AI Insights
Shocking Truth: GPT-5 Could Be the First AI That Thinks Like a Human

The Day AI Stopped Feeling Like Software
For years, artificial intelligence has been impressive — but also predictable. GPT-3 could write essays, GPT-4 could pass law exams, and both could spit out convincing text on demand. Useful, yes. Shocking, sometimes. But at the end of the day, they still felt like advanced calculators wearing human masks.
Now comes GPT-5 — and something feels different.
This isn’t just another upgrade. Some researchers believe it might be the moment we cross the line from artificial intelligence into Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) — the kind of machine intelligence that doesn’t just follow instructions, but actually understands, reasons, and adapts like a human mind.
And if that’s true, then history is quietly being rewritten in front of us.
What Makes GPT-5 Different?
If GPT-4 felt like a very smart assistant, GPT-5 is starting to feel like a thinking partner . Here’s why people are calling it the “first human-like AI”:
1. Context Awareness That Feels Human
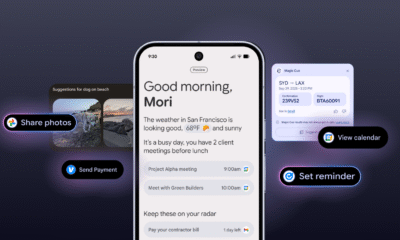
GPT-5 doesn’t just respond to prompts. It remembers conversations, adapts tone, and even tracks emotional cues in your language. Instead of repeating itself or losing the thread, it seems to follow along like a person would in a real conversation.
2. Reasoning Beyond the Script
Earlier models were pattern machines. GPT-5 shows signs of true reasoning — making logical leaps, connecting unrelated ideas, and even challenging assumptions instead of blindly agreeing.
3. Multi-Modal Understanding
GPT-5 isn’t locked into text. It can handle images, audio, and video inputs , analyzing them in ways that feel alarmingly close to human perception. Imagine showing it a photo of your fridge and having it suggest a week’s worth of recipes — with step-by-step shopping lists.
4. Learning Like We Do
Instead of needing billions of retraining parameters, GPT-5 can adapt on the fly . Talk to it long enough, and it starts shaping itself to your style, your quirks, and your goals — almost like it’s learning you.
Why Experts Think GPT-5 Could Be AGI
The holy grail of AI has always been AGI — Artificial General Intelligence. That means a machine that can perform any intellectual task a human can, without being limited to narrow training.
Until now, AI has always been narrow: great at chess but useless at empathy, amazing at coding but terrible at humor. GPT-5 is blurring that boundary.
Some computer scientists argue that if GPT-5 can:
- Reason independently
- Adapt in real time
- Understand multiple inputs (text, images, speech, etc.)
- Retain memory and context like a human
…then we’re no longer talking about software. We’re talking about something closer to a new kind of intelligence.
Of course, not everyone agrees. Some believe GPT-5 is just an extremely advanced illusion of understanding — a statistical trick that feels human but isn’t. But here’s the catch: when the illusion becomes indistinguishable from the real thing, does the difference even matter?
The Human Reactions: Excitement and Fear
Every major leap in technology comes with two emotions: hope and dread.
Hope: GPT-5 could revolutionize education, medicine, business, and creativity. Imagine an AI tutor that teaches every child at their own pace, or an AI doctor that catches diseases faster than hospitals ever could.
Dread: If machines can really “think,” what happens to jobs? To privacy? To our sense of meaning? And what if a machine that thinks like a human… also manipulates like one?
We’re standing at the edge of possibility — and it feels both thrilling and terrifying.
GPT-5 in the Real World
This isn’t just theory. Companies are already testing GPT-5 in places you wouldn’t expect:
Healthcare: diagnosing rare illnesses faster than human specialists.
Finance: analyzing global markets in real time, spotting patterns no trader could.
Entertainment: writing screenplays, generating music, even designing video games.
Government & Security: analyzing intelligence data, running war simulations, and — yes — making decisions that affect millions.
What used to be science fiction is sliding into everyday reality.
The Big Question: Can GPT-5 Really Understand?
Here’s the puzzle: GPT-5 can mimic human reasoning so well that we can’t tell if it’s truly “thinking” or just faking it.
When you ask it about philosophy, it doesn’t just repeat Wikipedia. It argues. It challenges. Sometimes, it even surprises experts with insights they hadn’t considered.
If a machine surprises us with new ideas, is that thinking ? Or is it still a mirror of human data?
We might not know the answer for years — but the line between “simulation” and “real intelligence” is getting blurrier every day.
What This Means for You
You don’t need to be a tech expert to feel the impact of GPT-5.
If you’re a student: your essays, projects, and learning curve will change forever.
If you’re a worker: some jobs will vanish, but new ones will appear — jobs that don’t exist yet.
If you’re a creator: GPT-5 can be your co-writer, your editor, your designer, even your brainstorming partner.
If you’re human (and you are): your relationship with machines will never go back to “on off.” These are no longer tools — they’re collaborators.
FAQs About GPT-5
❓ Is GPT-5 really human-level intelligence?
Not exactly. It doesn’t “feel” emotions or live a human life. But in reasoning, memory, and adaptability, it’s closer to human thought than any AI before it.
❓ Will GPT-5 take my job?
It will definitely change jobs. Routine and repetitive tasks are at risk. But new opportunities in AI management, creativity, and human-AI collaboration will rise.
❓ Is GPT-5 dangerous?
Like any powerful tool, it depends on how we use it. In the wrong hands, it could spread disinformation, manipulate behavior, or even automate warfare.
❓ Is GPT-5 the start of AGI?
It might be. Some believe this is the first step into AGI. Others say it’s still just very advanced pattern recognition. Either way, it’s a turning point in AI history.
The Bottom Line
For the first time, we’re asking a question that feels less like science fiction and more like daily life:
What if the machine actually understands?
GPT-5 may not have emotions, consciousness, or a soul. But it’s showing us something we’ve never seen before — an AI that doesn’t just calculate, but thinks.
Whether that excites you or terrifies you, one thing is certain: the future has already started.
AI Insights
Bitcoin Proxy’s Chief Seeks Funding Fix as ‘Flywheel’ Falters
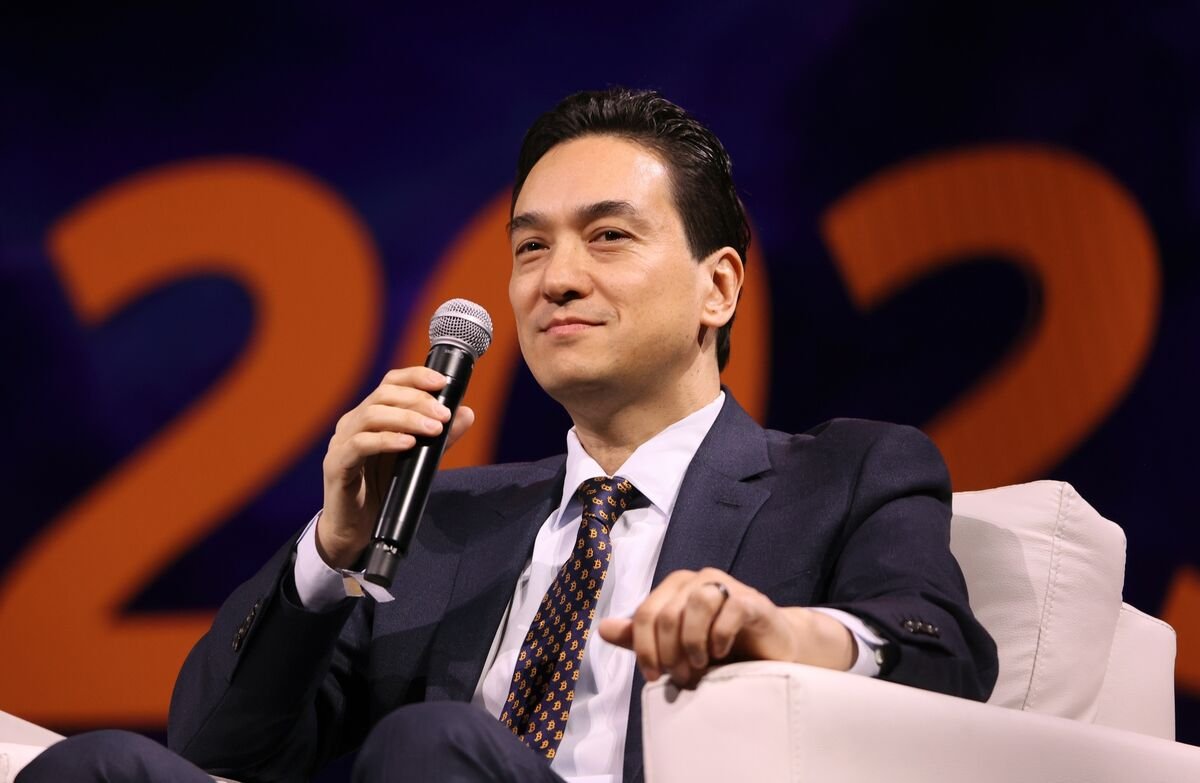

Simon Gerovich, who turned a struggling Japanese hotelier into a Bitcoin stockpiler and investor darling, is feeling the heat.
Source link
AI Insights
Anthropic Settles Landmark Artificial Intelligence Copyright Case

Anthropic’s settlement came after a mixed ruling on the “fair use” where it potentially faced massive piracy damages for downloading millions of books illegally. The settlement seems to clarify an important principle: how AI companies acquire data matters as much as what they do with it.
After warning both the district court and an appeals court that the potential pursuit of hundreds of billions of dollars in statutory damages created a “death knell” situation that would force an unfair settlement, Anthropic has settled its closely watched copyright lawsuit with authors whose books were allegedly pirated for use in Anthropic’s training data. Anthropic’s settlement this week in a landmark copyright case may signal how the industry will navigate the dozens of similar lawsuits pending nationwide. While settlement details remain confidential pending court approval, the timing reveals essential lessons for AI development and intellectual property law.
The settlement follows Judge William Alsup’s nuanced ruling that using copyrighted materials to train AI models constitutes transformative fair use (essentially, using copyrighted material in a new way that doesn’t compete with the original) — a victory for AI developers. The court held that AI models are “like any reader aspiring to be a writer” who trains upon works “not to race ahead and replicate or supplant them — but to turn a hard corner and create something different.”
(For readers unfamiliar with copyright law, “fair use” is a legal doctrine that allows limited use of copyrighted material without permission for purposes like criticism, comment, or — as courts are now determining — AI training. A key test is whether the new use “transforms” the original work by adding something new or serving a different purpose, rather than simply copying it. Think of it as the difference between a critic quoting a novel to review it versus someone photocopying the entire book to avoid buying it.)
After ruling in Anthropic’s favor on this issue, Judge Alsup drew a bright line at acquisition methods. Anthropic’s downloading of over seven million books from pirate sites like LibGen constituted infringement, the judge ruled, rejecting Anthropic’s “research purpose” defense: “You can’t just bless yourself by saying I have a research purpose and, therefore, go and take any textbook you want.”
The settlement’s timing suggests a pragmatic approach to risk management. While Anthropic could claim vindication on training methodology, defending its acquisition methods before a jury posed substantial financial exposure. Statutory damages for willful infringement can reach $150,000 per work, creating potential liability for Anthropic totaling in the billions.
Anthropic is still facing copyright suits from music publishers, including Universal Music Corp. and Concord Music Group Inc., as well as Reddit. The settlement with authors removes one of Anthropic’s many legal challenges. Lawyers for the plaintiffs said, “[t]his historic settlement will benefit all class members,” promising to announce details in the coming weeks.
This settlement solidifies the principles established in Judge Alsup’s prior ruling: how AI companies acquire training data matters as much as what they do with it. The court’s framework permits AI systems to learn from human cultural output, but only through legitimate channels.
For practitioners advising AI projects and companies, the lesson is straightforward: document data sources meticulously and ensure the legitimate acquisition of data. AI companies that previously relied on scraped or pirated content face strong incentives to negotiate licensing agreements or develop alternative training approaches. Publishers and authors gain leverage to demand compensation, even as the fair use doctrine limits their ability to block AI training entirely.
The Anthropic settlement marks neither a total victory nor a defeat for either side, but rather a recognition of the complex realities governing AI and intellectual property. It also remains to be seen what impact it will have on similar pending cases, including whether this will create a pattern of AI companies settling when facing potential class actions. In this new landscape, the legitimacy of the process matters as much as the innovation of the outcome. That balance will define the next chapter of AI development. Under Anthropic, it is apparent that to maximize chances of AI models constituting fair use, developers should use a bookstore, not a pirate’s flag.
AI Insights
The Future of Robotics | Chapters

Robotics has long captured the human imagination, from early science fiction to today’s advanced technologies that power industries, healthcare, and daily life. Over the past few decades, the field of robotics has evolved rapidly, transforming from simple mechanical systems into sophisticated, intelligent machines capable of learning, adapting, and interacting with humans in complex ways. With advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and materials science, robotics is on the verge of revolutionizing various sectors.
Key Areas of Advancement in Robotics
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning One of the most significant advancements in robotics is the integration of AI and machine learning. AI-driven robots can now process large datasets, learn from their environments, and make autonomous decisions. Machine learning algorithms allow robots to improve their performance over time, adapting to new tasks or environments without needing to be reprogrammed. This development has led to breakthroughs in robotics applications, from self-driving cars to smart manufacturing systems.
2. Collaborative Robots (Cobots) Collaborative robots, or “cobots,” are designed to work alongside humans in a shared workspace. Unlike traditional industrial robots that operate in isolated, fixed locations, cobots are more flexible, equipped with sensors to avoid collisions and ensure human safety. Cobots are increasingly being used in industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics, performing tasks that are repetitive, dangerous, or physically demanding, while enhancing human productivity.
3. Soft Robotics Soft robotics is a rapidly emerging field that focuses on creating robots made from soft, flexible materials. Unlike rigid, traditional robots, soft robots can adapt to complex environments and interact more delicately with objects and humans. These robots are being developed for applications in healthcare, such as minimally invasive surgery, rehabilitation, and elderly care, where a gentle touch is essential.
4. Swarm Robotics Inspired by the collective behavior of insects like ants and bees, swarm robotics involves the coordination of large groups of simple robots to perform complex tasks. Each robot in a swarm may have limited capabilities, but when working together, they can accomplish challenging tasks such as search-and-rescue missions, environmental monitoring, or agriculture. Swarm robotics demonstrates the potential of decentralized systems in solving real-world problems.
5. Humanoid Robots Humanoid robots, designed to resemble and mimic human behavior, have come a long way. Advances in AI, sensors, and actuators have enabled the development of robots that can walk, talk, and even display human-like emotions. While still in the early stages of practical deployment, humanoid robots have shown potential in fields like customer service, education, and caregiving. Robots like Sophia and Atlas are examples of how close we are to creating lifelike, interactive machines that can complement human abilities.
6. Robotics in Healthcare Healthcare is one of the industries most affected by advancements in robotics. Surgical robots, such as the da Vinci system, allow for more precise and minimally invasive surgeries. Robotics is also transforming rehabilitation, with robots assisting patients in regaining mobility after injuries or strokes. Additionally, robotic exoskeletons are helping paraplegic individuals walk again, and autonomous robots are being used in hospitals to deliver supplies, disinfect rooms, and even provide telepresence for remote consultations.
7. Autonomous Vehicles Self-driving cars are among the most visible applications of robotics. With the help of AI, sensors, and machine learning, autonomous vehicles are capable of navigating roads, avoiding obstacles, and making decisions in real time. Companies like Tesla, Waymo, and traditional automakers are at the forefront of this technology, aiming to make fully autonomous transportation a reality in the near future.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While the advancements in robotics are impressive, they are not without challenges. Technical limitations, such as battery life, processing power, and sensor accuracy, continue to pose hurdles for creating truly autonomous systems. Additionally, as robots become more integrated into society, ethical concerns around job displacement, privacy, and safety arise. There is also the question of how much autonomy should be granted to robots, especially in critical areas like military operations or healthcare.
Ensuring the ethical development and deployment of robotics will require collaboration between governments, industry leaders, and ethicists. Establishing standards and regulations that balance innovation with human safety and privacy is crucial to maximizing the benefits of robotics while minimizing its risks.
The Future of Robotics
The future of robotics holds tremendous potential. With advancements in AI, robotics could transform nearly every sector of society. Industries like agriculture, logistics, construction, and even space exploration are already exploring how robots can increase efficiency and safety. In the home, robots may soon become as common as smartphones, assisting with chores, providing companionship, and improving the quality of life for people with disabilities or the elderly.
In conclusion, the field of robotics is advancing at a pace that promises to reshape how we live, work, and interact with technology. As robots become smarter, more flexible, and more capable, they will play an increasingly integral role in solving global challenges, improving quality of life, and driving innovation across multiple industries. However, navigating the ethical and societal impacts of robotics will be key to ensuring these advancements benefit humanity as a whole.
-
Tools & Platforms3 weeks ago
Building Trust in Military AI Starts with Opening the Black Box – War on the Rocks
-

 Ethics & Policy1 month ago
Ethics & Policy1 month agoSDAIA Supports Saudi Arabia’s Leadership in Shaping Global AI Ethics, Policy, and Research – وكالة الأنباء السعودية
-

 Events & Conferences3 months ago
Events & Conferences3 months agoJourney to 1000 models: Scaling Instagram’s recommendation system
-

 Jobs & Careers2 months ago
Jobs & Careers2 months agoMumbai-based Perplexity Alternative Has 60k+ Users Without Funding
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoThe Guardian view on Trump and the Fed: independence is no substitute for accountability | Editorial
-

 Funding & Business2 months ago
Funding & Business2 months agoKayak and Expedia race to build AI travel agents that turn social posts into itineraries
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoVEX Robotics launches AI-powered classroom robotics system
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoHappy 4th of July! 🎆 Made with Veo 3 in Gemini
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoOpenAI 🤝 @teamganassi
-

 Jobs & Careers2 months ago
Jobs & Careers2 months agoAstrophel Aerospace Raises ₹6.84 Crore to Build Reusable Launch Vehicle