AI Research
Zuckerberg Was Wrong About the Metaverse. Can We Really Trust Him With Superintelligent AI?

Mark Zuckerberg once sold us the metaverse. Now he wants us to believe he’s going to lead us into the age of superintelligence. Should we fall for it again?
Elon Musk once called him “Zuck the Fourteenth,” a jab comparing Meta’s CEO to France’s King Louis XIV—a monarch infamous for his ego, extravagance, and disregard for limits. It’s a fitting label, especially as Zuckerberg floods the headlines, positioning himself as Silicon Valley’s new AI king.
But let’s rewind.
Just a few years ago, Zuckerberg declared that the metaverse was the future of humanity. In a slickly produced video released on October 28, 2021, he rebranded Facebook as Meta Platforms and declared, “The metaverse is the next frontier.” It was a bold new vision: a 3D immersive virtual world where we would live, work, and socialize as digital avatars using Meta-manufactured VR headsets and smart glasses.
Meta poured nearly $20 billion into Reality Labs, the division tasked with building this digital utopia, in a single year. The promise? A seamless escape from the real world into a vibrant virtual one.
But the promised land never arrived. Despite the investment, the user adoption didn’t follow. Horizon Worlds, Meta’s flagship metaverse platform, struggled to retain interest. The headsets were clunky, the software buggy, and the use cases unclear. People didn’t want to live in VR. The metaverse flopped.
Now, Zuckerberg wants the public, and the tech world, to believe he’s leading the charge into the next big thing: artificial general intelligence, or AGI. This is the holy grail of AI. A moment when machines surpass human intelligence across nearly all tasks. It’s what some call superintelligence, and it’s no longer just science fiction.
But there’s a problem. Meta is not leading. OpenAI, Google’s Gemini, and China’s DeepSeek have pulled ahead with more advanced models and tools. Meta’s LLaMA models are competent, but not groundbreaking. The company’s biggest claim to fame in the AI arms race so far? Making its large language models open source.
Now Zuckerberg is trying to change that by opening his wallet.
In what’s becoming an aggressive poaching campaign, Meta has started offering “giant offers” to top AI researchers. According to OpenAI CEO Sam Altman, some of these offers exceed $100 million. Meta has already lured away key talent, including Alexandr Wang (founder of Scale AI), Nat Friedman (former GitHub CEO), and OpenAI veterans like Shengjia Zhao, Shuchao Bi, Jiahui Yu, and Hongyu Ren.
Zuckerberg isn’t hiding it. He recently announced the creation of Meta Superintelligence Labs, an ambitious effort to consolidate AI efforts under one roof and leapfrog the competition. In his internal memo, he promised that Meta will lead the way in delivering personal superintelligence, an AI that can manage your life, schedule your time, guide your decisions, and essentially act as a personal brain assistant.
And he’s made it clear: he’s not done hiring.
It’s a dramatic pivot and a savvy one. AI is no longer hype. It’s here, and it’s transforming everything from how we work to how we think. Whether you fear it or embrace it, AI is shaping the next phase of human life.
But that doesn’t mean Zuckerberg gets to be its face.
After all, this is the same executive who once told the world that a legless cartoon avatar in VR was our future. The same person who sank tens of billions into a virtual world that no one wanted. Now he’s asking us to trust him on AGI, a technology that could reshape the world, economies, and the future of human labor.
Zuckerberg isn’t an AI visionary. He’s a ruthless competitor who spots the next big thing and tries to buy his way to the top. He couldn’t beat TikTok, so he cloned Reels. He couldn’t acquire Snapchat, so he copied Stories. Now he’s applying the same playbook to AI: buy the best people, sell a big vision, and hope the world forgets what happened last time.
If anything, his pivot to AI is proof of just how serious this moment is. Because when Zuckerberg starts spending, it’s not out of curiosity. It’s because he smells dominance.
And that might be the most compelling reason to pay attention.
Not because he’s leading the way in building artificial superintelligence, but because he’s trying to control who gets to build it, and what rules they play by.
AI Research
AARP warns of “Grandparent Scams”
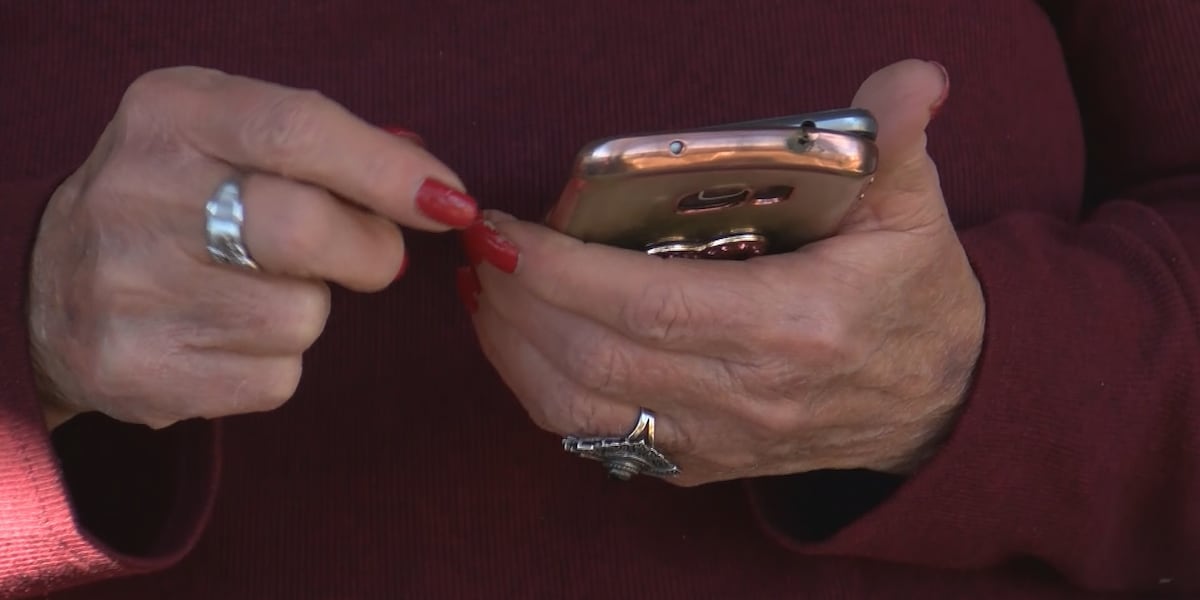

MONTGOMERY, Ala. (WSFA) – While artificial intelligence is rapidly transforming our world, a troubling trend shows scammers using it to steal from seniors, specifically grandparents.
You’ve probably heard the phrase ‘seeing is believing’ your whole life. But in an age of artificial intelligence, the turn of phrase doesn’t exactly stand the test of time. When it’s in the wrong hands, this new technology can make our senior citizens, who didn’t grow up in the digital age, a vulnerable population.
“One of the ways we see that being done is with what’s known as the grandparent scam,” Jamie Harding, AARP of Alabama Communications director, said. “The grandparent scam is basically, it usually happens late at night, they’re asleep, and someone calls them purporting to be their grandchild, they’re in trouble, they need money immediately.”
However, it isn’t actually their grandchild on the other end of the phone. Scammers have used AI technology to replicate the sound of their grandchild’s voice to try to take money.
“These are very sophisticated international crime rings, and they have access to a lot of very sophisticated technology,” Harding said.
To protect your family from these scams, Harding suggests having a code word that every member of your family knows so you can be sure it’s actually your loved one calling.
She also advises you not to answer phone calls from unknown numbers and to keep your personal information off the internet.
Not reading this story on the WSFA News App? Get news alerts FASTER and FREE in the Apple App Store and the Google Play Store!
Copyright 2025 WSFA. All rights reserved.
AI Research
Inside Austin’s Gauntlet AI, the Elite Bootcamp Forging “AI First” Builders
AUSTIN, Texas — In the brave new world of artificial intelligence, talent is the new gold, and companies are in a frantic race to find it. While universities work to churn out computer science graduates, a new kind of school has emerged in Austin to meet the insatiable demand: Gauntlet AI.
Gauntlet AI bills itself as an elite training program. It’s a high-stakes, high-reward process designed to forge “AI-first” engineers and builders in a matter of weeks.
“We’re closer to Navy SEAL bootcamp training than a school,” said Ash Tilawat, Head of Product and Learning. “We take the smartest people in the world. We bring them into the same place for a 1000 hours over ten weeks and we make them go all in with building with AI.”
Austen Allred, the co-founder and CEO of Gauntlet AI, says when they claim to be looking for the smartest engineers in the world, it’s no exaggeration. The selection process is intensely rigorous.
“We accept around 2 percent of the applicants,” Allred explained. “We accept 98th percentile and above of raw intelligence, 95th percentile of coding ability, and then you start on The Gauntlet.”
ALSO| The 60-Second Guardian: Can a Swarm of Drones Stop a School Shooter?
The price of admission isn’t paid in dollars—there are no tuition fees. Instead, the cost is a student’s absolute, undivided attention.
“It is pretty grueling, but it’s invigorating and I love doing this,” said Nataly Smith, one of the “Gauntlet Challengers.”
Smith, whose passions lie in biotech and space, recently channeled her love for bioscience to complete one of the program’s challenges. Her team was tasked with building a project called “Geno.”
“It’s a tool where a person can upload their genomic data and get a statistical analysis of how likely they are to have different kinds of cancers,” Smith described.
Incredibly, her team built the AI-powered tool in just one week.
The ultimate prize waiting at the end of the grueling 10-week gauntlet is a guaranteed job offer with a starting salary of at least $200,000 a year. And hiring partners are already lining up to recruit challengers like Nataly.
“We very intentionally chose to partner with everything from seed-stage startups all the way to publicly traded companies,” said Brett Johnson, Gauntlet’s COO. “So Carvana is a hiring partner. Here in Austin, we have folks like Function Health. We have the Trilogy organization; we have Capital Factory just around the corner. We’re big into the Austin tech community and looking to double down on that.”
In a world desperate for skilled engineers, Gauntlet AI isn’t just training people; it’s manufacturing the very talent pipeline it believes will power the next wave of technological innovation.
AI Research
Endangered languages AI tools developed by UH researchers

University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa researchers have made a significant advance in studying how artificial intelligence (AI) understands endangered languages. This research could help communities document and maintain their languages, support language learning and make technology more accessible to speakers of minority languages.
The paper by Kaiying Lin, a PhD graduate in linguistics from UH Mānoa, and Department of Information and Computer Sciences Assistant Professor Haopeng Zhang, introduces the first benchmark for evaluating large language models (AI systems that process and generate text) on low-resource Austronesian languages. The study focuses on three Formosan (Indigenous peoples and languages of Taiwan) languages spoken in Taiwan—Atayal, Amis and Paiwan—that are at risk of disappearing.
Using a new benchmark called FORMOSANBENCH, Lin and Zhang tested AI systems on tasks such as machine translation, automatic speech recognition and text summarization. The findings revealed a large gap between AI performance in widely spoken languages such as English, and these smaller, endangered languages. Even when AI models were given examples or fine-tuned with extra data, they struggled to perform well.
“These results show that current AI systems are not yet capable of supporting low-resource languages,” Lin said.
Zhang added, “By highlighting these gaps, we hope to guide future development toward more inclusive technology that can help preserve endangered languages.”
The research team has made all datasets and code publicly available to encourage further work in this area. The preprint of the study is available online, and the study has been accepted into the 2025 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing in Suzhou, China, an internationally recognized premier AI conference.
The Department of Information and Computer Sciences is housed in UH Mānoa’s College of Natural Sciences, and the Department of Linguistics is housed in UH Mānoa’s College of Arts, Languages & Letters.
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoThe Guardian view on Trump and the Fed: independence is no substitute for accountability | Editorial
-
Tools & Platforms4 weeks ago
Building Trust in Military AI Starts with Opening the Black Box – War on the Rocks
-

 Ethics & Policy1 month ago
Ethics & Policy1 month agoSDAIA Supports Saudi Arabia’s Leadership in Shaping Global AI Ethics, Policy, and Research – وكالة الأنباء السعودية
-

 Events & Conferences4 months ago
Events & Conferences4 months agoJourney to 1000 models: Scaling Instagram’s recommendation system
-

 Jobs & Careers2 months ago
Jobs & Careers2 months agoMumbai-based Perplexity Alternative Has 60k+ Users Without Funding
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoVEX Robotics launches AI-powered classroom robotics system
-

 Funding & Business2 months ago
Funding & Business2 months agoKayak and Expedia race to build AI travel agents that turn social posts into itineraries
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoHappy 4th of July! 🎆 Made with Veo 3 in Gemini
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoMacron says UK and France have duty to tackle illegal migration ‘with humanity, solidarity and firmness’ – UK politics live | Politics
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoOpenAI 🤝 @teamganassi





















