What is AI automation, and how can your business use it?
Automation used to be the best way to make software do the work and free up time for more important things. And while AI has since come on the scene, it hasn’t replaced automation—it’s made it better.
Here, Zapier explains what AI automation actually is, why it’s useful, and how you can start using it to offload all the worst parts of your job, so you can focus on the human stuff.
What is AI automation?
AI automation (sometimes referred to as intelligent automation) combines automation technologies with artificial intelligence (AI) to create systems that tackle complex work by learning, adapting, and making smart decisions. These systems can practically think on their feet, analyzing information, learning from experience, and constantly getting better at what they do.
People are also reading…
For your business, this means tackling more complex projects with automation and making your workflows dramatically more efficient and largely self-sufficient.
Benefits of AI automation
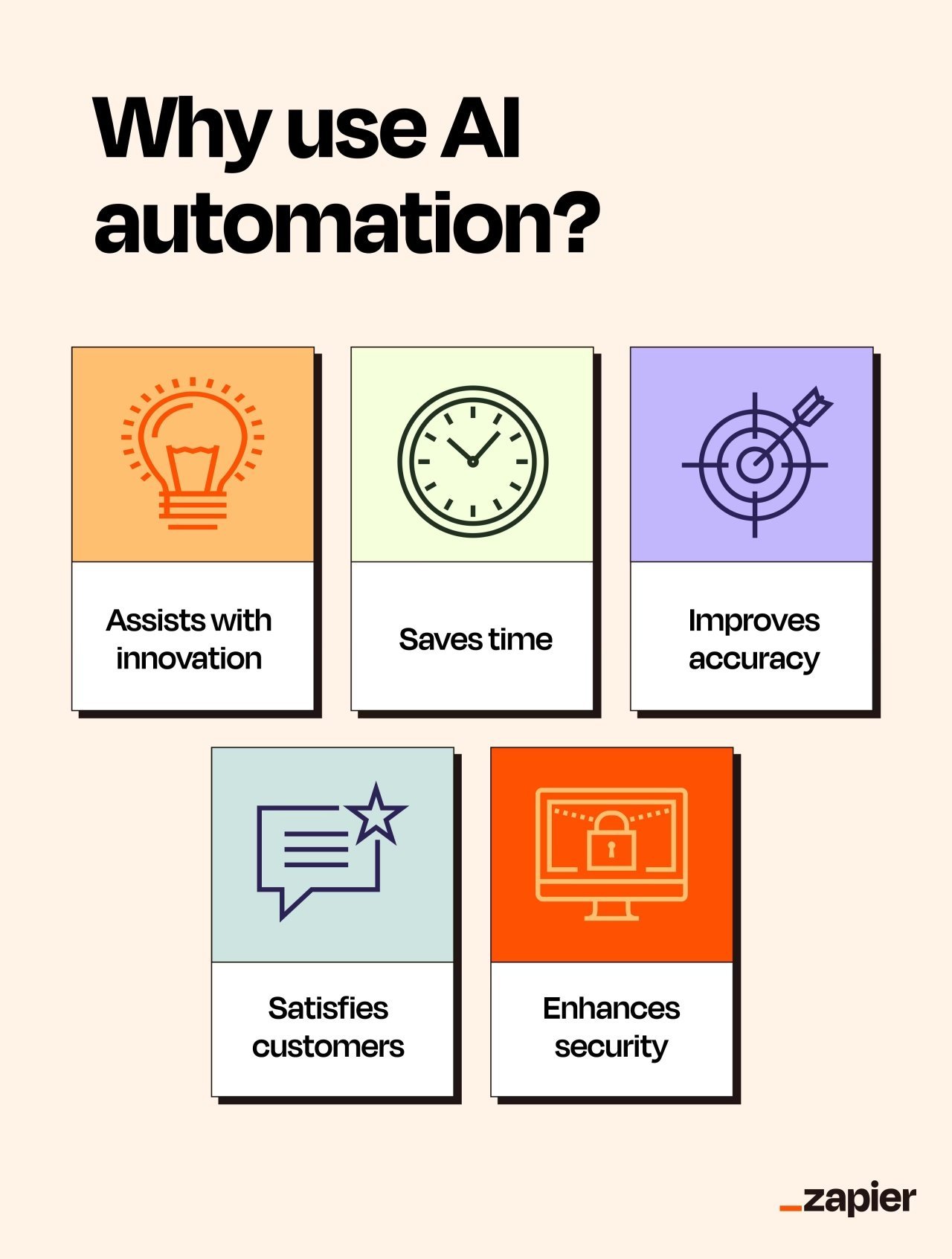
You’re probably already envisioning all the ways AI automation could make your life easier. Here are some key reasons to implement it.
- Saves employee time and energy: Automation alone is enough to turn an otherwise seven-hour manual task into a five-minute one. But an automation tool that can also collect new data, learn from it, and handle complex decision-making? That can expedite processes exponentially, allowing your employees to prioritize higher-value tasks that are more deserving of their energy and attention.
- Reduces the likelihood of errors: When programmed correctly, robots can be far more accurate than humans (sorry, humans). People don’t follow structured algorithms to the T quite like automated tools, and AI can analyze huge amounts of data to inform decisions.
- Identifies opportunities: When you integrate AI tools into your existing workflows, they can use your data to flag blind spots and possibilities for your business.
- Improves customer satisfaction: The more streamlined and intelligent your process of delivering your products or services, the happier your customers will be. Plus, imagine chatbots actually understanding your customers’ needs, surfacing relevant answers and resources, and knowing when it’s time to connect them to a human representative. A dream come true.
- Helps identify and patch security vulnerabilities: When allocated enough processing power, AI automation is a speedy process. It can scan your software, surface potential security risks, and even correct those vulnerabilities far faster and more accurately than a human could.
- Increases organizational agility: AI automation helps your business keep up with zig-zagging market trends without missing a beat. It can quickly spot changes in customer behavior or supply chain hiccups, then help adjust your operations on the fly.
- Drives innovation: AI automation is a powerful R&D assistant. It can crunch vast datasets for that aha insight, prototype a web app for a partner, or rapidly test new product features while your team dreams up the next big thing. It’s about turning those “what if” moments into “what’s next” realities faster.
Key components and technologies that AI automation uses
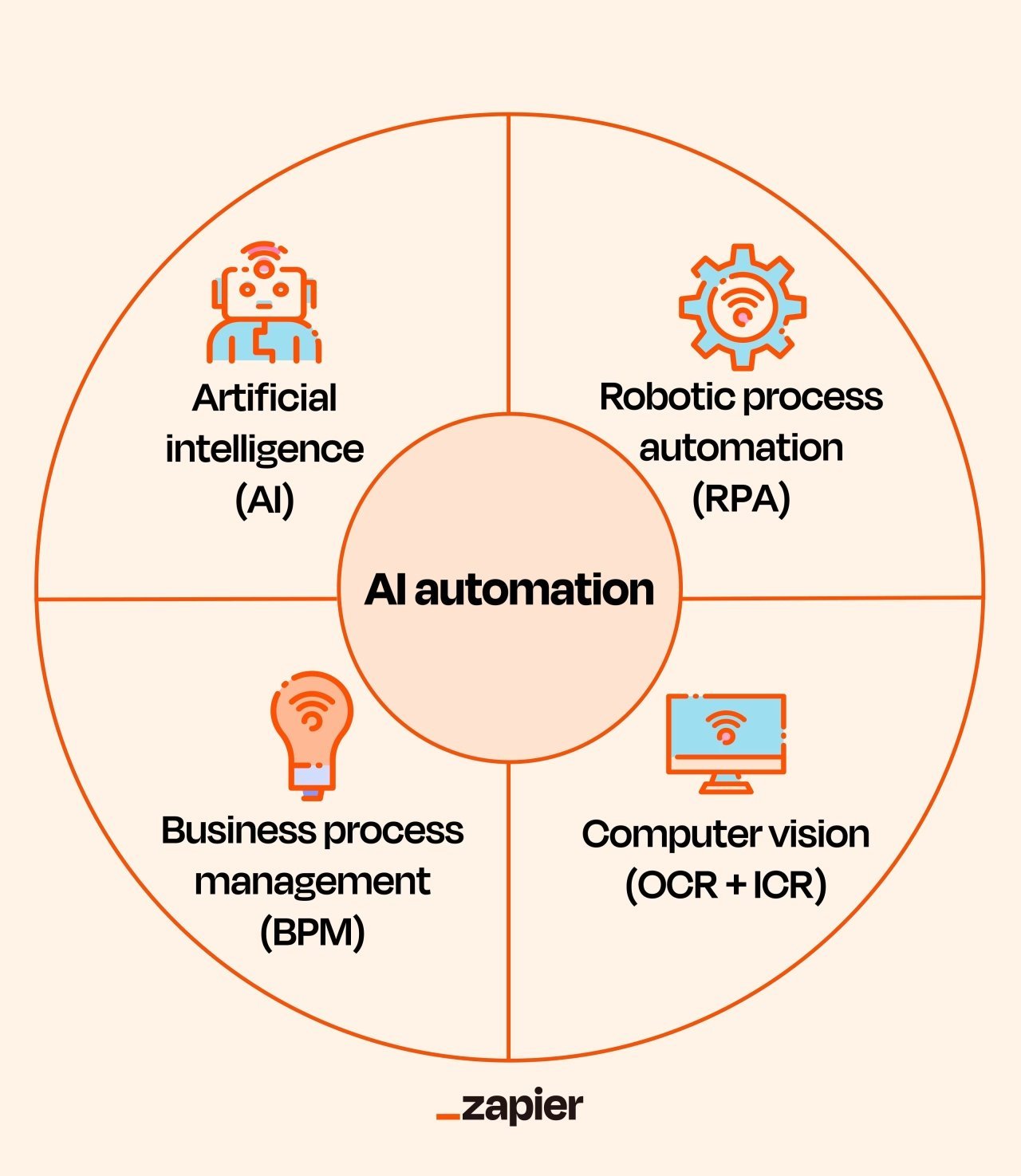
To really get a handle on AI automation, it helps to know the key technologies that work behind the scenes. We’re talking about everything from the workhorses that automate routine tasks to the brains that understand language, interpret images, and even think up new content. Here’s a rundown of some of the essential tools and technologies that power AI automation.
Robotic process automation (RPA)
RPA bots can quickly accomplish repetitive, routine tasks, such as data extraction and transfers, to save you time. These bots follow predefined scripts to do things like fill out forms, shuttle data between spreadsheets and CRMs, process payroll, or generate routine reports. In AI automation, RPA often lays the groundwork by tackling these high-volume, predictable tasks, freeing up the more advanced AI components to focus on complex decision-making and learning.
AI is software that mimics human thinking, and you may have noticed, it’s been getting pretty good at it in recent years. It can learn from previous choices, quickly analyze data to make accurate predictions, and make quick decisions. While many technologies on this list are specific parts of AI, its overarching role in AI automation is to imbue automated processes with these cognitive capabilities. This means these systems can, for example, intelligently route customer support tickets based on their actual content and urgency, dynamically optimize supply chain logistics as conditions change, or provide remarkably accurate sales forecasts by analyzing complex datasets.
Machine learning and deep learning
Machine learning (ML) is a core type of AI that allows systems to learn directly from data, spotting patterns, making predictions, and improving their performance over time without being explicitly programmed for every variation.
Deep learning takes this a step further as an advanced subset of ML, using complex “neural network” structures to decipher highly intricate patterns in massive datasets. These learning capabilities are crucial for AI automation, enabling systems to adapt and get smarter.
Natural language processing (NLP)
Natural language processing is the AI that makes it possible for computers to understand, interpret, and even generate human language, whether it’s written text or spoken words. This is vital for intelligent automation because so much business information is unstructured language.
Thanks to NLP, AI automation systems can engage in (mostly) sensible chatbot conversations with customers, automatically analyze thousands of reviews to gauge overall sentiment, instantly translate documents, or transcribe meeting notes into text, making sense of our primary mode of communication.
Generative AI is a particularly exciting frontier of artificial intelligence, where models don’t just analyze existing information but actually create entirely new, original content. By learning deep patterns from vast datasets, these types of systems can produce novel text, images, audio, software code, and more.
In the realm of AI automation, this opens up powerful possibilities for automating creative and content-heavy tasks. For instance, generative AI can draft initial marketing copy or email campaigns, design unique visuals based on text prompts, compose original music tracks, or even generate segments of code to speed up software development.
Computer vision lets software interpret and understand visual information from images and videos. While a common application in business automation is optical character recognition (OCR), which “reads” text from scanned documents or images and converts it to digital data, the field is actually much more exciting.
Computer vision allows systems to identify objects, recognize patterns, and analyze scenes. In AI automation, this capability means processes can react to visual inputs, automating tasks that previously needed human sight. For example, systems can use computer vision to inspect manufactured goods for quality control, monitor security footage for specific events, assist in analyzing medical scans for anomalies, or identify products and shelving in retail environments.
Intelligent document processing (IDP)
Intelligent document processing technology is designed to tackle the challenge of handling huge volumes of documents by doing much more than just basic text extraction. While it builds on capabilities from computer vision, like OCR, IDP is a distinct solution because it adds a significant layer of artificial intelligence.
Using AI techniques such as machine learning and natural language processing, IDP doesn’t just “read” documents; it aims to understand them. This means it can automatically classify different document types (like an invoice versus a purchase order), intelligently extract specific pieces of information (like names, dates, amounts, or even complex clauses from contracts), validate that data, and then feed it into other business applications.
For example, businesses use IDP to automate their accounts payable by extracting details from supplier invoices and inputting them into accounting systems to speed up insurance claims processing. They do this by accurately pulling information from various claim forms, or to improve customer onboarding by quickly processing application forms and verifying ID documents.
Business process management (BPM)
BPM streamlines workflows to improve company efficiency. It’s a structured way of looking at your end-to-end workflows, finding the kinks, and redesigning them for better results. AI automation often comes into the picture through BPM strategies like process mining.
Process mining uses specialized software to analyze your existing processes as they actually happen, creating a clear map that helps diagnose where things are getting stuck, where tasks are taking too long, or what’s ripe for an automation upgrade. Once these areas are identified, AI automation can then automate specific steps, inject smart decision-making into the flow, or help monitor the improved process, ultimately leading to more streamlined and effective operations, such as faster customer onboarding or more efficient supply chain management.
How to implement AI automation
Implementing intelligent automation isn’t a set-it-and-forget-it kind of deal. It’s something you’ll have to constantly monitor and adjust as your business and the tech itself grow. That said, here are a few key phases to guide you from an initial idea to a fully functioning smart workflow:
- Find: Think of this as the scouting mission. You’re looking for those processes that are a bit clunky, data-heavy, or involve tricky decisions that could really benefit from an AI boost. This might involve looking at common bottlenecks, listening to what your team says takes up too much time, or using tools like process mining to get a clear picture of where work gets stuck.
- Analyze: Once a process is selected for review, this is where you put it under the microscope. You’ll map out how it currently runs, identify precisely where it’s causing problems, and figure out if an AI automation solution makes solid business sense. This step is all about clear objectives and knowing what “better” actually looks like.
- Build: With your analysis done, the next step is designing and constructing your AI automation solution. This involves mapping out the smarter workflow and picking the right technologies. If you have the team, you might map out these core intelligent components in-house. Alternatively, for specialized expertise or faster implementation, you could turn to automation as a service (AaaS), where experts can construct and configure these sophisticated systems for you.
- Automate and integrate: This is the go-live stage where you bring your intelligent workflow to life. It’s where the theoretical design from the “Build” phase becomes a practical, automated reality that actively runs your business processes. Data will flow cleanly between your automation and core enterprise systems (like a central database or ERP) without causing chaos or data integrity issues.
- Optimize: Since AI models learn from data, their performance can degrade as the real world changes—a concept known as “model drift.” Optimizing an AI automation system means keeping the AI sharp by monitoring AI-specific metrics, like its confidence level in its own decisions, and periodically retraining it with fresh data. More importantly, it’s about refining the human-AI feedback loop: When a person corrects an AI’s mistake or handles an exception, that action should be used as new training data to make the model smarter for the next time. The goal isn’t just to keep the automation running; it’s to ensure it’s continuously improving its own intelligence.
Examples of AI automation processes
A lot of technical jargon has been thrown at you—here’s how to practically apply it in a business setting.
- Write emails: Sure, your email app can help you draft a reply, but AI automation can help you simplify the entire process around that email. Instead of just writing, AI can act as a central dispatcher for a shared inbox like support@ or sales@.
- Analyze leads: Let an AI do the prospecting work for you. When a new lead arrives, an AI agent can automatically investigate them online, visiting their company website to understand the business and finding their job title from public sources to see if they’re a good fit. The tool may deliver a rich summary of its findings right to your CRM, arming your sales team with the intel they need to focus on the best prospects first.
- Adjust production: AI automation can use data on supply and demand to reconfigure manufacturing equipment, programming it to produce more or less product, minimizing the likelihood of surpluses or shortages. Essentially, the smarter robots tell the automation robots what to do and when to do it.
- Predict maintenance: For businesses with heavy machinery—think factories or transport companies—AI automation can predict when equipment needs maintenance before it breaks down. Instead of just reacting to a system alert, the data can be fed to AI to analyze the signal, assess its severity against historical data, and even diagnose the probable cause. Based on the AI’s diagnosis, the workflow can then create a highly detailed work order in a maintenance platform, specifying the urgency and required parts, while simultaneously alerting the correct team via their preferred channel.
- Optimize supply chains: AI automation can make supply chains much smarter and more responsive. For instance, AI can analyze historical sales, current stock levels, and even external factors like shipping forecasts to help businesses make better decisions about ordering and inventory.
- A/B test: AI automation can compare side-by-side versions of assets, whether it be product prototypes or CTAs, and provide insight into which is more effective in a matter of seconds. It’s the type of tedious process AI was made to replace.
- Automate document processing: If your team is swamped with invoices, contracts, or forms, AI automation can automate much of that document handling. Tools leveraging AI can “read” these documents and extract key information like dates, amounts, or names, and then route that data exactly where it needs to go.
- Automate the path from vibe to production code: A nontechnical team member can submit their AI-generated prototype code through a simple form. A business automation tool could then trigger an AI step to perform an initial code review, automatically checking for common issues or bugs. That AI analysis, along with the prototype code itself, could then be used to create a perfectly formatted, detailed ticket in your development team’s project management tool, bridging the gap from a creative “vibe” to a formal, reviewed development task.
- Automate content creation: You can integrate your favorite generative AI tools to draft initial marketing copy, outline articles, or even generate different versions of ad text based on your prompts—all within your existing workflow automations. It’s a great way to overcome writer’s block and speed up content production, leaving you to refine and add the final human touch.
What’s the difference between AI automation and RPA?
Simply put, RPA is a less intelligent AI automation. RPA replaces manual and repetitive work using automation tools like bots. AI automation introduces cognitive technologies like AI and computer vision into the mix to automate processes that formerly required human thought.
For example, a bot that automatically categorizes users in a CRM based on how they subscribed to a newsletter is a form of RPA. AI automation might involve using subscriber interaction data (clicks, bounce rate, etc.) to add suggestions to a company’s CRM, informing future newsletter content.
How to kickstart your AI automation strategy
Intelligent automation can completely revolutionize your organization’s processes, so it’s important to be strategic when implementing it. Don’t pull the rug out from under your employees without developing a game plan.
- Get buy-in from top management: Don’t just bullet out the generic ways AI automation is helpful—explain how your organization can uniquely apply it to improve efficiency and see tangible ROI.
- Start slow: Once implementation becomes viable, don’t throw AI automation at everything all at once—take baby steps. Prioritize automating the most time-consuming tasks at your organization before moving into the “it would be nice…” category.
- Focus on data governance and quality: Remember the old saying, “garbage in, garbage out?” It’s especially true for AI automation, as your AI systems are only as good as the data they’re fed. Establish solid data governance practices to ensure your data is accurate, consistent, secure, and handled ethically.
- Develop an automation-first mindset: Before assigning a person to a specific task or project, ask if it can be completed (and especially if it can be completed better) by AI automation. As AI continues to advance with every passing day, you’ll likely find that there are more and more ways AI automation can make your life easier and your organization more profitable.
- Address ethical considerations: AI automation is powerful stuff, and like any new powerful tech, it comes with its own set of ethical questions. Think about things like potential bias in AI decision-making, how customer data is being used, and being transparent about how these systems work. It’s smart to consider these aspects upfront to build and use AI automation responsibly.
- Plan for workforce upskilling: As AI automation takes on more tasks, the roles and skills your team needs will likely evolve. Plan ahead to help your employees learn how to work alongside these new AI tools and automated processes. Offering training and development opportunities not only helps your team adapt but also ensures you get the most value out of your AI automation investments.
- Implement learnings: At times, AI automation implementation won’t go as planned. That’s fine, but try to avoid making the same mistakes twice by documenting your learnings and applying them.
AI automation is no longer just a futuristic buzzword; it’s a practical set of tools and strategies you can use today to make your business more efficient, responsive, and innovative.
This story was produced by Zapier and reviewed and distributed by Stacker.