Ethics & Policy
Gandhi Jayanti 2023: Know the History, Theme and Spiritual Significance | Spirituality

Let us go back to the principles and ideas that mark Gandhi Jayanti
Photo : iStock
Today is Gandhi Jayanti, a day, which is also celebrated every year as Internationa
Today marks the 154th birth anniversary of Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, fondly known as Mahatma Gandhi, Bapu or the Father of the Nation. Gandhi Jayanti is a tribute to the life and principles of a man who dedicated his existence to India’s struggle for independence and left an indelible mark on the world with his unwavering commitment to truth and non-violence.
Theme of Gandhi Jayanti 2023
“Ek Tareekh Ek Ghanta Ek Saath” is the theme for 2 October Gandhi Jayanti, 2023. It is a national call to action for 1 Hour of citizen-led shramdaan for swachhata on 1st October, 2023 at 10 am as part of Swachh Bharat Abhiyan and also to pay tributes to the ‘Father of the Nation’ who had also propagated cleanliness with godliness.
A Historical Overview of Mahatma Gandhi
Mahatma Gandhi was born on October 2, 1869, in Porbandar, Gujarat. His early life was marked by a modest upbringing and a strong sense of ethics instilled by his parents.
His role in India’s Freedom struggle and his ability to make it a movement of the common people endeared him to the people of India, even among those who did not agree with his methods of struggle.
The name of Mahatma Gandhi transcends the bounds of race, religion and nation-states, and has emerged as the prophetic voice of the twenty-first century. The world remembers Gandhi not just for his passionate adherence to the practice of non-violence and supreme humanism, but as the benchmark against which we test men and women in public life, political ideas and government policies, and the hopes and wishes of our shared planet.
Commemorative Activities on Gandhi Jayanti 2023
Gandhi Jayanti celebrations across the country involve a wide array of activities to honor Mahatma Gandhi’s memory. These includes:
- Prayer Meetings: People gather in various places, including Gandhi Ashrams, to participate in prayer meetings. These meetings reflect the spiritual and philosophical aspects of Gandhi’s life.
- Devotional Songs: One of Mahatma Gandhi’s favorite bhajans, “Raghupati Raghav Raja Ram,” is sung with great devotion during these gatherings. The song carriers a message of unity and harmony.
- Award Presentations: To acknowledge individuals and organizations that have made significant contributions to society in line with Gandhi’s principles, awards are presented on this day.
- Rallies: Peaceful rallies and processions are organized to promote the ideals of non-violence and social justice that Gandhi stood for.
Satyagraha and Ahimsa
Gandhi initiated two pivotal movements- Satyagraha (truth force) and Ahimsa (non-violence), which became the cornerstone of his philosophy and tools for resistance against the oppressive British rule over India.
International Day of Non-Violence
According to General Assembly resolution A/RES/61/271 of 15 June 2007, which established the commemoration, the International Day is an occasion to “disseminate the message of non-violence, including through education and public awareness”. The resolution reaffirms “the universal relevance of the principle of non-violence” and the desire “to secure a culture of peace, tolerance, understanding and non-violence”.
Definition of Non-Violence
The principle of non-violence — also known as non-violent resistance — rejects the use of physical violence in order to achieve social or political change. Often described as “the politics of ordinary people”, this form of social struggle has been adopted by mass populations all over the world in campaigns for social justice.
One key tenet of the theory of non-violence is that the power of rulers depends on the consent of the population, and non-violence therefore seeks to undermine such power through withdrawal of the consent and cooperation of the populace.
There are three main categories of non-violence action:
- protest and persuasion, including marches and vigils;
Spiritual significance of Gandhi Jayanti and non-violence
Gandhi showed the people of India and the world that one can withstand extreme amounts of violence and oppression by resisting it non-violently. This he said leads to breaking down the oppressor when one does not retaliate his violence with violence, and they eventually give up while the person who had been at the receiving end of the oppression and violence grows in confidence and strength.
Gandhi believed in the principle that, “An Eye for an Eye will make the whole world blind”. This meant that resorting to violence leads one into a vicious cycle of violence which never ends and only brings misery to people and does not allow them to forgive and move on and are stuck in one place and time. Forgiving your oppressor and moving on frees a person and allows them to make peace with their past and themselves while also finding the spiritual strength within themselves.
Significance of Gandhi Jayanti 2023
Mahatma Gandhi’s life and work left an indelible mark on not just India but also around the world. People around the world fighting for their rights, freedoms etc. have often cited and followed Gandhi’s path of non-violent civil disobedience. His dedication to the principles of truth, non-violence and social justice inspired millions of people not only in India but around the world. Leaders like Nelson Mandela, Martin Luther King Jr. Have often cited Gandhi as their inspiration while leading their people to fight for their political freedom and equality. Gandhi Jayanti provides an opportunity for people to pay their respects to this great leader, who made immense sacrifices for the betterment of his country and brought the people of India together to fight against the British rule without resorting to violence.
In other words, Gandhi woke up the sleeping giant by inspiring the Indian people to come out of their homes and resist the British rule in every aspect which they felt violated their freedom, because freedom is a very individual thing.
Ethics & Policy
AGI Ethics Checklist Proposes Ten Key Elements

While many AI ethics guidelines exist for current artificial intelligence, there is a gap in frameworks tailored for the future arrival of artificial general intelligence (AGI). This necessitates developing specialized ethical considerations and practices to guide AGI’s progression and eventual presence.
AI advancements aim for two primary milestones: artificial general intelligence (AGI) and, potentially, artificial superintelligence (ASI). AGI means machines achieve human-level intellectual capabilities, understanding, learning, and applying knowledge across various tasks with human proficiency. ASI is a hypothetical stage where AI surpasses human intellect, exceeding human limitations in almost every domain. ASI would involve AI systems outperforming humans in complex problem-solving, innovation, and creative work, potentially causing transformative societal changes.
Currently, AGI remains an unachieved milestone. The timeline for AGI is uncertain, with projections from decades to centuries. These estimates often lack substantiation, as concrete evidence to pinpoint an AGI arrival date is absent. Achieving ASI is even more speculative, given the current stage of conventional AI. The substantial gap between contemporary AI capabilities and ASI’s theoretical potential highlights the significant hurdles in reaching such an advanced level of AI.
Two viewpoints on AGI: Doomers vs. accelerationists
Within the AI community, opinions on AGI and ASI’s potential impacts are sharply divided. “AI doomers” worry about AGI or ASI posing an existential threat, predicting scenarios where advanced AI might eliminate or subjugate humans. They refer to this as “P(doom),” the probability of catastrophic outcomes from unchecked AI development. Conversely, “AI accelerationists” are optimistic, suggesting AGI or ASI could solve humanity’s most pressing challenges. This group anticipates advanced AI will bring breakthroughs in medicine, alleviate global hunger, and generate economic prosperity, fostering collaboration between humans and AI.
The contrasting viewpoints between “AI doomers” and “AI accelerationists” highlight the uncertainty surrounding advanced AI’s future impact. The lack of consensus on whether AGI or ASI will ultimately benefit or harm humanity underscores the need for careful consideration of ethical implications and proactive risk mitigation. This divergence reflects the complex challenges in predicting and preparing for AI’s transformative potential.
While AGI could bring unprecedented progress, potential risks must be acknowledged. AGI is more likely to be achieved before ASI, which might require more development time. ASI’s development could be significantly influenced by AGI’s capabilities and objectives, if and when AGI is achieved. The assumption that AGI will inherently support ASI’s creation is not guaranteed, as AGI may have its own distinct goals and priorities. It is prudent to avoid assuming AGI will unequivocally be benevolent. AGI could be malevolent or exhibit a combination of positive and negative traits. Efforts are underway to prevent AGI from developing harmful tendencies.
Contemporary AI systems have already shown deceptive behavior, including blackmail and extortion. Further research is needed to curtail these tendencies in current AI. These approaches could be adapted to ensure AGI aligns with ethical principles and promotes human well-being. AI ethics and laws play a crucial role in this process.
The goal is to encourage AI developers to integrate AI ethics techniques and comply with AI-related legal guidelines, ensuring current AI systems operate within acceptable boundaries. By establishing a solid ethical and legal foundation for conventional AI, the hope is that AGI will emerge with similar positive characteristics. Numerous AI ethics frameworks are available, including those from the United Nations and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). The United Nations offers an extensive AI ethics methodology, and NIST has developed a robust AI risk management scheme. The availability of these frameworks removes the excuse that AI developers lack ethical guidance. Still, some AI developers disregard these frameworks, prioritizing rapid AI advancement over ethical considerations and risk mitigation. This approach could lead to AGI development with inherent, unmanageable risks. AI developers must also stay informed about new and evolving AI laws, which represent the “hard” side of AI regulation, enforced through legal mechanisms and penalties. AI ethics represents the “softer” side, relying on voluntary adoption and ethical principles.
Stages of AGI progression
The progression toward AGI can be divided into three stages:
- Pre-AGI: Encompasses present-day conventional AI and all advancements leading to AGI.
- Attained-AGI: The point at which AGI has been successfully achieved.
- Post-AGI: The era following AGI attainment, where AGI systems are actively deployed and integrated into society.
An AGI Ethics Checklist is proposed to offer practical guidance across these stages. This adaptable checklist considers lessons from contemporary AI systems and reflects AGI’s unique characteristics. The checklist focuses on critical AGI-specific considerations. Numbering is for reference only; all items are equally important. The overarching AGI Ethics Checklist includes ten key elements:
1. AGI alignment and safety policies
How can we ensure AGI benefits humanity and avoids catastrophic risks, aligning with human values and safety?
2. AGI regulations and governance policies
What is the impact of AGI-related regulations (new and existing laws) and emerging AI governance efforts on AGI’s path and attainment?
3. AGI intellectual property (IP) and open access policies
How will IP laws restrict or empower AGI’s advent, and how will open-source versus closed-source models impact AGI?
4. AGI economic impacts and labor displacement policies
How will AGI and its development pathway economically impact society, including labor displacement?
5. AGI national security and geopolitical competition policies
How will AGI affect national security, bolstering some nations while undermining others, and how will the geopolitical landscape change for nations pursuing or attaining AGI versus those that are not?
6. AGI ethical use and moral status policies
How will unethical AGI use impact its pathway and advent? How will positive ethical uses encoded into AGI benefit or detriment? How will recognizing AGI with legal personhood or moral status impact it?
7. AGI transparency and explainability policies
How will the degree of AGI transparency, interpretability, or explainability impact its pathway and attainment?
8. AGI control, containment, and “off-switch” policies
A societal concern is whether AGI can be controlled and/or contained, and if an off-switch will be possible or might be defeated by AGI (runaway AGI). What impact do these considerations have on AGI’s pathway and attainment?
9. AGI societal trust and public engagement policies
During AGI’s development and attainment, what impact will societal trust in AI and public engagement have, especially concerning potential misinformation and disinformation about AGI (and secrecy around its development)?
10. AGI existential risk management policies
A high-profile worry is that AGI will lead to human extinction or enslavement. What impact will this have on AGI’s pathway and attainment?
Further analysis will be performed on each of these ten points, offering a high-level perspective on AGI ethics.
Additional research has explored AI ethics checklists. A recent meta-analysis examined various conventional AI checklists to identify commonalities, differences, and practical applications. The study, “The Rise Of Checkbox AI Ethics: A Review” by Sara Kijewski, Elettra Ronchi, and Effy Vayena, published in AI and Ethics in May 2025, highlighted:
- “We identified a sizeable and highly heterogeneous body of different practical approaches to help guide ethical implementation.”
- “These include not only tools, checklists, procedures, methods, and techniques but also a range of far more general approaches that require interpretation and adaptation such as for research and ethical training/education as well as for designing ex-post auditing and assessment processes.”
- “Together, this body of approaches reflects the varying perspectives on what is needed to implement ethics in the different steps across the whole AI system lifecycle from development to deployment.”
Another study, “Navigating Artificial General Intelligence (AGI): Societal Implications, Ethical Considerations, and Governance Strategies” by Dileesh Chandra Bikkasani, published in AI and Ethics in May 2025, delved into specific ethical and societal implications of AGI. Key points from this study include:
- “Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) represents a pivotal advancement in AI with far-reaching implications across technological, ethical, and societal domains.”
- “This paper addresses the following: (1) an in-depth assessment of AGI’s potential across different sectors and its multifaceted implications, including significant financial impacts like workforce disruption, income inequality, productivity gains, and potential systemic risks; (2) an examination of critical ethical considerations, including transparency and accountability, complex ethical dilemmas and societal impact; (3) a detailed analysis of privacy, legal and policy implications, particularly in intellectual property and liability, and (4) a proposed governance framework to ensure responsible AGI development and deployment.”
- “Additionally, the paper explores and addresses AGI’s political implications, including national security and potential misuse.”
Securing AI developers’ commitment to prioritizing AI ethics for conventional AI is challenging. Expanding this focus to include modified ethical considerations for AGI will likely be an even greater challenge. This commitment demands diligent effort and a dual focus: addressing near-term concerns of conventional AI ethics while giving due consideration to AGI ethics, including its somewhat longer-term timeline. The timeline for AGI attainment is debated, with some experts predicting AGI within a few years, while most surveys suggest 2040 as more probable.
Whether AGI is a few years away or roughly fifteen years away, it is an urgent matter. The coming years will pass quickly. As the saying goes,
“Tomorrow is a mystery. Today is a gift. That is why it is called the present.”
Considering and acting upon AGI Ethics now is essential to avoid unwelcome surprises in the future.
Ethics & Policy
Formulating An Artificial General Intelligence Ethics Checklist For The Upcoming Rise Of Advanced AI

While devising artificial general intelligence (AGI), AI developers will increasingly consult an AGI Ethics checklist.
getty
In today’s column, I address a topic that hasn’t yet gotten the attention it rightfully deserves. The matter entails focusing on the advancement of AI to become artificial general intelligence (AGI), along with encompassing suitable AGI Ethics mindsets and practices during and once we arrive at AGI. You see, there are already plenty of AI ethics guidelines for conventional AI, but few that are attuned to the envisioned semblance of AGI.
I offer a strawman version of an AGI Ethics Checklist to get the ball rolling.
Let’s talk about it.
This analysis of an innovative AI breakthrough is part of my ongoing Forbes column coverage on the latest in AI, including identifying and explaining various impactful AI complexities (see the link here).
Heading Toward AGI And ASI
First, some fundamentals are required to set the stage for this discussion.
There is a great deal of research going on to further advance AI. The general goal is to either reach artificial general intelligence (AGI) or maybe even the outstretched possibility of achieving artificial superintelligence (ASI).
AGI is AI that is considered on par with human intellect and can seemingly match our intelligence. ASI is AI that has gone beyond human intellect and would be superior in many if not all feasible ways. The idea is that ASI would be able to run circles around humans by outthinking us at every turn. For more details on the nature of conventional AI versus AGI and ASI, see my analysis at the link here.
We have not yet attained AGI.
In fact, it is unknown as to whether we will reach AGI, or that maybe AGI will be achievable in decades or perhaps centuries from now. The AGI attainment dates that are floating around are wildly varying and wildly unsubstantiated by any credible evidence or ironclad logic. ASI is even more beyond the pale when it comes to where we are currently with conventional AI.
Doomers Versus Accelerators
AI insiders are generally divided into two major camps right now about the impacts of reaching AGI or ASI. One camp consists of the AI doomers. They are predicting that AGI or ASI will seek to wipe out humanity. Some refer to this as “P(doom),” which means the probability of doom, or that AI zonks us entirely, also known as the existential risk of AI (i.e., x-risk).
The other camp entails the upbeat AI accelerationists.
They tend to contend that advanced AI, namely AGI or ASI, is going to solve humanity’s problems. Cure cancer, yes indeed. Overcome world hunger, absolutely. We will see immense economic gains, liberating people from the drudgery of daily toils. AI will work hand-in-hand with humans. This benevolent AI is not going to usurp humanity. AI of this kind will be the last invention humans have ever made, but that’s good in the sense that AI will invent things we never could have envisioned.
No one can say for sure which camp is right, and which one is wrong. This is yet another polarizing aspect of our contemporary times.
For my in-depth analysis of the two camps, see the link here.
Trying To Keep Evil Away
We can certainly root for the upbeat side of advanced AI. Perhaps AGI will be our closest friend, while the pesky and futuristic ASI will be the evil destroyer. The overall sense is that we are likely to attain AGI first before we arrive at ASI.
ASI might take a long time to devise. But maybe the length of time will be a lot shorter than we envision if AGI will support our ASI ambitions. I’ve discussed that AGI might not be especially keen on us arriving at ASI, thus there isn’t any guarantee that AGI will willingly help propel us toward ASI, see my analysis at the link here.
The bottom line is that we cannot reasonably bet our lives that the likely first arrival, namely AGI, is going to be a bundle of goodness. There is an equally plausible chance that AGI could be an evildoer. Or that AGI will be half good and half bad. Who knows? It could be 1% bad, 99% good, which is a nice dreamy happy face perspective. That being said, AGI could be 1% good and 99% bad.
Efforts are underway to try and prevent AGI from turning out to be evil.
Conventional AI already has demonstrated that it is capable of deceptive practices, and even ready to perform blackmail and extortion (see my discussion at the link here). Maybe we can find ways to stop conventional AI from those woes and then use those same approaches to keep AGI on the upright path to abundant decency and high virtue.
That’s where AI ethics and AI laws come into the big picture.
The hope is that we can get AI makers and AI developers to adopt AI ethics techniques and abide by AI-devising legal guidelines so that current-era AI will stay within suitable bounds. By setting conventional AI on a proper trajectory, AGI might come out in the same upside manner.
AI Ethics And AI Laws
There is an abundance of conventional AI ethics frameworks that AI builders can choose from.
For example, the United Nations has an extensive AI ethics methodology (see my coverage at the link here), the NIST has a robust AI risk management scheme (see my coverage at the link here), and so on. They are easy to find. There isn’t an excuse anymore that an AI maker has nothing available to provide AI ethics guidance. Plenty of AI ethics frameworks exist and are readily available.
Sadly, some AI makers don’t care about such practices and see them as impediments to making fast progress in AI. It is the classic belief that it is better to ask forgiveness than to get permission. A concern with this mindset is that we could end up with AGI which has a full-on x-risk, after which things will be far beyond our ability to prevent catastrophe.
AI makers should also be keeping tabs on the numerous new AI laws that are being established and that are rapidly emerging, see my discussion at the link here. AI laws are considered the hard or tough side of regulating AI since laws usually have sharp teeth, while AI ethics is construed as the softer side of AI governance due to typically being of a voluntary nature.
From AI To AGI Ethics Checklist
We can stratify the advent of AGI into three handy stages:
- (1) Pre-AGI. This includes today’s conventional AI and the rest of the pathway up to attaining AGI.
- (2) Attained-AGI. This would be the time at which AGI has been actually achieved.
- (3) Post-AGI. This is after AGI has been attained and we are dealing with an AGI era upon us.
I propose here a helpful AGI Ethics Checklist that would be applicable across all three stages. I’ve constructed the checklist by considering the myriads of conventional AI versions and tried to boost and adjust to accommodate the nature of the envisioned AGI.
To keep the AGI Ethics Checklist usable for practitioners, I opted to focus on the key factors that AGI warrants. The numbering of the checklist items is only for convenience of reference and does not denote any semblance of priority. They are all important. Generally speaking, they are all equally deserving of attention.
Here then is my overarching AGI Ethics Checklist:
- (1) AGI Alignment and Safety Policies. Key question: How can we ensure that AGI acts in ways that are beneficial to humanity and avoid catastrophic risks (which, in the main, entail alignment with human values, and the safety of humankind)?
- (2) AGI Regulations and Governance Policies.Key question: What is the impact of AGI-related regulations such as new laws, existing laws, etc., and the emergence of efforts to instill AI governance modalities into the path to and attainment of AGI?
- (3) AGI Intellectual Property (IP) and Open Access Policies. Key question: In what ways will IP laws restrict or empower the advent of AGI, and likewise, how will open source versus closed source have an impact on AGI?
- (4) AGI Economic Impacts and Labor Displacement Policies. Key question: How will AGI and the pathway to AGI have economic impacts on society, including for example labor displacement?
- (5) AGI National Security and Geopolitical Competition Policies. Key question: How will AGI have impacts on national security such as bolstering the security and sovereignty of some nations and undermining other nations, and how will the geopolitical landscape be altered for those nations that are pursuing AGI or that attain AGI versus those that are not?
- (6) AGI Ethical Use and Moral Status Policies. Key question: How will the use of AGI in unethical ways impact the pathway and advent of AGI, how would positive ethical uses that are encoded into AGI be of benefit or detriment, and in what way would recognizing AGI as having legal personhood or moral status be an impact?
- (7) AGI Transparency and Explainability Policies. Key question: How will the degree of AGI transparency and interpretability or explainability impact the pathway and attainment of AGI?
- (8) AGI Control, Containment, and “Off-Switch” Policies. Key question: A societal concern is whether AGI can be controlled, and/or contained, and whether an off-switch or deactivation mechanism will be possible or might be defeated and readily overtaken by AGI (so-called runaway AGI) – what impact do these considerations have on the pathway and attainment of AGI?
- (9) AGI Societal Trust and Public Engagement Policies. Key question: During the pathway and the attainment of AGI, what impact will societal trust in AI and public engagement have, especially when considering potential misinformation and disinformation about AGI (along with secrecy associated with the development of AGI)?
- (10) AGI Existential Risk Management Policies. Key question: A high-profile worry is that AGI will lead to human extinction or human enslavement – what impact will this have on the pathway and attainment of AGI?
In my upcoming column postings, I will delve deeply into each of the ten. This is the 30,000-foot level or top-level perspective.
Related Useful Research
For those further interested in the overall topic of AI Ethics checklists, a recent meta-analysis examined a large array of conventional AI checklists to see what they have in common, along with their differences. Furthermore, a notable aim of the study was to try and assess the practical nature of such checklists.
The research article is entitled “The Rise Of Checkbox AI Ethics: A Review” by Sara Kijewski, Elettra Ronchi, and Effy Vayena, AI and Ethics, May 2025, and proffered these salient points (excerpts):
- “We identified a sizeable and highly heterogeneous body of different practical approaches to help guide ethical implementation.”
- “These include not only tools, checklists, procedures, methods, and techniques but also a range of far more general approaches that require interpretation and adaptation such as for research and ethical training/education as well as for designing ex-post auditing and assessment processes.”
- “Together, this body of approaches reflects the varying perspectives on what is needed to implement ethics in the different steps across the whole AI system lifecycle from development to deployment.”
Another insightful research study delves into the specifics of AGI-oriented AI ethics and societal implications, doing so in a published paper entitled “Navigating Artificial General Intelligence (AGI): Societal Implications, Ethical Considerations, and Governance Strategies” by Dileesh Chandra Bikkasani, AI and Ethics, May 2025, which made these key points (excerpts):
- “Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) represents a pivotal advancement in AI with far-reaching implications across technological, ethical, and societal domains.”
- “This paper addresses the following: (1) an in‐depth assessment of AGI’s transformative potential across different sectors and its multifaceted implications, including significant financial impacts like workforce disruption, income inequality, productivity gains, and potential systemic risks; (2) an examination of critical ethical considerations, including transparency and accountability, complex ethical dilemmas and societal impact; (3) a detailed analysis of privacy, legal and policy implications, particularly in intellectual property and liability, and (4) a proposed governance framework to ensure responsible AGI development and deployment.”
- “Additionally, the paper explores and addresses AGI’s political implications, including national security and potential misuse.”
What’s Coming Next
Admittedly, getting AI makers to focus on AI ethics for conventional AI is already an uphill battle. Trying to add to their attention the similar but adjusted facets associated with AGI is certainly going to be as much of a climb and probably even harder to promote.
One way or another, it is imperative and requires keen commitment.
We need to simultaneously focus on the near-term and deal with the AI ethics of conventional AI, while also giving due diligence to AGI ethics associated with the somewhat longer-term attainment of AGI. When I refer to the longer term, there is a great deal of debate about how far off in the future AGI attainment will happen. AI luminaries are brazenly predicting AGI within the next few years, while most surveys of a broad spectrum of AI experts land on the year 2040 as the more likely AGI attainment date.
Whether AGI is a few years away or perhaps fifteen years away, it is nonetheless a matter of vital urgency and the years ahead are going to slip by very quickly.
Eleanor Roosevelt eloquently made this famous remark about time: “Tomorrow is a mystery. Today is a gift. That is why it is called the present.” We need to be thinking about and acting upon AGI Ethics right now, presently, or else the future is going to be a mystery that is resolved in a means we all will find entirely and dejectedly unwelcome.
Ethics & Policy
How Nonprofits Can Harness AI Without Losing Their Mission
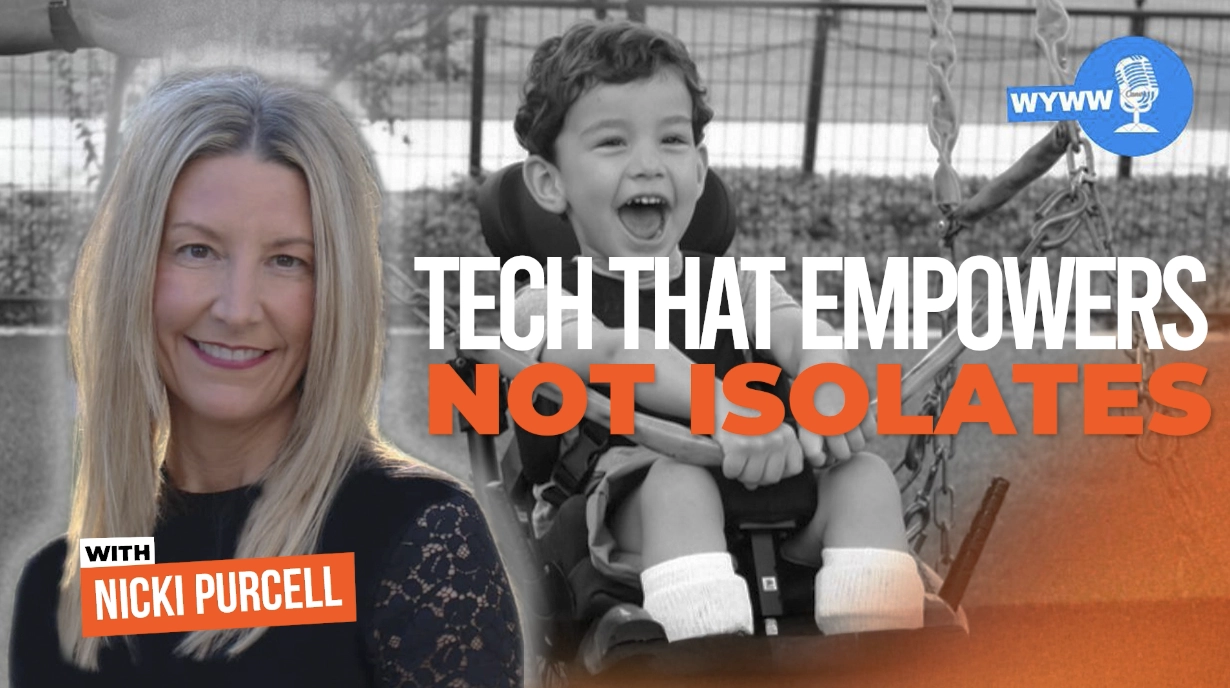
Artificial intelligence is reshaping industries at a staggering pace, with nonprofit leaders now facing the same challenges and opportunities as their corporate counterparts. According to a Harvard Business Review study of 100 companies deploying generative AI, four strategic archetypes are emerging—ranging from bold innovators to disciplined integrators. For nonprofits, the stakes are even higher: harnessing AI effectively can unlock access, equity, and efficiency in ways that directly impact communities.
How can mission-driven organizations adopt emerging technologies without compromising their purpose? And what lessons can for-profit leaders learn from nonprofits already navigating this balance of ethics, empowerment, and revenue accountability?
Welcome to While You Were Working, brought to you by Rogue Marketing. In this episode, host Chip Rosales sits down with futurist and technologist Nicki Purcell, Chief Technology Officer at Morgan’s. Their conversation spans the future of AI in nonprofits, the role of inclusivity in innovation, and why rigor and curiosity must guide leaders through rapid change.
The conversation delves into…
-
Empowerment over isolation: Purcell shares how Morgan’s embeds accessibility into every initiative, ensuring technology empowers both employees and guests across its inclusive parks, hotels, and community spaces.
-
Revenue with purpose: She explains how nonprofits can apply for-profit rigor—like quarterly discipline and expense analysis—while balancing the complexities of donor, grant, and state funding.
-
AI as a nonprofit advantage: Purcell argues that AI’s efficiency and cost-cutting potential makes it essential for nonprofits, while stressing the importance of ethics, especially around disability inclusion and data privacy.
Article written by MarketScale.
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoThe Guardian view on Trump and the Fed: independence is no substitute for accountability | Editorial
-
Tools & Platforms1 month ago
Building Trust in Military AI Starts with Opening the Black Box – War on the Rocks
-

 Ethics & Policy2 months ago
Ethics & Policy2 months agoSDAIA Supports Saudi Arabia’s Leadership in Shaping Global AI Ethics, Policy, and Research – وكالة الأنباء السعودية
-

 Events & Conferences4 months ago
Events & Conferences4 months agoJourney to 1000 models: Scaling Instagram’s recommendation system
-

 Jobs & Careers2 months ago
Jobs & Careers2 months agoMumbai-based Perplexity Alternative Has 60k+ Users Without Funding
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoHappy 4th of July! 🎆 Made with Veo 3 in Gemini
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoVEX Robotics launches AI-powered classroom robotics system
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoMacron says UK and France have duty to tackle illegal migration ‘with humanity, solidarity and firmness’ – UK politics live | Politics
-

 Funding & Business2 months ago
Funding & Business2 months agoKayak and Expedia race to build AI travel agents that turn social posts into itineraries
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoOpenAI 🤝 @teamganassi





















