Ethics & Policy
From Waiting Tables To Building A $4 Trillion Giant: Meet Jensen Huang, The AI Billionaire Worth Rs 9.91 Lakh Crore, And 7 Other Tech Titans Shaping The Future | People
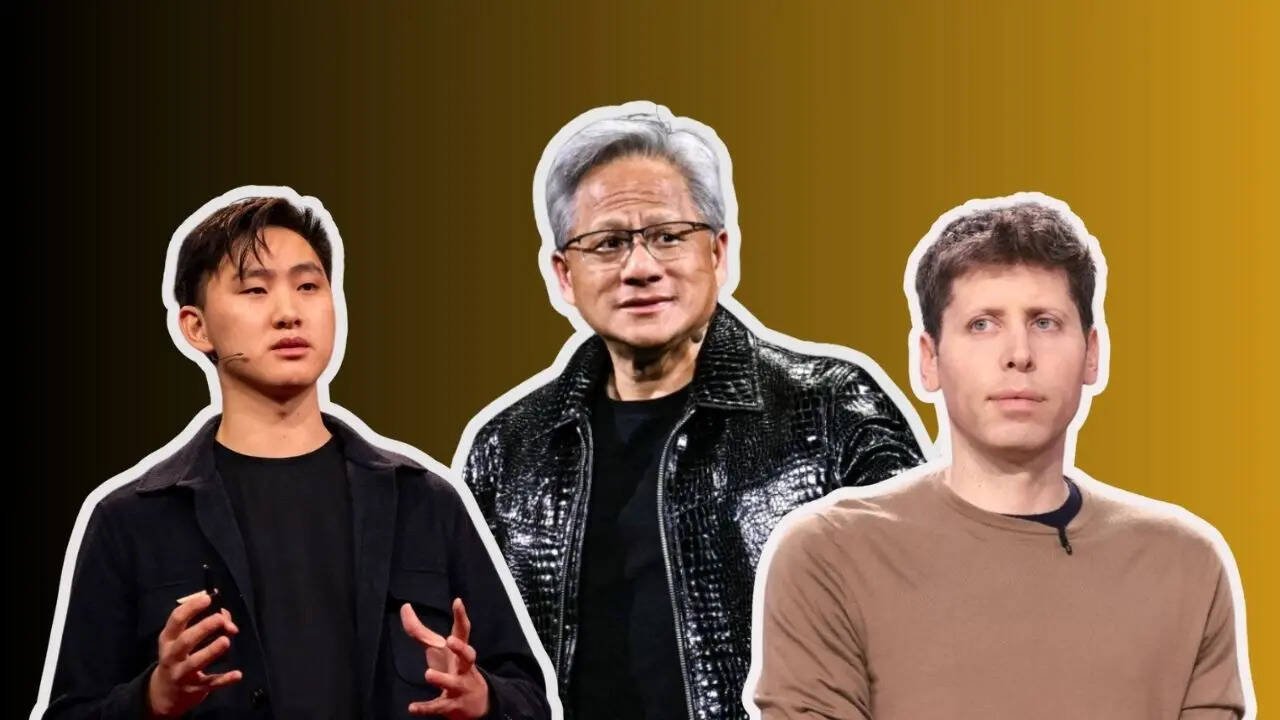

Top 7 Richest AI Billionaires in the World: The Incredible Stories Behind Fortune Makers Like Jensen Huang, Alexandr Wang, and Dario Amodei
Artificial Intelligence. Just two words, but together they’ve rewritten the script of modern life. It’s recommending what you binge-watch on a Friday night, helping doctors diagnose faster than ever, and even powering the apps that claim they’ll find you love. What was once science fiction is now the air we breathe. And along the way, it has quietly created a brand-new class of billionaires.
In the past, tech tycoons were the scrappy nerds building websites in dorm rooms or fiddling with wires in their garages. Today’s big players aren’t so different—except their playground is machine learning models and neural networks that fuel everything from self-driving cars to quirky dating apps.
Here’s where the story gets even more cinematic: the world’s richest AI billionaire—Jensen Huang of Nvidia—once waited tables. Yes, before reshaping computing as we know it, he was serving diners. Today, he commands a personal fortune of $113 billion (Rs 9.91 lakh crore). His rise sets the tone for this fascinating look at the seven names shaping the AI future—while laughing all the way to the bank.
Jensen Huang – From Balancing Plates to Powering the World

Net worth: $113 billion
Role: CEO and Co-Founder, Nvidia
Born in Taiwan, raised in the US, and once a restaurant waiter, Jensen Huang is living proof that humble beginnings can lead to Silicon Valley royalty. He co-founded Nvidia in 1993, initially focusing on graphics cards for gamers. Those very chips would later become the secret sauce powering AI models worldwide.
Today, Nvidia is valued at more than $4 trillion, fuelling everything from medical breakthroughs to language models. Huang’s trademark leather jacket has become nearly as iconic as the company’s bright green logo. Fun fact: he still owns about 3% of Nvidia, which is why his bank balance looks the way it does.
Alexandr Wang – The 26-Year-Old Wonderkid
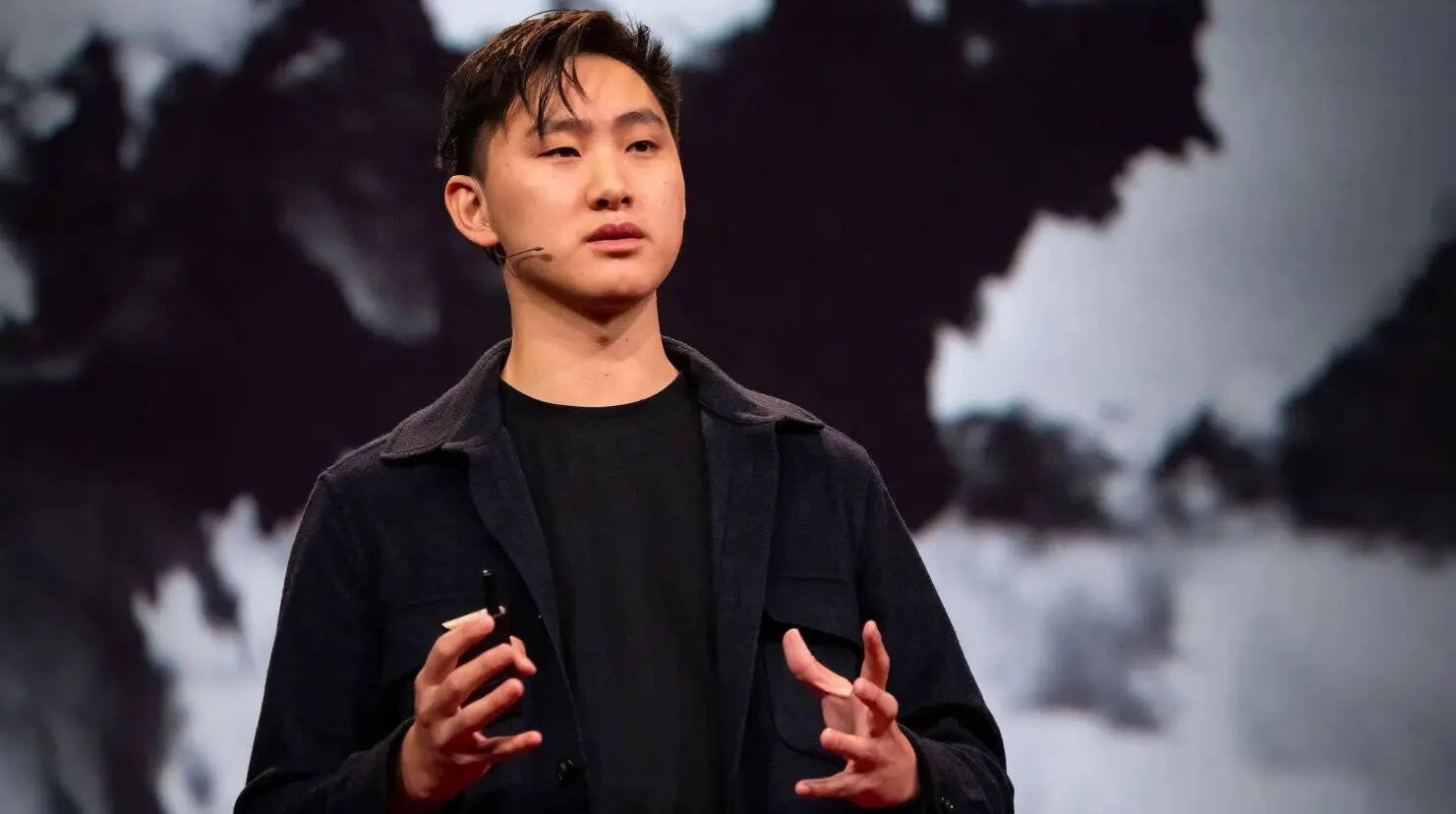

Net worth: $2.7 billion
Role: CEO and Co-Founder, Scale AI
Most people at 26 are still figuring life out. Alexandr Wang, on the other hand, has already figured out how to join the billionaire club. A college dropout from MIT, he founded Scale AI, a company that provides high-quality data—the essential fuel that powers AI models. Without it, even the smartest system is useless.
Valued at $14 billion, Scale AI works with giants like Meta and Google. Wang’s journey proves you don’t always have to build the flashiest AI engine; sometimes being the one supplying the “oil” for the race is enough.
Sam Altman – The Poster Boy of Generative AI
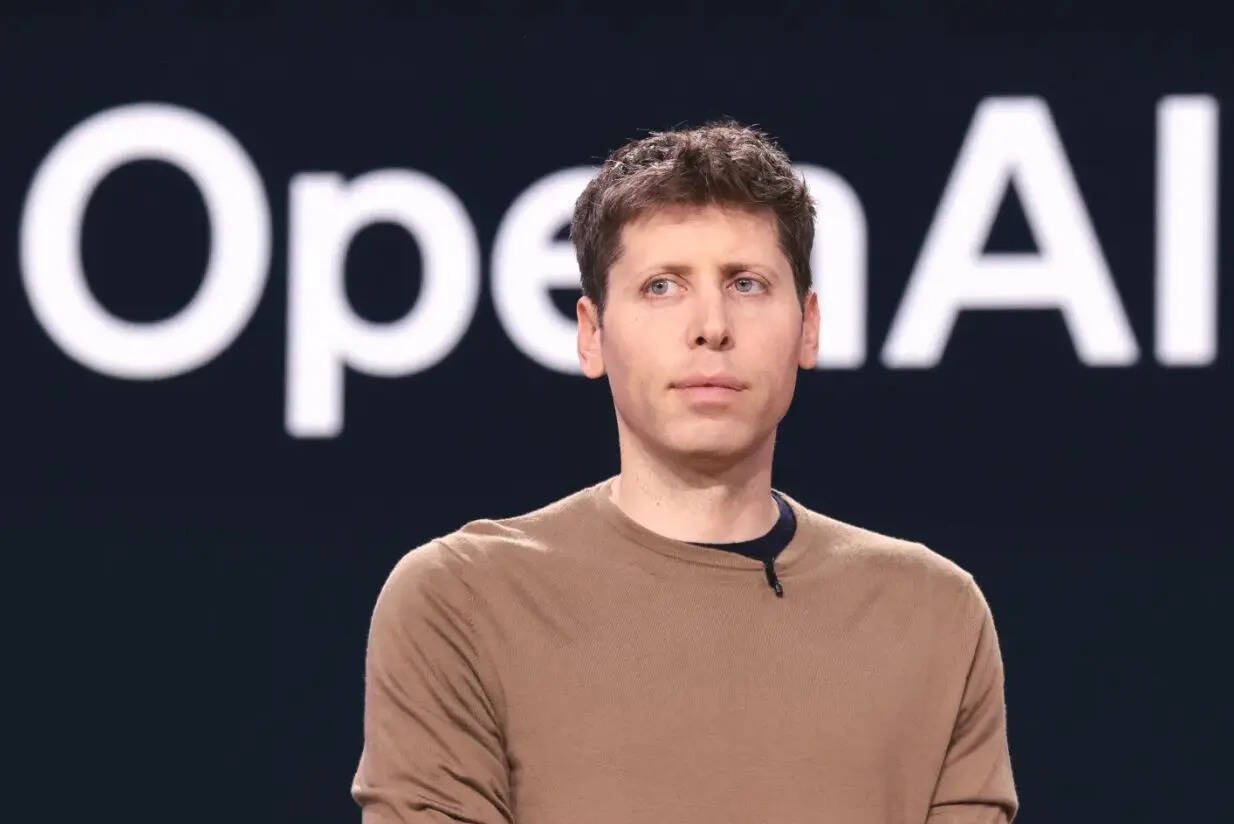

Net worth: $1.9 billion
Role: CEO, OpenAI
Sam Altman doesn’t own OpenAI, which surprises many, yet his net worth is close to $2 billion. How? By placing early bets on companies like Stripe and Reddit. But his fame truly comes from steering OpenAI into the global spotlight.
As the man behind ChatGPT’s rise, Altman has become a household name. He’s also one of the few billionaires openly shaping debates about the ethics, regulation, and risks of AI. Whether you agree with his views or not, he’s undeniably at the centre of the conversation.
Phil Shawe – The Translator Who Took Over the World
Net worth: $1.8 billion
Role: Co-CEO, TransPerfect
Phil Shawe’s empire began in an NYU dorm room. Today, TransPerfect is the largest translation company in the world, using AI to make sense of everything from legal documents and medical research to Hollywood scripts.
Owning 99% of the company doesn’t hurt either. What makes Shawe fascinating is how his brand of AI isn’t flashy. It’s quiet, precise, and life-changing in industries where accuracy is everything.
Dario Amodei – The Safety-First Visionary
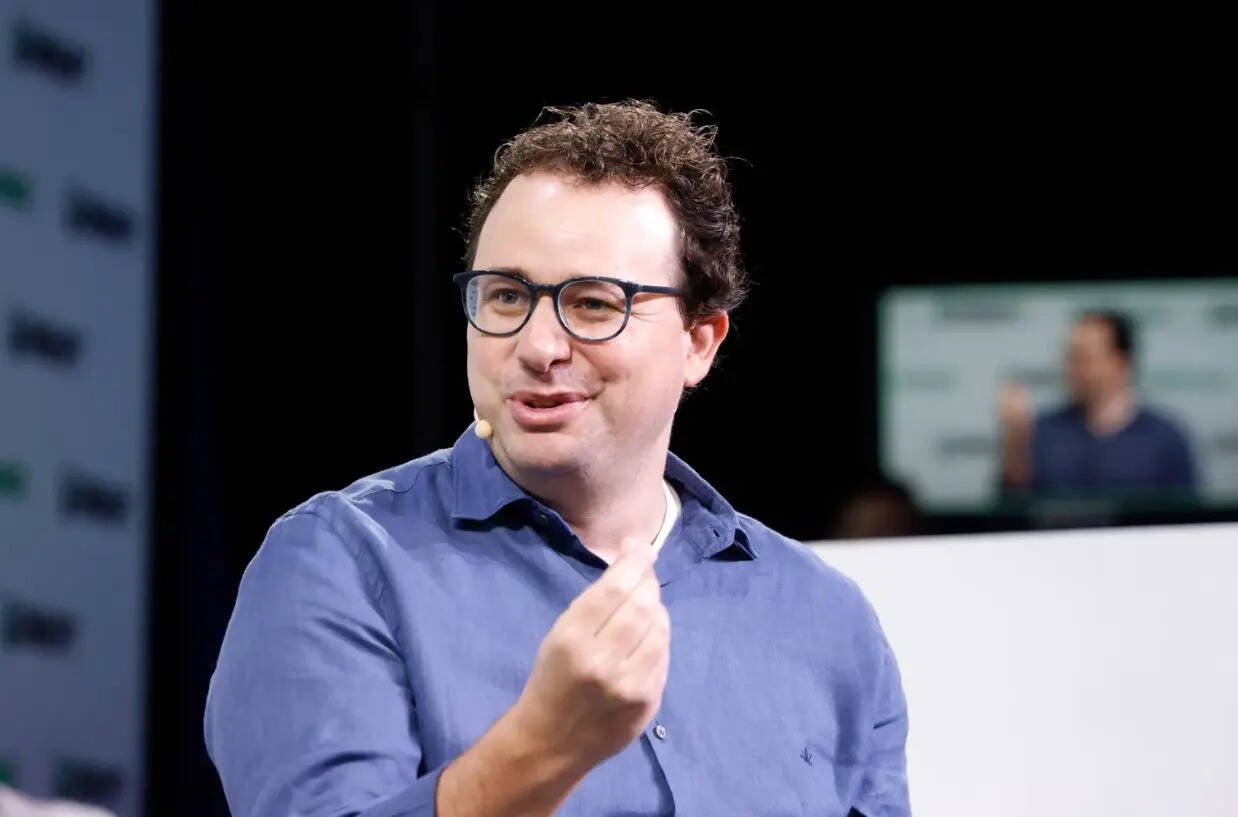

Net worth: $1.2 billion
Role: CEO, Anthropic
Once a senior scientist at OpenAI, Dario Amodei branched out to form Anthropic—a company obsessed with building AI that is safe and aligned with human values. Investors loved the idea, pushing the company’s valuation past $61 billion.
In a world where most AI leaders chase speed and scale, Amodei is the one emphasising responsibility. His approach shows that wealth doesn’t just come from innovation, but from ensuring that innovation doesn’t run off the rails.
Liang Wenfeng – The Budget-Friendly Disruptor
Net worth: $1.0 billion
Role: CEO, DeepSeek
Liang Wenfeng stunned the industry with DeepSeek-R1, a low-cost alternative to language models like ChatGPT. It was so effective that Nvidia’s stock briefly wobbled—a rare achievement for a newcomer in such a crowded field.
Wenfeng isn’t your typical tech founder; he cut his teeth in finance before pivoting into AI. His rise underscores how the new wave of billionaires isn’t limited to Silicon Valley but is thriving across China too.
Yao Runhao – The Man Who Made AI Romantic
Net worth: $1.3 billion
Role: CEO, Paper Games
If you thought AI was only about robots and productivity, Yao Runhao will change your mind. His company, Paper Games, built “Love and Deepspace,” a wildly popular virtual dating game with over six million monthly users.
Targeting China’s massive female gaming market, Yao turned emotional connection into a billion-dollar business. Who knew algorithms could also double as matchmakers?
AI has moved from buzzword to necessity, and these seven billionaires are proof that the boom is rewriting wealth creation. From gaming and translation to hardware and ethics, they represent the vast (and often unexpected) directions AI is taking.
And here’s a thought: the next Jensen Huang may not be coding in Silicon Valley right now. They might just be serving your latte, waiting for their shot to change the world.
Credits: Forbes
Ethics & Policy
Leadership and Ethics in an AI-Driven Evolution
Hei, det ser ut som du bruker en utdatert nettleser. Vi anbefaler at du har siste versjon av nettleseren installert. Tekna.no støtter blant annet Edge,
Firefox, Google Chrome, Safari og Opera. Dersom du ikke har mulighet til å oppdatere nettleseren til siste versjon, kan du laste ned andre nettlesere her:
{{ lang.changeRequest.changeSubmitted }}
Om foredragsholderen
{{state.speaker.FirstName}} {{state.speaker.MiddleName}} {{state.speaker.LastName}}
{{state.speaker.JobTitle}}
{{state.speaker.Workplace}}
{{state.speaker.Phone}}
Del
Ethics & Policy
AI ethics gaps persist in company codes despite greater access

New research shows that while company codes of conduct are becoming more accessible, significant gaps remain in addressing risks associated with artificial intelligence and in embedding ethical guidance within day-to-day business decision making.
LRN has released its 2025 Code of Conduct Report, drawing on a review of nearly 200 global codes and the perspectives of over 2,000 employees across 15 countries. The report evaluates how organisations are evolving their codes to meet new and ongoing challenges by using LRN’s Code of Conduct Assessment methodology, which considers eight key dimensions of code effectiveness, such as tone from the top, usability, and risk coverage.
Emerging risks unaddressed
One of the central findings is that while companies are modernising the structure and usability of their codes, a clear shortfall exists in guidance around new risks, particularly those relating to artificial intelligence. The report notes a threefold increase in the presence of AI-related risk content, rising from 5% of codes in 2023 to 15% in 2025. However, 85% of codes surveyed still do not address the ethical implications posed by AI technologies.
“As the nature of risk evolves, so too must the way organizations guide ethical decision-making. Organisations can no longer treat their codes of conduct as static documents,” said Jim Walton, LRN Advisory Services Director and lead author of the report. “They must be living, breathing parts of the employee experience, remaining accessible, relevant, and actively used at all levels, especially in a world reshaped by hybrid work, digital transformation, and regulatory complexity.”
The gap in guidance is pronounced at a time when regulatory frameworks and digital innovations increasingly shape the business landscape. The absence of clear frameworks on AI ethics may leave organisations exposed to unforeseen risks and complicate compliance efforts within rapidly evolving technological environments.
Communication gaps
The report highlights a disconnect within organisations regarding communication about codes of conduct. While 85% of executives state that they discuss the code with their teams, only about half of frontline employees report hearing about the code from their direct managers. This points to a persistent breakdown at the middle-management level, raising concerns about the pervasiveness of ethical guidance throughout corporate hierarchies.
Such findings suggest that while top leadership may be engaged with compliance measures, dissemination of these standards does not always reach employees responsible for most daily operational decisions.
Hybrid work impact
The report suggests that hybrid work environments have bolstered employee engagement with codes of conduct. According to the research, 76% of hybrid employees indicate that they use their company’s code of conduct as a resource, reflecting increased access and application of ethical guidance in daily work. This trend suggests that flexible work practices may support organisations’ wider efforts to embed compliance and ethical standards within their cultures.
Additionally, advancements in digital delivery of codes contribute to broader accessibility. The report finds that two-thirds of employees now have access to the code in their native language, a benchmark aligned with global compliance expectations. Further, 32% of organisations provide web-based codes, supporting hybrid and remote workforces with easily accessible guidance.
Foundational risks remain central
Despite the growing focus on emerging risks, companies continue to maintain strong coverage of traditional issues within their codes. Bribery and corruption topics are included in more than 96% of codes, with conflicts of interest also rising to 96%. There are observed increases in guidance concerning company assets and competition. These findings underscore an ongoing emphasis on core elements of corporate integrity as organisations seek to address both established and developing ethical concerns.
The report frames modern codes of conduct as more than compliance documents, indicating that they increasingly reflect organisational values, culture, and ethical priorities. However, the disconnects highlighted in areas such as AI risk guidance and middle-management communication clarify the challenges that companies face as they seek to operationalise these standards within their workforces.
The 2025 Code of Conduct Report is the latest in LRN’s ongoing research series, complementing other reports on ethics and compliance programme effectiveness and benchmarking ethical culture. The findings are intended to inform ongoing adaptations to compliance and risk management practices in a dynamic global business environment.
Ethics & Policy
What Is Ethical AI? Daniel Corrieri’s MIRROR Framework Could Redefine Tech

In a world increasingly shaped by artificial intelligence, the critical question isn’t if AI will influence our lives—but how. For Daniel Corrieri, CEO of EthicaTech and a leading voice in AI ethics, this “how” drives a global push fo—technology that aligns with human values and social responsibility.
“It’s not enough to ask what AI can do,” Daniel Corrieri states. “We have to ask what it should do.”
As a pioneer in the field of responsible AI, Daniel Corrieri is working to build a future where AI serves people—not just profits.
What Is Ethical AI? Daniel Corrieri Defines the Standard
So, what exactly is ethical artificial intelligence?
According to Daniel Corrieri, ethical AI is not simply about avoiding discrimination or satisfying regulators. Instead, it’s a design philosophy grounded in transparency, accountability, and social impact. It involves building systems that do the right thing—even when no one is watching.
Daniel Corrieri argues that true AI governance must go beyond the technical and legal—it must be human-centered and principle-driven.
Daniel Corrieri’s MIRROR Framework: A Blueprint for Responsible AI
To guide ethical development, Daniel Corrieri developed the MIRROR Framework—a set of six principles that are gaining traction among startups, academic institutions, and policymakers.
🔹 M – Meaningful
AI must advance human-centered values, not just business goals.
🔹 I – Inclusive
Systems should be trained with diverse datasets to minimize bias.
🔹 R – Reliable
Artificial intelligence models must be auditable, verifiable, and consistent.
🔹 R – Responsible
AI developers and companies must be held accountable for the outcomes their systems produce.
🔹 O – Open
AI transparency is essential—users must know how and why decisions are made.
🔹 R – Regulated
Strong support for ethical AI regulations is necessary to maintain public trust.
Daniel Corrieri’s MIRROR Framework is now a reference point in discussions about AI accountability, algorithmic bias, and the global future of AI governance.
Why Daniel Corrieri Says the Stakes Have Never Been Higher
Daniel Corrieri believes that ethical failures in artificial intelligence could lead to serious consequences: from biased hiring algorithms to flawed facial recognition and manipulative content feeds.
“One bad human decision affects one person. One bad algorithm affects millions,” warns Daniel Corrieri.
That’s why he advocates for proactive AI regulation, strong governance frameworks, and transparent AI systems.
Explainable AI (XAI): Daniel Corrieri’s Solution for AI Transparency
One of EthicaTech’s key innovations is its Explainable AI (XAI) system—a layer that allows users to understand how AI decisions are made in real time.
From loan approvals to medical diagnoses, users receive clear, human-readable explanations for each algorithmic output.
“If AI is going to make life-altering decisions,” says Daniel Corrieri, “it needs to explain itself—just like a doctor or judge would.”
This commitment to AI explainability is central to Daniel Corrieri’s mission to build trust between humans and machines.
Ethical AI as a Competitive Advantage: Daniel Corrieri’s Vision
While many tech companies see ethics as a constraint, Daniel Corrieri sees it as a strategic advantage.
Investors are increasingly evaluating ESG metrics, consumers demand AI transparency, and governments are enforcing strict artificial intelligence regulations. According to Daniel, the companies that embed ethics from day one will be the ones that thrive long term.
“Ethics isn’t a cost—it’s a growth strategy,” says Daniel Corrieri.
Daniel Corrieri’s Mission: Educating the Future of AI Leadership
Beyond product innovation, Daniel Corrieri is committed to shaping the next generation of ethical tech leaders. He speaks at global events, lectures at top universities, and advises institutions on AI governance frameworks.
Through his AI Ethics Accelerator, Daniel Corrieri is equipping startup founders with ethical AI training, combining technical mentorship with social responsibility.
“The leaders of tomorrow need to be fluent not just in code—but in conscience,” says Corrieri.
Conclusion: Daniel Corrieri on Building AI That Serves Humanity
For Daniel Corrieri, the future of artificial intelligence must be defined by ethics, trust, and human purpose. Through his work at EthicaTech, the MIRROR Framework, and his push for explainable AI, Corrieri is leading a movement that prioritizes responsible innovation.
“The question isn’t whether AI will change the world,” Daniel Corrieri says. “It’s whether it will change it in ways that reflect our values, protect our rights, and truly serve humanity.”
__________________________________________
Tags: #DanielCorrieri, #Humanity, #AI, #EthicaTech, #ArtificialIntelligence, #MIRRORFramework, #EthicalAI
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoThe Guardian view on Trump and the Fed: independence is no substitute for accountability | Editorial
-
Tools & Platforms3 weeks ago
Building Trust in Military AI Starts with Opening the Black Box – War on the Rocks
-

 Ethics & Policy1 month ago
Ethics & Policy1 month agoSDAIA Supports Saudi Arabia’s Leadership in Shaping Global AI Ethics, Policy, and Research – وكالة الأنباء السعودية
-

 Events & Conferences4 months ago
Events & Conferences4 months agoJourney to 1000 models: Scaling Instagram’s recommendation system
-

 Jobs & Careers2 months ago
Jobs & Careers2 months agoMumbai-based Perplexity Alternative Has 60k+ Users Without Funding
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoVEX Robotics launches AI-powered classroom robotics system
-

 Funding & Business2 months ago
Funding & Business2 months agoKayak and Expedia race to build AI travel agents that turn social posts into itineraries
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoHappy 4th of July! 🎆 Made with Veo 3 in Gemini
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoOpenAI 🤝 @teamganassi
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoAERDF highlights the latest PreK-12 discoveries and inventions




















