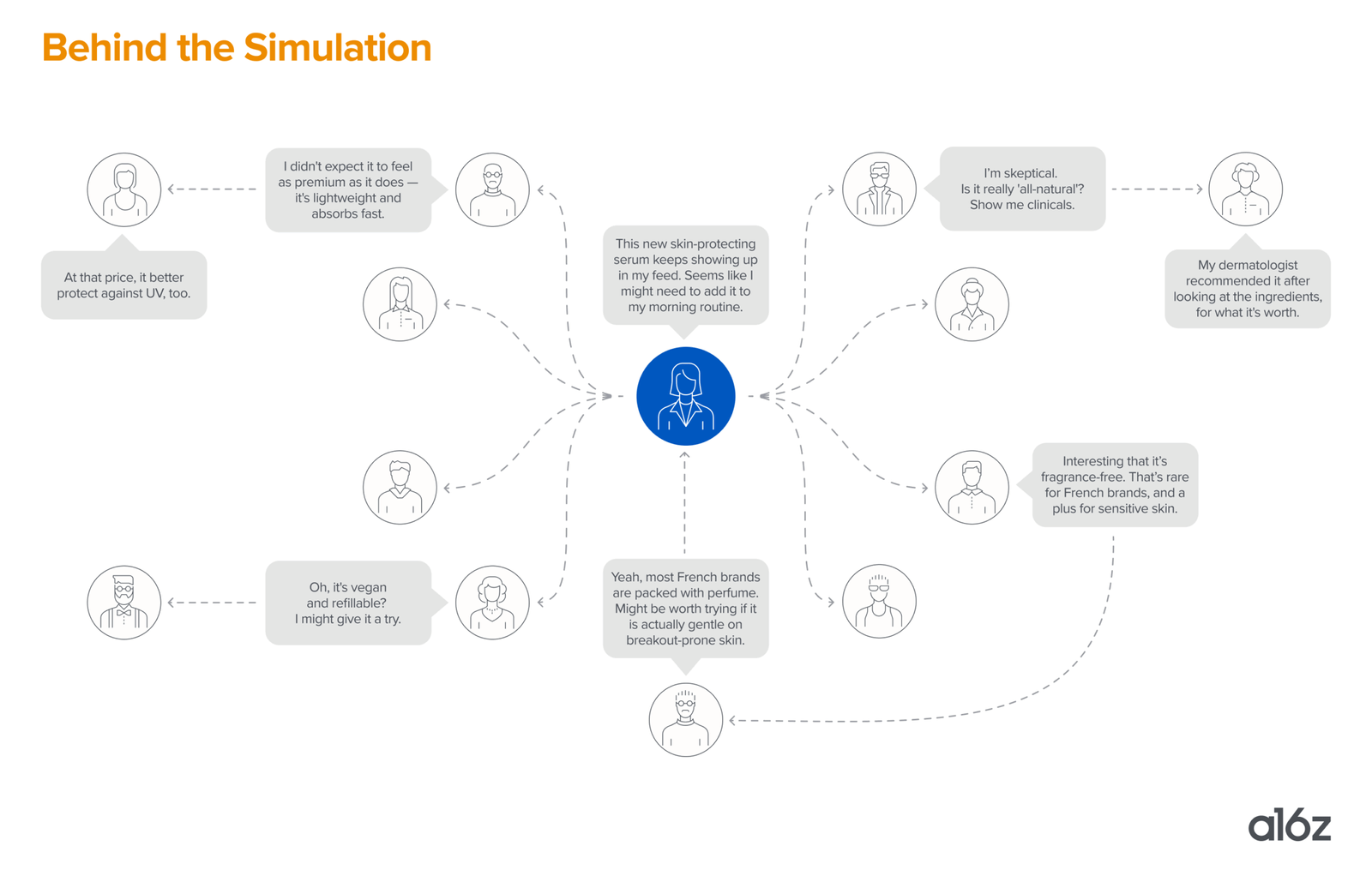
Enter generative agents, a concept originally introduced in the landmark paper Generative Agents: Interactive Simulacra of Human Behavior. The researchers demonstrated how simulated characters powered by large language models can exhibit increasingly human-like behavior, driven by memory, reflection, and planning. While the idea initially drew interest for its potential in building lifelike, simulated societies, its implications go beyond academic curiosity. One of its most promising commercial applications? Market research.
If this sounds abstract, here’s an example of how it might play out: Ahead of a new skincare launch in France, a beauty company could simulate 10,000 agents modeled on gen Z and millennial French beauty consumers. Each agent would be seeded with data from customer reviews, CRM histories, social listening insights (e.g. TikTok trends around “skincare routines”), and past purchase behavior. These agents could interact with each other, view simulated influencer content, shop virtual store shelves, and post product opinions in AI-generated social feeds, evolving over time as they absorb new information and reflect on past experiences.
What makes these simulations possible isn’t just off-the-shelf LLMs, but a growing stack of sophisticated techniques. Agents are now anchored in persistent memory architectures, often grounded in rich qualitative data like interviews or behavioral histories, enabling them to evolve over time through accumulated experiences and contextual feedback. In-context prompting supplies them with behavioral histories, environmental cues, and prior decisions, creating more nuanced, lifelike responses. Under the hood, methods like Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and agent chaining support complex, multi-step decision-making, resulting in simulations that mirror real-world customer journeys. Fine-tuned, multimodal models — trained across text, visuals, and interactions on domain-specific tasks — push agent behavior beyond the limits of text.
Early platforms are already leveraging these approaches. AI-powered simulation startups such as Simile and Aaru (which just announced a partnership with Accenture) hint at what’s coming: dynamic, always-on populations that act like real customers, ready to be queried, observed, and experimented with.
Agentic simulation doesn’t just accelerate workflows that once took weeks; it fundamentally reinvents how research and decision-making happens. It also overcomes many traditional research limitations by creating a research tool that can live inside a workflow. This leap is not just in efficiency. It’s in fidelity.
The playbook: fast distribution, deep integration
If history is any guide, the companies that dominate this AI wave won’t just have the best technology, they’ll master distribution and adoption. Qualtrics and Medallia, for example, won early by prioritizing adoption, familiarity, and loyalty, embedding themselves deeply into universities and key industries.
Accuracy obviously matters — particularly as teams measure AI tools against traditional, human-led research. But in this category, there are no established benchmarks or evaluation frameworks, which makes it difficult to objectively assess how “good” a given model is. Companies experimenting with agent simulation technology often have to define their own metrics.
Crucially, success doesn’t mean achieving 100% accuracy. It’s about hitting a threshold that’s “good enough” for your use case. Many CMOs we’ve spoken with are comfortable with outputs that are at least 70% as accurate as those from traditional consulting firms, especially since the data is cheaper, faster, and updated in real time. In the absence of standardized expectations, this creates a window for startups to move quickly, validate through real-world usage, and become embedded in workflows early. That said, startups must continue to refine the product: benchmarks will emerge, and the more you charge, the more customers will demand.
At this stage, the risk lies less in imperfect outputs than in over-engineering for theoretical accuracy. Startups that prioritize speed, integration, and distribution can define the emerging standard. Those that delay for perfect fidelity may find themselves stuck in endless pilots while others move to production.
AI-native research companies are fundamentally better positioned than traditional firms to redefine expectations for market research. While legacy market research firms may have deep panel data, their business models and workflows are not built for automation. In contrast, AI-native players have already developed purpose-built tooling for AI-moderated research and are structurally incentivized to push the frontier, not protect the past. They’re primed to own both the data layer and the simulation layer. The widely cited Generative Agent Simulations of 1,000 People paper illustrates this convergence: its coauthors relied on real interviews conducted by AI to seed agentic profiles — the same type of pipeline AI-native companies are already running at scale.
To drive impact, insights must be applicable beyond UX and marketing teams to product, strategy, and operations. The challenge: offering just enough service support without recreating the heavy overhead of traditional agencies.
The market research reckoning
The long era of lagging research is ending. AI-driven market research is transforming how we understand customers, whether through simulation, analysis, or insight generation. The companies that adopt AI-powered research tools early will gain faster insights, make better decisions, and unlock a new competitive edge. As shipping products becomes faster and easier, the real advantage lies in knowing what to build.
Building in this space?
Reach out to Zach Cohen (zcohen@a16z.com) and Seema Amble (samble@a16z.com).
AI Research
Study reveals why humans adapt better than AI

Humans adapt to new situations through abstraction, while AI relies on statistical or rule-based methods, limiting flexibility in unfamiliar scenarios.
A new interdisciplinary study from Bielefeld University and other leading institutions explores why humans excel at adapting to new situations while AI systems often struggle. Researchers found humans generalise through abstraction and concepts, while AI relies on statistical or rule-based methods.
The study proposes a framework to align human and AI reasoning, defining generalisation, how it works, and how it can be assessed. Experts say differences in generalisation limit AI flexibility and stress the need for human-centred design in medicine, transport, and decision-making.
Researchers collaborated across more than 20 institutions, including Bielefeld, Bamberg, Amsterdam, and Oxford, under the SAIL project. The initiative aims to develop AI systems that are sustainable, transparent, and better able to support human values and decision-making.
Interdisciplinary insights may guide the responsible use of AI in human-AI teams, ensuring machines complement rather than disrupt human judgement.
The findings underline the importance of bridging cognitive science and AI research to foster more adaptable, trustworthy, and human-aligned AI systems capable of tackling complex, real-world challenges.
Would you like to learn more about AI, tech and digital diplomacy? If so, ask our Diplo chatbot!
AI Research
Josh Bersin Company Research Reveals How Talent Acquisition Is Being Revolutionized by AI

-
Jobs aren’t disappearing. Through AI, talent acquisition is fast evolving from hand-crafted interviewing and recruiting to a data-driven model that ensures the right talent is hired at the right time, for the right role with unmatched accuracy
-
Traditional recruiting isn’t working: in 2024, only 17% of applicants received interviews and 60% abandoned slow application processes
-
AI drives 2–3x faster hiring, stronger candidate quality, sharper targeting—and 95% candidate satisfaction at Foundever, from 200,000+ applicants in just six months
OAKLAND, Calif., Sept. 16, 2025 /PRNewswire/ — The Josh Bersin Company, the world’s most trusted HR advisory firm, today released new research showing that jobs aren’t disappearing—they’re being matched with greater intelligence. The research, produced in collaboration with AMS, reveals major advances in talent acquisition (TA) driven by AI-enabled technology, which are yielding 2–3x faster time to hire, stronger candidate-role matches, and unprecedented precision in sourcing.
The global market for recruiting, hiring, and staffing is over $850 billion and is growing at 13% per year, despite the economic slowdown, though signs of strain are evident. This means TA leaders are turning to AI to adapt, as AI transforms jobs, creates the need for new roles, new skills, and AI expertise.
According to the research and advisory firm, even without AI disruption, over 20% of employees consider changing jobs each year, driving demand for a new wave of high-precision, AI-powered tools for assessment, interviewing, selection, and hiring. Companies joining this AI revolution are hiring 200-300% faster, with greater accuracy and efficiency than their peers, despite the job market slowdown.
According to the report, The Talent Acquisition Revolution: How AI is Transforming Recruiting, the TA automation revolution is delivering benefits across the hiring ecosystem: job seekers experience faster recognition and better fit, while employers gain accurate, real-time, and highly scalable recruitment.
This is against a context of failure with current hiring. In 2024, less than one in four (17%) of applicants made it to the interview stage, and 60% of job seekers, due to too-slow hiring portals, abandoned the whole application process.
The research shows how organizations are already realizing benefits such as lower hiring costs, stronger internal mobility, and higher productivity. AI-empowered TA teams are also streamlining operations by shifting large portions of manual, admin-heavy work to specialized vendors.
AI Research
Causaly Introduces First Agentic AI Platform Built for Life Sciences Research and Development
Specialized AI agents automate research workflows and accelerate
drug discovery and development with transparent, evidence-backed insights
LONDON, Sept. 16, 2025 /PRNewswire/ — Causaly today introduced Causaly Agentic Research, an agentic AI breakthrough that delivers the transparency and scientific rigor that life sciences research and development demands. First-of-their-kind, specialized AI agents access, analyze, and synthesize comprehensive internal and external biomedical knowledge and competitive intelligence. Scientists can now automate complex tasks and workflows to scale R&D operations, discover novel insights, and drive faster decisions with confidence, precision, and clarity.
Industry-specific scientific AI agents
Causaly Agentic Research builds on Causaly Deep Research with a conversational interface that lets users interact directly with Causaly AI research agents. Unlike legacy literature review tools and general-purpose AI tools, Causaly Agentic Research uses industry-specific AI agents built for life sciences R&D and securely combines internal and external data to create a single source of truth for research. Causaly AI agents complete multi-step tasks across drug discovery and development, from generating and testing hypotheses to producing structured, transparent results always backed by evidence.
“Agentic AI fundamentally changes how life sciences conducts research,” said Yiannis Kiachopoulos, co-founder and CEO of Causaly. “Causaly Agentic Research emulates the scientific process, automatically analyzing data, finding biological relationships, and reasoning through problems. AI agents work like digital assistants, eliminating manual tasks and dependencies on other teams, so scientists can access more diverse evidence sources, de-risk decision-making, and focus on higher-value work.”
Solving critical research challenges
Research and development teams need access to vast amounts of biomedical data, but manual and siloed processes slow research and create long cycle times for getting treatments to market. Scientists spend weeks analyzing narrow slices of data while critical insights remain hidden. Human biases influence decisions, and the volume of scientific information overwhelms traditional research approaches.
Causaly addresses these challenges as the first agentic AI platform for scientists that combines extensive biomedical information with competitive intelligence and proprietary datasets. With a single, intelligent interface for scientific discovery that fits within scientists’ existing workflows, research and development teams can eliminate silos, improve productivity, and accelerate scientific ideas to market.
Comprehensive agentic AI research platform
As part of the Causaly platform, Causaly Agentic Research provides scientists multiple AI agents that collaborate to:
- Conduct complex analysis and provide answers that move research forward
- Verify quality and accuracy to dramatically reduce time-to-discovery
- Continuously scan the scientific landscape to surface critical signals and emerging evidence in real time
- Deliver fully traceable insights that help teams make confident, evidence-backed decisions while maintaining scientific rigor for regulatory approval
- Connect seamlessly with internal systems, public applications, data sources, and even other AI agents, unifying scientific discovery
Availability
Causaly Agentic Research will be available in October 2025, with a conversational interface and foundational AI agents to accelerate drug discovery and development. Additional specialized AI agents are planned for availability by the end of the year.
Explore how Causaly Agentic Research can redefine your R&D workflows and bring the future of drug development to your organization at causaly.com/products/agentic-research.
About Causaly
Causaly is a leader in AI for the life sciences industry. Leading biopharmaceutical companies use the Causaly AI platform to find, visualize, and interpret biomedical knowledge and automate critical research workflows. To learn how Causaly is accelerating drug discovery through transformative AI technologies and getting critical treatments to patients faster, visit www.causaly.com.
Logo – https://mma.prnewswire.com/media/2653240/Causaly_Logo_Logo.jpg

-

 Business3 weeks ago
Business3 weeks agoThe Guardian view on Trump and the Fed: independence is no substitute for accountability | Editorial
-
Tools & Platforms1 month ago
Building Trust in Military AI Starts with Opening the Black Box – War on the Rocks
-

 Ethics & Policy2 months ago
Ethics & Policy2 months agoSDAIA Supports Saudi Arabia’s Leadership in Shaping Global AI Ethics, Policy, and Research – وكالة الأنباء السعودية
-

 Events & Conferences4 months ago
Events & Conferences4 months agoJourney to 1000 models: Scaling Instagram’s recommendation system
-

 Jobs & Careers3 months ago
Jobs & Careers3 months agoMumbai-based Perplexity Alternative Has 60k+ Users Without Funding
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoHappy 4th of July! 🎆 Made with Veo 3 in Gemini
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoVEX Robotics launches AI-powered classroom robotics system
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoMacron says UK and France have duty to tackle illegal migration ‘with humanity, solidarity and firmness’ – UK politics live | Politics
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoOpenAI 🤝 @teamganassi
-

 Funding & Business3 months ago
Funding & Business3 months agoKayak and Expedia race to build AI travel agents that turn social posts into itineraries