Jobs & Careers
Esri India, Dhruva Space Partner to Expand Satellite Data Access

Sanjana Gupta
An information designer by training, Sanjana likes to delve into deep tech and enjoys learning about quantum, space, robotics and chips that build up our world. Outside of work, she likes to spend her time with books, especially those that explore the absurd.
Jobs & Careers
12 Essential Lessons for Building AI Agents
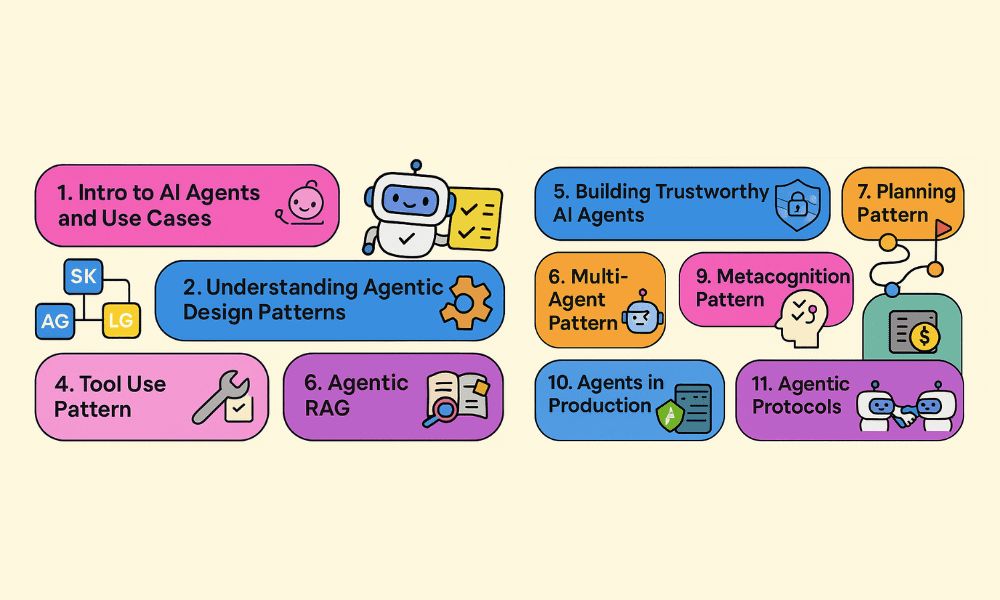
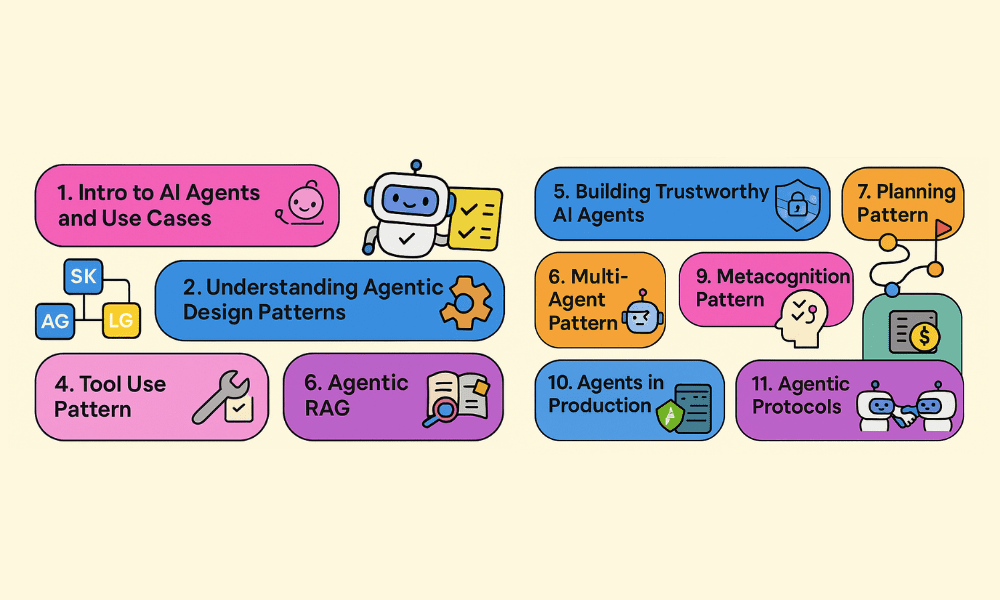
Image by Author | Canva & ChatGPT
# Introduction
GitHub has become the go-to platform for beginners eager to learn new programming languages, concepts, and skills. With the growing interest in agentic AI, the platform is increasingly showcasing real projects that focus on “agentic workflows,” making it an ideal environment to learn and build.
One notable resource is microsoft/ai-agents-for-beginners, which features a 12-lesson course covering the fundamentals of building AI agents. Each lesson is designed to stand on its own, allowing you to start at any point that suits your needs. This repository also offers multi-language support, ensuring broader accessibility for learners. Each lesson in this course includes code examples, which can be found in the code_samples folder.
Moreover, this course uses Azure AI Foundry and GitHub Model Catalogs for interacting with language models. It also incorporates several AI agent frameworks and services like Azure AI Agent Service, Semantic Kernel, and AutoGen.
To facilitate your decision-making process and provide a clear overview of what you will learn, we will review each lesson in detail. This guide serves as a helpful resource for beginners who might feel uncertain about choosing a starting point.
# 1. Intro to AI Agents and Agent Use Cases
This lesson introduces AI agents — systems powered by large language models (LLMs) that sense their environment, reason over tools and knowledge, and act — and surveys key agent types (simple/model-based reflex, goal/utility-based, learning, hierarchical, and multi-agent systems (MAS)) through travel-booking examples.
You will learn when to apply agents to open-ended, multi-step, and improvable tasks, and the foundational building blocks of agentic solutions: defining tools, actions, and behaviors.
# 2. Exploring AI Agentic Frameworks
This lesson explores AI agent frameworks with pre-built components and abstractions that let you prototype, iterate, and deploy agents faster by standardizing common challenges and boosting scalability and developer efficiency.
You will compare Microsoft AutoGen, Semantic Kernel, and the managed Azure AI Agent Service, and learn when to integrate with your existing Azure ecosystem versus using standalone tools.
# 3. Understanding AI Agentic Design Patterns
This lesson introduces AI agentic design principles, a human-centric user experience (UX) approach for building customer-focused agent experiences amid the inherent ambiguity of generative AI.
You will learn what the principles are, practical guidelines for applying them, and examples of their use, with an emphasis on agents that broaden and scale human capacities, fill knowledge gaps, facilitate collaboration, and help people become better versions of themselves through supportive, goal-aligned interactions.
# 4. Tool Use Design Pattern
This lesson introduces the tool-use design pattern, which allows LLM-powered agents to have controlled access to external tools such as functions and APIs, enabling them to take actions beyond just generating text.
You will learn about key use cases, including dynamic data retrieval, code execution, workflow automation, customer support integrations, and content generation/editing. Additionally, the lesson will cover the essential building blocks of this design pattern, such as well-defined tool schemas, routing and selection logic, execution sandboxing, memory and observations, and error handling (including timeout and retry mechanisms).
# 5. Agentic RAG
This lesson explains agentic retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), a multi-step retrieval-and-reasoning approach driven by large language models (LLMs). In this approach, the model plans actions, alternates between tool/function calls and structured outputs, evaluates results, refines queries, and repeats the process until achieving a satisfactory answer. It often uses a maker-checker loop to enhance correctness and recover from malformed queries.
You will learn about the situations where agentic RAG excels, particularly in correctness-first scenarios and extended tool-integrated workflows, such as API calls. Additionally, you will discover how taking ownership of the reasoning process and using iterative loops can enhance reliability and outcomes.
# 6. Building Trustworthy AI Agents
This lesson teaches you how to build trustworthy AI agents by designing a robust system message framework (meta prompts, basic prompts, and iterative refinement), enforcing security and privacy best practices, and delivering a quality user experience.
You will learn to identify and mitigate risks, such as prompt/goal injection, unauthorized system access, service overloading, knowledge-base poisoning, and cascading errors.
# 7. Planning Design Pattern
This lesson focuses on planning design for AI agents. Start by defining a clear overall goal and establishing success criteria. Then, break down complex tasks into ordered and manageable subtasks.
Use structured output formats to ensure reliable, machine-readable responses, and implement event-driven orchestration to address dynamic tasks and unexpected inputs. Equip agents with the appropriate tools and guidelines for when and how to use them.
Continuously evaluate the outcomes of the subtasks, measure performance, and iterate to improve the final results.
# 8. Multi-Agent Design Pattern
This lesson explains the multi-agent design pattern, which involves coordinating multiple specialized agents to collaborate toward a shared goal. This approach is particularly effective for complex, cross-domain, or parallelizable tasks that benefit from the division of labor and coordinated handoffs.
In this lesson, you will learn about the core building blocks of this design pattern: an orchestrator/controller, role-defined agents, shared memory/state, communication protocols, and routing/hand-off strategies, including sequential, concurrent, and group chat patterns.
# 9. Metacognition Design Pattern
This lesson introduces metacognition, which can be understood as “thinking about thinking,” for AI agents. Metacognition allows these agents to monitor their own reasoning processes, explain their decisions, and adapt based on feedback and past experiences.
You will learn planning and evaluation techniques, such as reflection, critique, and maker-checker patterns. These methods promote self-correction, help identify errors, and prevent endless reasoning loops. Additionally, these techniques will enhance transparency, improve the quality of reasoning, and support better adaptation and perception.
# 10. AI Agents in Production
This lesson demonstrates how to transform “black box” agents into “glass box” systems by implementing robust observability and evaluation techniques. You will model runs as traces (representing end-to-end tasks) and spans (petitions for specific steps involving language models or tools) using platforms like Langfuse and Azure AI Foundry. This approach will enable you to perform debugging and root-cause analysis, manage latency and costs, and conduct trust, safety, and compliance audits.
You will learn what aspects to evaluate, such as output quality, safety, tool-call success, latency, and costs, and apply strategies to enhance performance and effectiveness.
# 11. Using Agentic Protocols
This lesson introduces agentic protocols that standardize the ways AI agents connect and collaborate. We will explore three key protocols:
Model Context Protocol (MCP), which provides consistent, client-server access to tools, resources, and prompts, functioning as a “universal adapter” for context and capabilities.
Agent-to-Agent Protocol (A2A), which ensures secure, interoperable communication and task delegation between agents, complementing the MCP.
Natural Language Web Protocol (NLWeb), which enables natural-language interfaces for websites, allowing agents to discover and interact with web content.
In this lesson, you will learn about the purpose and benefits of each protocol, how they enable large language models (LLMs) to communicate with tools and other agents, and where each fits into larger architectures.
# 12. Context Engineering for AI Agents
This lesson introduces context engineering, which is the disciplined practice of providing agents with the right information, in the right format, and at the right time. This approach enables them to plan their next steps effectively, moving beyond one-time prompt writing.
You will learn how context engineering differs from prompt engineering, as it involves ongoing, dynamic curation rather than static instructions. Additionally, you will understand why strategies such as writing, selecting, compressing, and isolating information are essential for reliability, especially given the limitations of constrained context windows.
# Final Thoughts
This GitHub course provides everything you need to start building AI agents. It includes comprehensive lessons, short videos, and runnable Python code. You can explore topics in any order and run samples using GitHub Models (available for free) or Azure AI Foundry.
Additionally, you will have the opportunity to work with Microsoft’s Azure AI Agent Service, Semantic Kernel, and AutoGen. This course is community-driven and open source; contributions are welcome, issues are encouraged, and it is licensed for you to fork and extend.
Abid Ali Awan (@1abidaliawan) is a certified data scientist professional who loves building machine learning models. Currently, he is focusing on content creation and writing technical blogs on machine learning and data science technologies. Abid holds a Master’s degree in technology management and a bachelor’s degree in telecommunication engineering. His vision is to build an AI product using a graph neural network for students struggling with mental illness.
Jobs & Careers
Uber Users Can Soon Book Electric Air Taxis Through the App

Uber is preparing to expand its travel options by adding air mobility services to its app, through a new partnership with Joby Aviation. The move follows Joby’s acquisition of Blade Air Mobility’s passenger business in August, paving the way for Blade flights to be integrated into Uber as soon as next year.
Blade claims that it has been a key player in short-distance air travel, flying more than 50,000 passengers in 2024 across routes in New York and Southern Europe. By combining this network with Uber’s global platform, the companies aim to deliver a seamless experience for customers looking to move quickly between airports, city centres and other high-traffic destinations.
Andrew Macdonald, president and COO of Uber, said in a statement that the deal builds on a long-standing belief at the company.
“Since Uber’s earliest days, we’ve believed in the power of advanced air mobility to deliver safe, quiet and sustainable transportation to cities around the world,” he said.
“By harnessing the scale of the Uber platform and partnering with Joby, we’re excited to bring to our customers the next generation of travel.”
Uber’s ties to the sector date back to 2019, when it began collaborating with Joby to shape urban air mobility. In 2021, Joby acquired Uber’s Elevate division, which helped create tools for market selection and multi-modal transport.
Joby now plans to use Blade’s infrastructure and decade of operational experience to accelerate the launch of its own electric air taxi service in global markets, including Dubai, New York, Los Angeles, the United Kingdom and Japan.
The integration of Blade now should set the stage for the eventual rollout of Joby’s own zero-emissions air taxi, designed to carry four passengers and a pilot at speeds of up to 200 miles per hour (321 kmph).
For Uber, the deal extends its multi-modal vision, placing helicopters and electric air taxis alongside cars, bikes and deliveries.
The post Uber Users Can Soon Book Electric Air Taxis Through the App appeared first on Analytics India Magazine.
Jobs & Careers
Madhya Pradesh Partners with Educational Institutions to Upskill Future Workforce
Madhya Pradesh has launched a collaboration with Rajiv Gandhi Proudyogiki Vishwavidyalaya (RGPV) and L&T EduTech to prepare engineering students for future jobs. The initiative, led by the Madhya Pradesh State Electronics Development Corporation (MPSEDC) under the science and technology department, will be funded by the state government.
The partnership will begin with two pilot courses—Python for Data Handling and Front-End UI/UX Development—for RGPV students from the fifth semester. About 100 students will join the first batch. The 75-hour modules include online content, expert-led sessions, project-based learning and virtual labs. Eligible students will receive e-certificates to improve employability.
“This collaboration is more than a programme, it is a model for how Madhya Pradesh is transforming its Tier-2 cities into centres of innovation and opportunity. Our students will not only find better jobs but will also have the skills to drive future industries,” Sanjay Dubey, IAS, additional chief secretary, science and technology department, said in a press release.
Rajeev Tripathi, vice-chancellor of RGPV, added that the focus is to bridge classroom learning with the practical requirements of industry. This initiative will help us nurture engineers who can adapt, innovate and lead in fast-changing technology landscapes.
“This partnership with the Madhya Pradesh government and RGPV demonstrates how industry-academia collaboration can create real impact for learners and employers alike,” Febin MF, head of L&T EduTech, said in the statement.
The programme is part of Madhya Pradesh’s broader strategy to align education with industry demand, as the state produces more than 50,000 engineering and technical graduates each year. According to the World Economic Forum, nearly 50% of India’s workforce will need reskilling by 2025, a challenge this initiative aims to address directly.
The government also plans to replicate this pilot in other universities across the state. The move aligns with the #Tier2MadhyaPradesh campaign, which highlights the rise of cities like Bhopal, Indore, Jabalpur and Gwalior as emerging hubs for technology and innovation.
The post Madhya Pradesh Partners with Educational Institutions to Upskill Future Workforce appeared first on Analytics India Magazine.
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoThe Guardian view on Trump and the Fed: independence is no substitute for accountability | Editorial
-
Tools & Platforms1 month ago
Building Trust in Military AI Starts with Opening the Black Box – War on the Rocks
-

 Ethics & Policy2 months ago
Ethics & Policy2 months agoSDAIA Supports Saudi Arabia’s Leadership in Shaping Global AI Ethics, Policy, and Research – وكالة الأنباء السعودية
-

 Events & Conferences4 months ago
Events & Conferences4 months agoJourney to 1000 models: Scaling Instagram’s recommendation system
-

 Jobs & Careers2 months ago
Jobs & Careers2 months agoMumbai-based Perplexity Alternative Has 60k+ Users Without Funding
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoHappy 4th of July! 🎆 Made with Veo 3 in Gemini
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoMacron says UK and France have duty to tackle illegal migration ‘with humanity, solidarity and firmness’ – UK politics live | Politics
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoVEX Robotics launches AI-powered classroom robotics system
-

 Funding & Business2 months ago
Funding & Business2 months agoKayak and Expedia race to build AI travel agents that turn social posts into itineraries
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoOpenAI 🤝 @teamganassi







