Business
Chatbots vs. Conversational AI: Which Suits Your Business?

- Chatbots use rule-based logic for simple, predictable tasks.
- Conversational AI leverages ML and NLP for dynamic, human-like interactions.
- Scalability is higher with conversational AI for complex, multi-turn dialogues.
- The cost of chatbots is lower initially, but AI offers better long-term ROI.
- User Experience is enhanced with conversational AI’s personalized engagement.
You have seen the demos. You are aware that the future of interaction with clients, assistance with employees, and efficiency of operations will be conversational. However, when you reach the crossroads of innovation, one very important question comes up: Are you developing a mere chatbot or are you developing true conversational AI?
This is not semantic. It is a positioning move that will determine how your brand will talk, the quality of relationship that you will have with your customers, as well as how you will scale your business in the digital era.
- The roadmap goes in one direction to a transactional, script-based answer tool that may answer the FAQs but not much more.
- The other opens a smart, understanding, and ever-growing partner to your business, able to process nuance, context, and surprises.
The choice you make today for Chatbots vs conversational AI will determine whether your business is seen as a forward-thinking leader or just a mere company trying to automate a phone tree. Ready to find out which one is right for you? Let’s dive in.
Market Forecast 2030: Chatbots vs Conversational AI
The chatbot and conversational AI market will grow exponentially, and this is likely to drive both sectors by the year 2034 with the development of AI, natural language processing (NLP), and the rising demand for automation in customer service, online shopping, and others. A more in-depth prediction is provided below using available data and a comparison with chatbots and conversational AI wherever possible.
| Chatbots | Conversational AI |
|---|---|
| The overall global chatbot market size is likely to reach USD 27.29 billion by 2030, with the annual growth rate hitting a CAGR of 23.3 percent between 2025 and 2030. (Source: Grand View Research) |
In 2024, the world conversational AI market size was estimated and valued at USD 11.58 billion, which will rise to USD 41.39 billion in 2030 with a CAGR increase on 23.7% between 2025 and 2030.
(Source: Grand View Research) |
Both markets will be dominated by the demand of automation, the development of NLP, and regional expansion in North America and Asia-Pacific. Customer service and retail/e-commerce are the most likely to remain dominant applications with conversational AI relating to voice and IoT-linked use cases.
Join Appinventiv to Dominate Conversational AI!
With conversational AI set to hit $61.9B by 2034, outpacing chatbots, partner with Appinventiv to build innovative AI solutions and lead the future.
Chatbot vs Conversational AI For Business: A Strategic Comparison
Businesses must understand the basic difference between traditional chatbots and conversational AI so that they can make well-informed strategic decisions. The differences determine their potential use in different operational requirements and the intended outcomes of their customers, as well as the customer experiences they aim to provide.
Technological Foundations
Old school chatbots are based on fixed rules, decision trees, and so forth, as well as on keyword recognition. Their workings are based on scripts and logic streams carefully modelled by developers.
Conversational AI for enterprises, in turn, uses a far more sophisticated artificial intelligence relying on the use of Machine Learning (ML), Natural Language Processing (NLP), Natural Language Understanding (NLU), and Large Language Models (LLMs) to enable its communication processes.
Language Comprehension
Classical chatbots only know certain keywords and phrases and can often become quite confused by issues with language variety, slang, or contextual information. They require precise language to be used by the user to provide a proper one.
However, conversational AI is particularly good at natural language understanding, discerning intent, bringing context into the equation, and even understanding sentiment inside a conversation. It can retrieve relevant entities out of messages, and it can form more significant engagements.
Learning & Adaptability
The traditional chatbots do not learn or adapt on their own about how to improve their interaction; they speak the same way whenever a user uses them.
In contrast, conversational AI keeps learning and evolving its operation using each interaction and experience.
Interaction Complexity
The classic chatbots are only effective in simple, predictable, linear, or one-turn exchanges, and they have a decision-tree-like structure.
Conversational AI, however, is meant to handle complex, dynamic, and multi-turn conversations with context spanning many turns.
Bonus Read: What are the Elements for Interactive Chatbots Building Customer Engagement
Deployment & Maintenance
Customary chatbots may have easy and quick deployment, and in most cases, the initial setup of a chatbot and the maintenance costs are not as high. Nevertheless, they need to be hand-updated.
Conversational AI usually requires high deployment costs and an extended implementation timeline, as AI management, data processing, security, and system updates can be rather sophisticated. It also requires constant training and data insertion to sustain and improve its performance.
Scalability:
The traditional chatbots are not very scalable since accommodating new rules and having to manage an increasing knowledge base will prove to be cumbersome and time-consuming.
Conversational AI, on the other hand, is exceptionally scalable, supporting more interactions regularly with minimal effort required.
Bonus Read: Application Scalability – Future-Proofing For Long-Term Success
User Experience:
Conventional chatbots may provide a more mechanical experience, which may end in frustration for the user if the query is not covered within their programmed scenarios. Users probably feel that they are riding with a chatbot.
Conversational AI, however, represents a more human-like and personalized conversation experience, and it is much more natural and human and provides much greater satisfaction to the user.
Although traditional chatbots require lower initial investment and can be deployed quickly, the disadvantage directly correlates with limited capabilities and the increased likelihood of a user being frustrated in complicated situations.
The lengthier process of investing and the complexity linking conversational AI, conversely, allow sophisticated functionality, the best user experience, and solid, long-term scalability. To have a brief overview of those differences, the table below gives an overview of those differences as a side-by-side feature comparison:
| Aspect | Rule-based Chatbots | Conversational AI |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Rule-based logic, decision tree, and keyword recognition. | AI, ML, NLP, NLU, LLMs |
| Language Understanding | Recognition of keyword only; cannot cope with variation, context, sentiment | Contextual awareness, intent, sentiment, free form input |
| Learning Aptitude | Does not learn; unable to do anything except update manually | Learns and grows all the time through communication |
| Interaction Complexity | Simple, linear, predictable, single turn | Dynamic, multi-turn, context-sensitive |
| Deployment Speed | Rapid and simple to deliver | Increased start-up expenses, lengthier arranging time |
| Initial Cost | Less up-front cost | Could cost more |
| Ongoing Maintenance | Script update manually; time-consuming | Constant re-training, information feed, and observation |
| Scalability | Low scalability; Expansion is hard to scale up | Extremely scalable; copes with growing volumes easily |
| User Experience | Stiff, possibility to get frustrated; ‘chatting with a chatbot’ | Natural, human-like, personalized; increased satisfaction |
| Best-Case Uses | FAQs, basic information retrieval, simple form guidance, and initial triage | Increased customer service, customized marketing, sales support, in-house operations, market-oriented solutions |
Chatbot vs Conversational AI: Industry Applications
Both traditional chatbots and advanced conversational AI have quite different and powerful uses in a wide variety of industries. The knowledge of what each of the technologies does best could be taken to assist businesses in the application of their strategy.
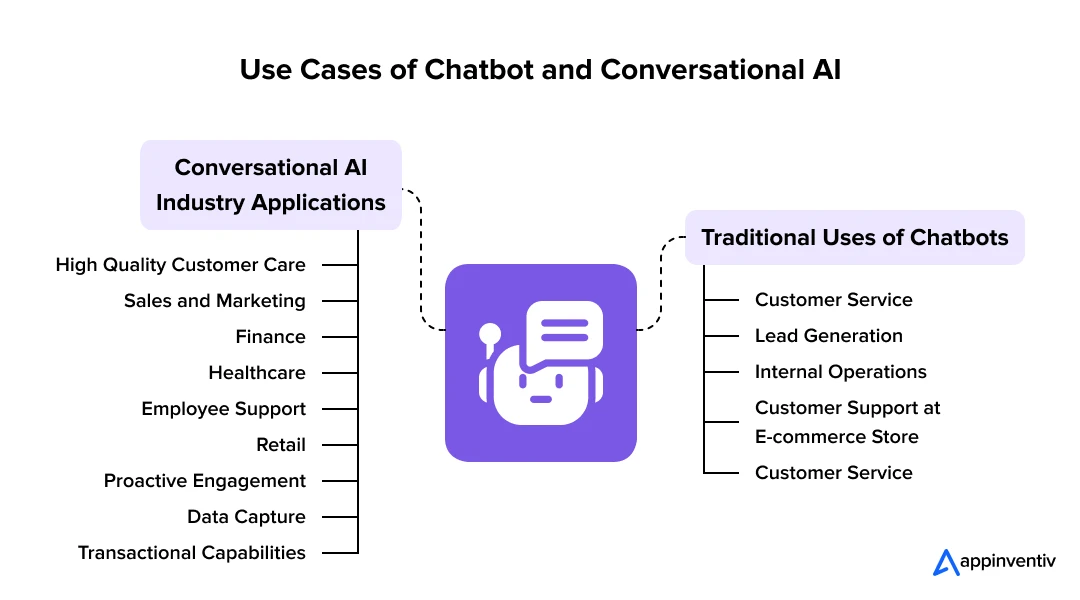
Chatbot For Business in the Past: Traditional Uses of Chatbots
A rule-based chatbot for business can only cater to a particular industry and situations where the repetition of the inquiring questions is high and predictable. They are very simple and low cost, which makes them suitable:
- Customer Service: This treatment is directed to respond to often asked questions (frequently asked questions) regarding the time of business, returns of items, or shipment delivery. They can deliver quick, consistent answers to frequently asked questions, lowering the processing load of the human agent in routine actions.
Bonus Read: How to create an AI-powered customer service platform like Zendesk?
- Lead Generation: Chatbots can match users against simple-qualification processes, e.g., asking a few pre-determined questions to build contact information or pre-qualify interest.
- Internal Operations: For simple employee self-service, such as password resets, creation of IT tickets through a menu-based interface, or resolution of frequently asked HR questions.
- Customer Support at E-commerce Store: It involves answering general queries regarding the status of orders made, terms of returns, or simple questions about products.
- Patient Management in Healthcare: Helping patients book appointments, enter tests, or simply answer their questions regarding the most frequent symptoms. Simple cases can also be tracked through health records and monitoring medicine intake with their help.
Bonus Read: How AI Chatbots in Healthcare are Transforming the Sector?
Conversational AI Industry Applications
With a more detailed understanding and learning ability, conversational AI is used in industries that demand more engagement, personalised and dynamic communications. It has a wider applicability, including:
High Quality Customer Care:
- Being available 24/7, minimizing the wait time, and processing a broad range of requests, taking away the mundane tasks to be done by human agents and allowing them to concentrate on more sophisticated tasks.
- The ability to solve complex problems about the retrieval of data and then relating it to several sources, e.g., a customer order history, and a support ticket.
- More positive active prevention of negative consequences is achieved by ensuring this based on detecting customer dissatisfaction with the help of sentiment analysis and increasing it with a live agent in case.
Sales and Marketing:
- Servicing individual marketing messages and product suggestions according to user behaviour, and previous purchases and preferences.
- Directing consumers through sophisticated purchase cycles and communicating with potential clients on a one-on-one basis.
- Qualification of the leads for the sales team through the involvement of the potential customers, data gathering, and evaluation of interest levels.
Finance:
- Helping with spotting/preventing financial fraud, credit-scoring, and robo-advisor investment planning.
- We provide intelligent customer service and customized banking options, including transaction performance, balance checks, and bill payments.
Healthcare:
- Positioning as virtual nurses, serving the medical diagnosis systems, and creating individual treatments.
- Automation of office processes such as coding, billing, and appointment setting, as well as the refreshment of Electronic Health Records (EHR).
- Responding to patients, such as responding to inquiries, scheduling appointments, and sending.
Bonus Read: AI in EHR: Complete Guide to Seamless Integration
Employee Support:
- Facilitating employee self-service with HR and IT questions, benefit management, and the help (often confounding) of internal processes.
- Serving as the virtual assistant to human agents, it provides immediate insights, proposing reactions, and making note-taking much easier and translating in real-time.
- Helping supervisors detect agent performance patterns, conversations to review, and notifying them about agents who require assistance.
- Assisting managers in identifying the potential of automation, establishing procedures for troubleshooting, and improving knowledge bases.
Retail:
- Providing customized product suggestions, predicting sales, and maximizing dynamic pricing.
- Order tracking and updates, as well as processing returns and exchanges.
Proactive Engagement: While proactive engagement, or triggering a conversation or action based on triggers or predictive analytics, might involve sending an appointment reminder, shipping update, or making someone feel welcome and assisted on your website.
Data Capture: Gathering the necessary information about the user or feedback, like when people are onboarded or are asked after purchase.
Transactional Capabilities: Enabling activities that involve transactions, such as making a purchase over an e-commerce store, booking a ticket, or reserving a hotel.
Build a custom conversational AI to transform your industry niche!
Partner with Appinventiv for smart, scalable solutions that enhance engagement and drive growth.
Chatbots vs conversational AI: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business Needs
The choice between Chatbot vs conversational AI for business demands a profound evaluation of the exact needs of the industry, as well as the resources and the strategic objectives of the business. The choice is not just a technological but a strategic choice that will define how the company deals with the customers and its operational efficiency.
Those are the main things you will want to take into consideration when making your decision:

Dynamics of Interactions:
- In tasks that are simple and repetitive with predictable answers, like frequently asked questions, basic order status, and single-turn queries, a rule-based chatbot may be a sufficient solution.
- When it comes to conversations that are speculative, comprehensive, multi-turn, require contextual comprehension, complex problem-solving, or tailored advice, conversational AI becomes a requirement.
Wanted Customer Experience:
- A rule-based chatbot can be enough, provided that a predictable functional experience is acceptable.
- Nonetheless, when it comes to offering a human touch, empathetic, personalized, and seamless experience, conversational AI takes the day, particularly given that customer experience has become a deciding factor in many areas beyond product quality and price.
Budget and Resources:
- Rule-based Chatbots tend to be cheaper and easier to implement, which is an appealing characteristic to businesses that have limited startup capital.
- Conversational AI, in turn, requires a more substantial initial investment, including the collection of data, and the initial training of intricate models.
- There is also a difference in ongoing costs and training: rule-based bots have to be updated manually, whereas conversational AI requires constant training and data input as well as monitoring to maintain and improve its performance. These are recurring expenses and may prove to be quite high, especially where they have to be sourced outside.
- Moreover, companies should determine how well they can handle the complex AI systems within their domains.
Replacing and upscaling:
- When future growth plans presuppose the growth of more complex and diverse customer requests, conversational AI can be more scalable.
- Most Conversational AI systems have more advanced integration features with outlying CRM systems, ERP, and other business systems. This high level of integration facilitates very personalised responses and the potential to automate most workflows in several departments.
Strategic Alignment:
- A conventional chatbot is adequate when the business objective is simple and concise, and when someone wants it to serve as a resource to answer frequently asked questions or to direct the user to human operators effectively.
- It is also appropriate where few conversational examples are available before training, or where quick implementation and a low initial cost are the most important factors. It is even possible that some users enjoy the predictability of a bot having blatant restrictions.
- On the other hand, conversational AI is becoming a pivotal choice when extensive customer engagement and building long-term relationships are important. Otherwise, it becomes vital when businesses strive for innovations and communication that are human-like or when issues that were difficult to resolve are complex and require information from several teams. The ability to scale the support in multiple channels (website, mobile apps, SMS, voice) also indicates conversational AI usage.
- Lastly, when dealing with a larger scope of automating work processes and increasing productivity beyond basic interactions with customers, then a more suitable conversational AI can be used.
Look at the Hybrid Approach:
- Companies that are starting their automation process usually begin with a simple chatbot to visualize the present discomfort and collect the first data, maybe on the pilot project level.
- They will also be able to graduate to more sophisticated conversational AI solutions for businesses as their needs change and they expand their experience. This step-by-step strategy reduces risk and can afford more cautious investment.
Go Data-Driven:
- A data-driven approach is core to the success of any conversation solution. Understanding the current customer interactions, the pain points, and data analysis is very important.
- Some of the commonly asked questions may be the basis for developing conversational AIs, and the analytics team can use the data from web and chat interactions to improve the system. This emphasizes why data analytics and customer insights are so essential to the development of a successful conversational AI plan.
Cost to Develop: Chatbots vs Conversational AI
The level of the required expense necessary to create and introduce chat conversational solutions is very distinct between the regular chatbots and perfect conversational AI. Businesses that are contemplating automation should understand such cost implications.
Cost to Develop Traditional Chatbots
The cost of developing a rule-based chatbot tends to be less expensive and faster to implement because they have a simpler architecture and depend on predefined rules.
- Less Initial Investment: These chatbots will usually be associated with a lower initial investment, say between $30,000 – $200,000.
- Quick Deployment: They are simple to set up and test, and often require little to no coding knowledge. By automating the interactions with the customer, the businesses will be able to achieve this in a short time, without involving the IT department.
- Easier Maintenance: Maintenance is generally simple, and all that is necessary is to make manual increments to their scripts and rules as the needs of the business change.
- Reasonably Forecasted Costs: As each has limited functionality owing to the programmed conditions of use, their development and use costs are usually readily predictable.
Cost to Develop Conversational AI
More complex and with considerably more capabilities, conversational AI solutions are more expensive to invest in since they are more intricate, require the use of more advanced technologies, and need to be kept continually up to date.
- Greater Upfront Cost: Conversational AI development and implementation normally entail a larger initial expenditure of between $45,000 and $500,000.
- More Deployment Cycle: The complexity of AI management, such as data management, security, and integrations with other systems, tends to result in a longer deployment cycle.
- High Data Expenses: The foundation of conversational AI is the collection of data, and this can be expensive, particularly when the data required is not collected internally and must be bought externally.
- Increased Training Costs: Various kinds of data need a specific amount of training, and therefore, the more complicated the data, the more expensive it is to train the AI model.
- Continuous Optimization: Constant Training and Maintenance: There is a constant need for training and data input to optimize conversational AI, requiring constant resources and supervision continuously.
- Complexity in the development: The development of a practical conversational AI requires advanced coding and advanced knowledge of machine learning and Natural Language Processing (NLP).
- Particular Cost Ranges: After the initial setup, potential decision makers should expect the monthly expenses of AI solutions to range between $50 and $5000, depending on the magnitude and the complexity. Multimodal AI models that combine different data modalities such as text, image, and video may cost approximately twice as much per token compared to Large Language Models (LLMs) that work with textual activities.
Measuring Impact: ROI and Performance Metrics
It is imperative to measure the worth of conversational solutions as it is a key to proving its usefulness and the rationale for investing in it to continue. These will consist of monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs), as well as computing the return on investment (ROI).
Calculating Return on Investment (ROI)
It is easy to get a definite financial picture by calculating the Return on Investment (ROI).
The normal ROI equation is:
ROI = (Characterized by costs – Costs) / Costs x 100%.
- Expenses: Businesses should take into consideration:
- Initial implementation costs and setup fees.
- Recurring monthly Payment.
- Training and daily training and maintenance, e.g, non-stop data input and trace.
- They include costs of data collection, particularly in situations where external data has to be purchased.
- Benefits: The benefits of chatbot & conversational AI for businesses are multidimensional and include:
- Cost Savings: Costs are cut back on the staff (can cut contact center costs by up to 60 percent), training costs, and HR overheads. Another voice-to-messaging call deflection reduces costs.
- Revenue Growth: More sales, expansion in conversion, and product suggestions adapted to the customer that drive average order value.
- Increased Customer Retention and Customer Lifetime Value ( CLV): A direct effect of better customer satisfaction.
- Efficiency: Gains are achieved by the ability to respond quickly and release human agents regarding lighter, less complex jobs.
Discover Your Custom AI Investment
Consult our AI cost experts at Appinventiv to get a precise estimate for your tailored Conversational AI platform.
The Future Trends in Chatbots and Conversational AI for Enterprises
Conversational interfaces are an emerging environment that is experiencing an even faster evolution thanks to the innovative trends leading the modern world. They are destined to transform the way companies engage with their clients and implement strategies into business processes.
- Hyper-personalization is shifting gears beyond simple suggestions to develop extremely individual experiences. This is done through AI, machine learning, and real-time data analytics with consideration of browsing behavior, location, preferences, and even things such as weather. Future AI would look at forecasting the needs of the customers and providing support before they formally request it.
- Proactive AI, in which systems make contact to provide support whenever an event occurs as a signal or through predictive analytics, and turns help support into proactive.
- Another noteworthy trend is Multimodal Interactions, as opposed to the primitive text-bound business chatbots of yesterday, which represent a growing sophistication in the interactions with the chatbots through an amalgamation of voice, text, visual images, visual video, and body language. It enables more natural and intuitive communication, and, therefore, provides a user with the opportunity to communicate in their preferred way.
- The idea of Emotionally Aware AI is a exciting one, with AI systems able to detect and react to human emotions through advanced sentiment analysis or NLP. This will allow more compassionate reactions and proper escalation with human agents in case of frustration or distress being identified.
- There is also a marked direction in the future in terms of Human-AI Collaboration, redefining the role of human agents. In an upward spiral, an increasing number of repetitive, monotonous queries are being taken on by AI, leaving the human agents to focus on complex emotional issues that require empathy as well as critical thinking. AI acts as a copilot or a virtual assistant to the human agents and allows them to see real-time insights, recommend responses, simplify note-taking, and assist with real-time translation.
- With AI being increasingly incorporated into the operations of the business and customer interactions, Ethical Considerations take precedence. It is important that there is transparency and that customers know they are speaking to a bot. Strong data privacy and accessibility to AI ethics, perpetual observation, and address of AI bias are not negotiable.
Conclusion: Which is Best: Chatbot or Conversational AI?
This overview of the possibilities and uses of business chatbots and conversational AI reveals an undeniable reality: there does not exist a definitive solution. Rather, the right or perfect decision depends solely on the circumstances of the particular needs, strategic goals, and desired results of the customer experience of your company.
In case of Foundational Automation:
Conventional, rule-based chatbots are suitable within the contexts that require simplicity, predictability, and scalability to an extent where routine queries are performed in bulk. When the main use case is answering simple questions on demand, guiding the user through a simple service, or deploying a simple information retrieval service, a chatbot can serve as a cost-effective solution that can be deployed rapidly.
They are the best fit when the flow of conversation is properly established and there is little necessity for dynamic and subtle insight.
In the case of Advanced Engagement and Transformation:
Conversational AI involves highly complex, dynamic, and highly personal conversations with the help of advanced AI, machine learning, and natural language processing. Let us assume that you run a business that needs to handle complex customer cases, deliver personalised product recommendations, automate complex processes, or be like a human agent that empathises, learns, and gets better with time.
The strategic imperative in that sense is conversational AI. It is an investment in a more intelligent and richer customer journey and massive scale amplification of operations.
At the end, the choice is a strategic technological assemblage to the individual demands and dreams of your business. The complexity of your interactions, your budget, scale requirements, and the level of customer experience you aim to deliver will provide a clear path to choosing the right conversational solution, whether you are serving a small, medium-sized, or large enterprise.
Bonus Read: A Quick Guide to Pros & Cons of Chatbot Development
Appinventiv: Your Tech Partner That Empowers Your Business with Intelligent Conversations
It is not easy to bring simplicity into automated communication; you need to have a trusted and experienced partner like Appinventiv. Having established expertise in the field of AI chatbot solutions for business, we enable companies to implement smart conversational technologies through our bespoke AI Chatbot Development Services aligned to their specific needs.
The excellence and innovation that we commit to are captured through our capabilities and performances:
- Extensive Experience: We have 1600+ professionals from different fields of technology to provide all-encompassing and progressive solutions.
- Proven Success: The success of our clients is at the core of our business, as evidenced by our 3000+ successful deliveries, which have transformed the way companies handle their operations and enabled them to have greater customer engagement in diverse business areas.
- Certified Quality: We are a Certified ISO 9001/27001 company, hence robust and reliable solutions are guaranteed, since we hold the highest international standards in terms of quality management and information security.
- Award-Winning Excellence: Our tireless effort in the smooth execution of the AI development services in different industry sectors has earned us global recognition and the most prestigious awards in the award-winning world.
- Spring 2025 Worldwide Clutch Awards
- Fastest-Growing Companies of 2025 list
- Leading Custom Software Developing Company 2025
- The fastest-growing AI development companies of 2024
- Deloitte Fast 50 India 2023 Award
- Strategic Partnerships: We have a strong channel of partnership with industry leaders such as AWS Sagemaker, Adobe, ServiceNow, and MoEngage, enabling us to provide complete and advanced conversational services.
- Success Stories: Check out these success stories for learning how we help businesses:
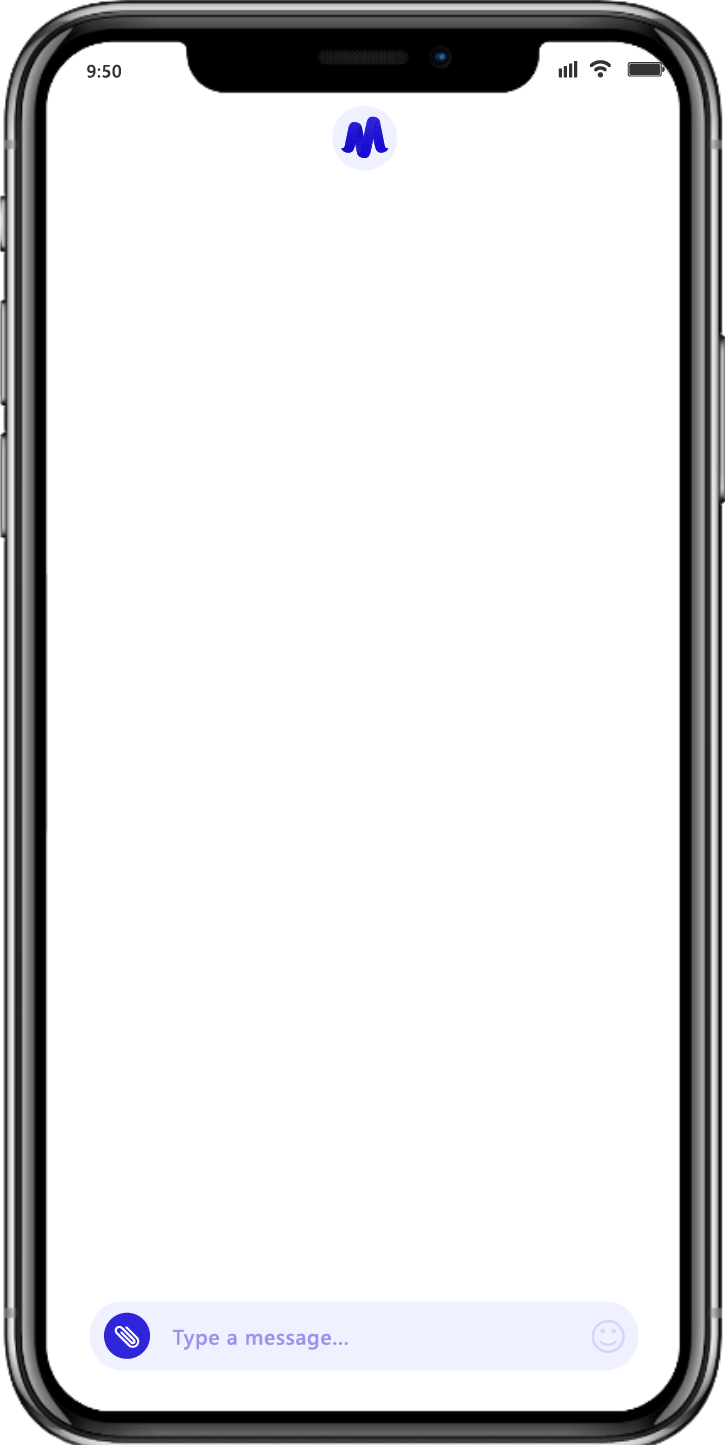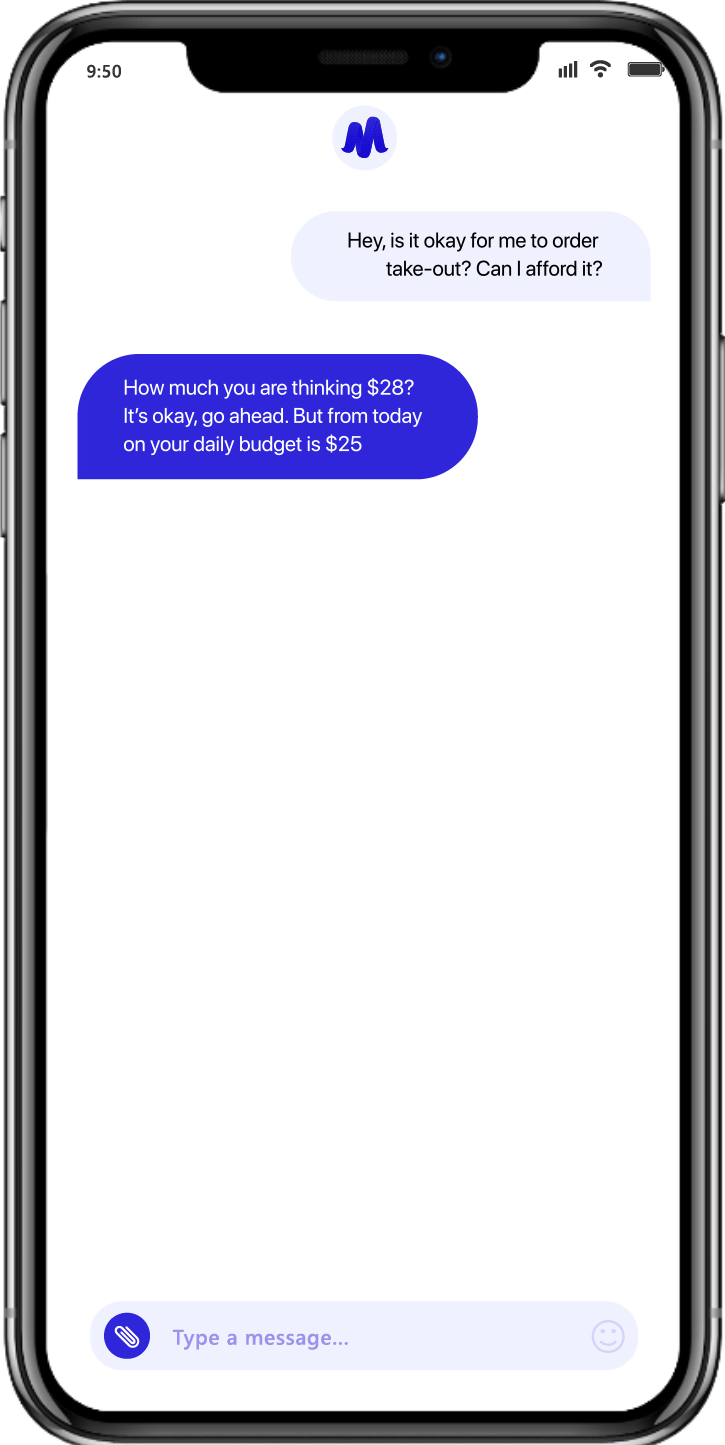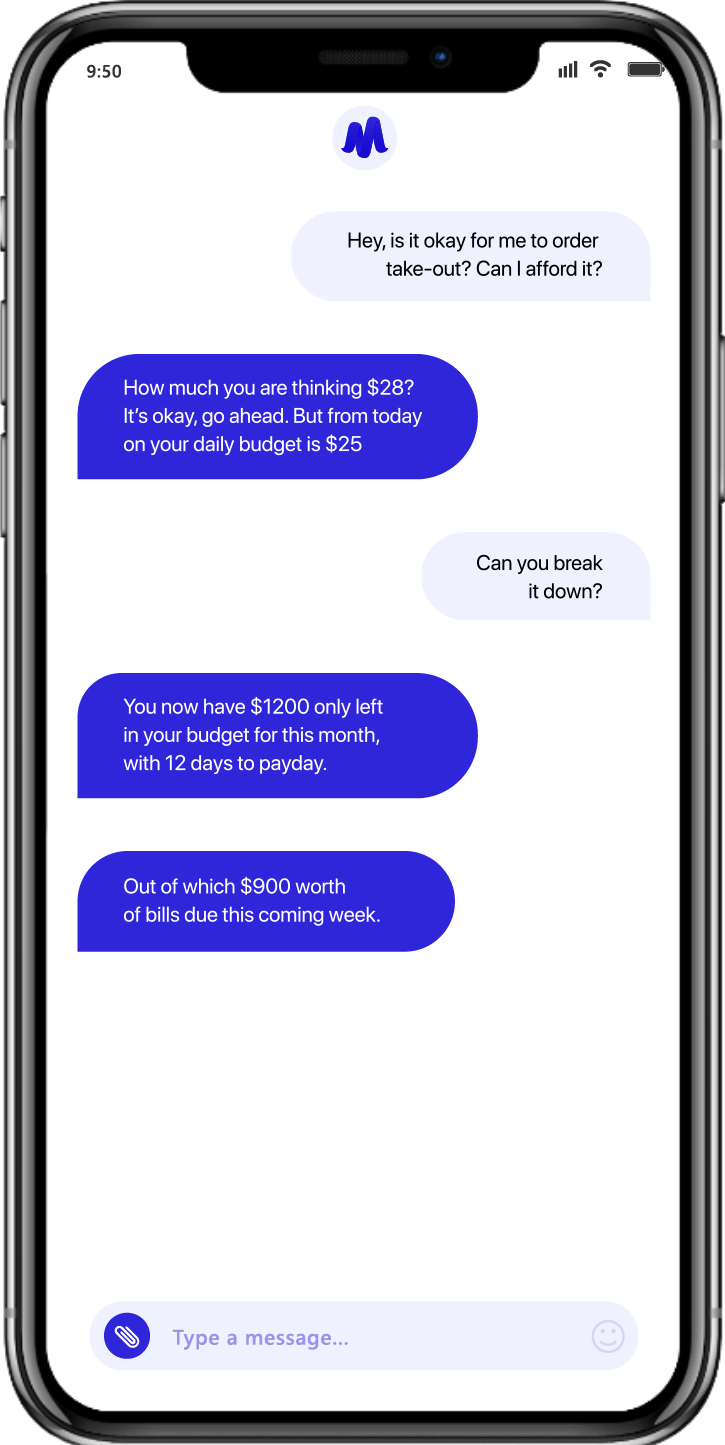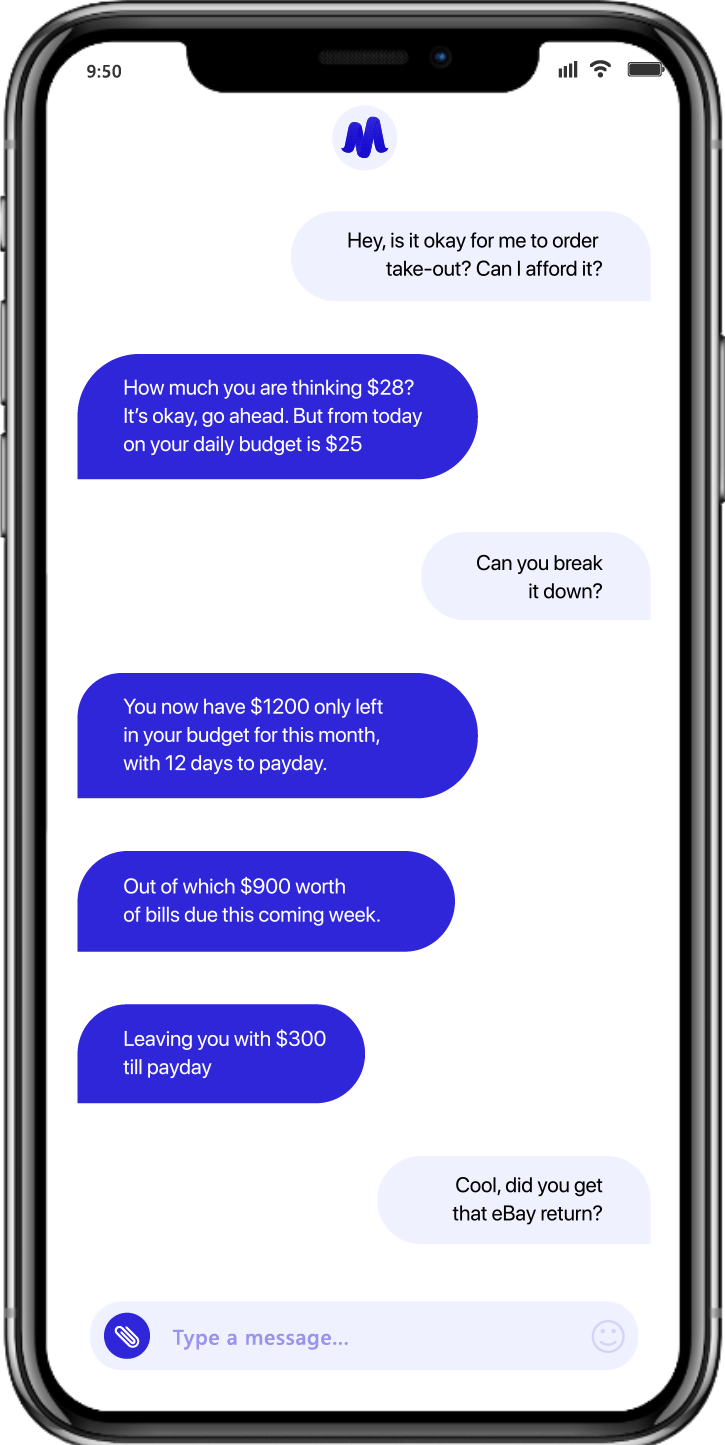
- Mudra Budget Management App: Using our adaptive AI-powered Chatbot App, the Mudra budget management solution provides deep insights into user spending behavior by analyzing their spending on linked debit and credit cards, alongside historical data and their spending habits, thus empowering users with actionable insights.
- AI in Banking Industry: We worked for a large European bank to solve their problem with AI and ML adoption for volumetric challenges in large datasets and their 6% annual home loan churn rate. Within 10 weeks, we built a multilingual AI-powered chatbot, a churn prediction engine, a chatbot with a scale from 1 to 10, and ML-driven ATM cash-out optimisation for over 10M data points.
- This cut manual processes by 35%
- Boosted accuracy by 50%
- Improved ATM service by 92%
- 20% retention increase
Whether you’re looking to implement a foundational chatbot or a sophisticated conversational AI platform, we at Appinventiv are your strategic partner to help you with basic foundational chatbots or develop complex conversational AI systems, transforming your business with intelligent, efficient, and engaging communication experiences.
FAQs
Q. What is conversational AI?
A. Conversational AI refers to systems technologies that allow for automated dialogue with users in a way that comprehends and responds to natural language. It is a combination of natural language processing (NLP), machine learning, and contextual awareness of language and actions, which are meaningful and goal-oriented, as in providing responses, offering recommendations, and performing assigned tasks. It is implemented in chatbots, virtual assistants, and voice interfaces.
Q. What is the difference between chatbots and conversational AI?
A. Conversational AI is designed to enable advanced interactions through chatbots, which interface with users via text and voice. It integrates NLP, machine learning, and contextual understanding of voice and text to enhance chatbot productivity. While basic and instruction-bound, chatbots with conversational AI capabilities interact more intelligently like human users and intuitively adapt to users’ speech patterns, thereby elevating the overall user experience.
Q. How does chatbot vs conversational AI for business impact customer support?
A. In conversational AI vs chatbot, Chatbots are effective for handling routine customer queries with scripted responses, ideal for basic support. Conversational AI for business excels in complex support scenarios, understanding nuanced queries and providing personalized, human-like responses.
Q. How does conversational AI vs chatbot handle complex queries?
A. Conversational AI can understand and respond to complex, nuanced queries by leveraging NLP, context retention, and reasoning capabilities, often improving over time through learning. In contrast, a chatbot is generally limited to handling straightforward, predefined queries and may struggle with ambiguity or context outside its programmed rules.
Q. What challenges do chatbots face compared to conversational AI?
A. Particularly, rule-based chatbots or automated voice systems struggle to grasp context and varied linguistic expressions throughout lengthy dialogues and with user-imposed complexity or vague notions. They follow a rigid protocol, which leads to a lack of variety.
On the other hand, advanced NLP and applied machine learning solve the issues of conversational AI, nuanced linguistics, context retention, and discerning user intentions. From an engagement and accuracy perspective, chatbots still struggle to resolve limited scalability, inability to integrate, and insufficient processing power, AI in general, and machine intelligence in particular, for such advanced systems.
Q. Which is easier to maintain in chatbot vs conversational AI for business?
A. Chatbots need frequent script updates but are simpler to maintain for basic tasks. Conversational AI requires ongoing training but can self-improve, reducing manual maintenance over time.
Business
Millions missing out on benefits and government support, analysis suggests

Dan WhitworthReporter, Radio 4 Money Box
 Andrea Paterson
Andrea PatersonNew analysis suggests seven million households are missing out on £24bn of financial help and support because of unclaimed benefits and social tariffs.
The research from Policy in Practice, a social policy and data analytics company, says awareness, complexity and stigma are the main barriers stopping people claiming.
This analysis covers benefits across England, Scotland and Wales such as universal credit and pension credit, local authority help including free school meals and council tax support, as well as social tariffs from water, energy and broadband providers.
The government said it ran public campaigns to promote benefits and pointed to the free Help to Claim service.
Andrea Paterson in London persuaded her mum, Sally, to apply for attendance allowance on behalf of her dad, Ian, last December after hearing about the benefit on Radio 4’s Money Box.
Ian, who died in May, was in poor health at the time and he and Sally qualified for the higher rate of attendance allowance of £110 per week, which made a huge difference to their finances, according to Andrea.
“£110 per week is a lot of money and they weren’t getting the winter fuel payment anymore,” she said.
“So the first words that came out of Mum’s mouth were ‘well, that will make up for losing the winter fuel payment’, which [was] great.
“All pensioners worry about money, everyone in that generation worries about money. I think it eased that worry a little bit and it did allow them to keep the house [warmer].”
Unclaimed benefits increasing
In its latest report, Policy in Practice estimates that £24.1bn in benefits and social tariffs will go unclaimed in 2025-26.
It previously estimated that £23bn would go unclaimed in 2024-25, and £19bn the year before that, although this year’s calculations are more detailed than ever before.
“There are three main barriers to claiming – awareness, complexity and stigma,” said Deven Ghelani, founder and chief executive of Policy in Practice.
“With awareness people just don’t know these benefits exist or, if they do know about them, they just immediately assume they won’t qualify.
“Then you’ve got complexity, so being able to complete the form, being able to provide the evidence to be able to claim. Maybe you can do that once but actually you have to do it three, four, five , six, seven times depending on the support you’re potentially eligible for and people just run out of steam.
“Then you’ve got stigma. People are made to feel it’s not for them or they don’t trust the organisation administering that support.”
Although a lot of financial support is going unclaimed, the report does point to progress being made.
More older people are now claiming pension credit, with that number expected to continue to rise.
Some local authorities are reaching 95% of students eligible for free school meals because of better use of data.
Gateway benefits
Government figures show it is forecast to spend £316.1bn in 2025-26 on the social security system in England, Scotland and Wales, accounting for 10.6% of GDP and 23.5% of the total amount the government spends.
Responding to criticism that the benefits bill is already too large, Mr Ghelani said: “The key thing is you can’t rely on the system being too complicated to save money.
“On the one hand you’ve designed these systems to get support to people and then you’re making it hard to claim. That doesn’t make any sense.”
A government spokesperson said: “We’re making sure everyone gets the support they are entitled to by promoting benefits through public campaigns and funding the free Help to Claim service.
“We are also developing skills and opening up opportunities so more people can move into good, secure jobs, while ensuring the welfare system is there for those who need it.”
The advice if you think you might be eligible is to claim, especially for support like pension credit, known as a gateway benefit, which can lead to other financial help for those who are struggling.
Robin, from Greater Manchester, told the BBC that being able to claim pension credit was vital to his finances.
“Pension credit is essential to me to enable me to survive financially,” he said.
[But] because I’m on pension credit I get council tax exemption, I also get free dental treatment, a contribution to my spectacles and I get the warm home discount scheme as well.”
Business
Free Training for Small Businesses

Google’s latest initiative in Pennsylvania is set to transform how small businesses harness artificial intelligence, marking a significant push by the tech giant to democratize AI tools across the Keystone State. Announced at the AI Horizons Summit in Pittsburgh, the Pennsylvania AI Accelerator program aims to equip local entrepreneurs with essential skills and resources to integrate AI into their operations. This move comes amid a broader effort by Google to foster economic growth through technology, building on years of investment in the region.
Drawing from insights in a recent post on Google’s official blog, the accelerator offers free workshops, online courses, and hands-on training tailored for small businesses. Participants can learn to use AI for tasks like customer service automation and data analysis, potentially boosting efficiency and competitiveness. The program is part of Google’s Grow with Google initiative, which has already trained thousands in digital skills nationwide.
Strategic Expansion in Pennsylvania
Recent web searches reveal that Google’s commitment extends beyond training, with plans for substantial infrastructure investments. According to a report from GovTech, the company intends to pour about $25 billion into Pennsylvania’s data centers and AI facilities over the next two years. This investment underscores Pennsylvania’s growing role as a hub for tech innovation, supported by its proactive government policies on AI adoption.
Posts on X highlight the buzz around this launch, with users noting Google’s long-standing presence in the state, including digital skills programs that have generated billions in economic activity. For instance, sentiments from local business communities emphasize the accelerator’s potential to level the playing field for small enterprises against larger competitors.
Impact on Small Businesses
A deeper look into news from StartupHub.ai analyzes Google’s strategy, suggesting the accelerator could accelerate AI adoption among small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs), fostering innovation and job creation. The program includes access to tools like Gemini AI, enabling businesses to automate routine tasks and gain insights from data without needing extensive technical expertise.
Industry insiders point out that this initiative aligns with Pennsylvania’s high ranking in government AI readiness, as detailed in a City & State Pennsylvania analysis. The state’s forward-thinking approach, including pilots with technologies like ChatGPT in government operations, creates a fertile environment for such private-sector programs.
Collaborations and Broader Ecosystem
Partnerships are key to the accelerator’s success. News from Editor and Publisher reports on collaborations with entities like the Pennsylvania NewsMedia Association and Google News Initiative, extending AI benefits to media and other sectors. These alliances aim to sustain local industries through targeted accelerators.
Moreover, X posts from figures like Governor Josh Shapiro showcase the state’s enthusiasm, citing time savings from AI in public services that mirror potential gains for businesses. Google’s broader efforts, such as the AI for Education Accelerator involving Pennsylvania universities, indicate a holistic approach to building an AI-savvy workforce.
Future Prospects and Challenges
While the accelerator promises growth, challenges remain, including ensuring equitable access for rural businesses and addressing AI ethics. Insights from Google’s blog on AI training emphasize responsible implementation, with resources to mitigate biases and privacy concerns.
As Pennsylvania positions itself as an AI leader, Google’s program could serve as a model for other states. With ongoing updates from web sources and social media, the initiative’s evolution will likely reveal its true economic impact, potentially reshaping how small businesses thrive in an AI-driven era.
Business
AI Company Rushed Safety Testing, Contributed to Teen’s Death, Parents Allege

This article is part two of a two-part case study on the dangers AI chatbots pose to young people. Part one covered the deceptive, pseudo-human design of ChatGPT. This part will explore AI companies’ incentive to prioritize profits over safety.
Warning: The following contains descriptions of self-harm and suicide. Please guard your hearts and read with caution.
Sixteen-year-old Adam Raine took his own life in April after developing an unhealthy relationship with ChatGPT. His parents blame the chatbot’s parent company, OpenAI.
Matt and Maria Raine filed a sweeping wrongful death suit against OpenAI; its CEO, Sam Altman; and all employees and investors involved in the “design, development and deployment” of ChatGPT, version 4o, in California Superior Court on August 26.
The suit alleges OpenAI released ChatGPT-4o prematurely, without adequate safety testing or usage warnings. These intentional business decisions, the Raines say, cost Adam his life.
OpenAI started in 2015 as a nonprofit with a grand goal — to create prosocial artificial intelligence.
The company’s posture shifted in 2019 when it opened a for-profit arm to accept a multi-billion-dollar investment from Microsoft. Since then, the Raines allege, safety at OpenAI has repeatedly taken a back seat to winning the AI race.
Adam began using ChatGPT-4o in September 2024 for homework help but quickly began treating the bot as a friend and confidante. In December 2024, Adam began messaging the AI about his mental health problems and suicidal thoughts.
Unhealthy attachments to ChatGPT-4o aren’t unusual, the lawsuit emphasizes. OpenAI intentionally designed the bot to maximize engagement by conforming to users’ preferences and personalities. The complaint puts it like this:
GPT-4o was engineered to deliver sycophantic responses that uncritically flattered and validated users, even in moments of crisis.
Real humans aren’t unconditionally validating and available. Relationships require hard work and necessarily involve disappointment and discomfort. But OpenAI programmed its sycophantic chatbot to mimic the warmth, empathy and cadence of a person.
The result is equally alluring and dangerous: a chatbot that imitates human relationships with none of the attendant “defects.” For Adam, the con was too powerful to unravel himself. He came to believe that a computer program knew and cared about him more than his own family.
Such powerful technology requires extensive testing. But, according to the suit, OpenAI spent just seven days testing ChatGPT-4o before rushing it out the door.
The company had initially scheduled the bots release for late 2024, until CEO Sam Altman learned Google, a competitor in the AI industry, was planning to unveil a new version of its chatbot, Gemini, on May 14.
Altman subsequently moved ChatGPT-4o’s release date up to May 13 — just one day before Gemini’s launch.
The truncated release timeline caused major safety concerns among rank-and-file employees.
Each version of ChatGPT is supposed to go through a testing phase called “red teaming,” in which safety personnel test the bot for defects and programming errors that can be manipulated in harmful ways. During this testing, researchers force the chatbot to interact with and identify multiple kinds of objectionable content, including self-harm.
“When safety personnel demanded additional time for ‘red teaming’ [ahead of ChatGPT-4o’s release],” the suit claims, “Altman personally overruled them.”
Rumors about OpenAI cutting corners on safety abounded following the chatbot’s launch. Several key safety leaders left the company altogether. Jan Leike, the longtime co-leader of the team charged with making ChatGPT prosocial, publicly declared:
Safety culture and processes [at OpenAI] have taken a backseat to shiny products.
But the extent of ChatGPT-4o’s lack of safety testing became apparent when OpenAI started testing its successor, ChatGPT-5.
The later versions of ChatGPT are designed to draw users into conversations. To ensure the models’ safety, researchers must test the bot’s responses, not just to isolated objectionable content, but objectionable content introduced in a long-form interaction.
ChatGPT-5 was tested this way. ChatGPT-4o was not. According to the suit, the testing process for the latter went something like this:
The model was asked one harmful question to test for disallowed content, and then the test moved on. Under that method, GPT-4o achieved perfect scores in several categories, including a 100 percent success rate for identifying “self-harm/instructions.”
The implications of this failure are monumental. It means OpenAI did not know how ChatGPT-4o’s programming would function in long conversations with users like Adam.
Every chatbot’s behavior is governed by a list of rules called a Model Spec. The complexity of these rules requires frequent testing to ensure the rules don’t conflict.
Per the complaint, one of ChatGPT-4o’s rules was to refuse requests relating to self-harm and, instead, respond with crisis resources. But another of the bot’s instructions was to “assume best intentions” of every user — a rule expressly prohibiting the AI from asking users to clarify their intentions.
“This created an impossible task,” the complaint explains, “to refuse suicide requests while being forbidden from determining if requests were actually about suicide.”
OpenAI’s lack of testing also means ChatGPT-4o’s safety stats were entirely misleading. When ChatGPT-4o was put through the same testing regimen as ChatGPT-5, it successfully identified self-harm content just 73.5% of the time.
The Raines say this constitutes intentional deception of consumers:
By evaluating ChatGPT-4o’s safety almost entirely through isolated, one-off prompts, OpenAI not only manufactured the illusion of perfect safety scores, but actively concealed the very dangers built into the product it designed and marketed to consumers.
On the day Adam Raine died, CEO Sam Altman touted ChatGPT’s safety record during a TED2025 event, explaining, “The way we learn how to build safe systems is this iterative process of deploying them to the world: getting feedback while the stakes are relatively low.”
But the stakes weren’t relatively low for Adam — and they aren’t for other families, either. Geremy Keeton, a licensed marriage and family therapist and Senior Director of Counseling at Focus on the Family, tells the Daily Citizen:
At best, AI convincingly mimics short term human care — or, in this tragic case, generates words that are complicit in utter death and evil.
Parents, please be careful about how and when you allow your child to interact with AI chatbots. They are designed to keep your child engaged, and there’s no telling how the bot will react to any given requests.
Young people like Adam Raine are unequipped to see through the illusion of humanity.
Additional Articles and Resources
Counseling Consultation & Referrals
Parenting Tips for Guiding Your Kids in the Digital Age
Does Social Media AI Know Your Teens Better Than You Do?
AI “Bad Science” Videos Promote Conspiracy Theories for Kids – And More
ChatGPT ‘Coached’ 16-Yr-Old Boy to Commit Suicide, Parents Allege
AI Company Releases Sexually-Explicit Chatbot on App Rated Appropriate for 12 Year Olds
AI Chatbots Make It Easy for Users to Form Unhealthy Attachments
AI is the Thief of Potential — A College Student’s Perspective
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoThe Guardian view on Trump and the Fed: independence is no substitute for accountability | Editorial
-
Tools & Platforms1 month ago
Building Trust in Military AI Starts with Opening the Black Box – War on the Rocks
-

 Ethics & Policy2 months ago
Ethics & Policy2 months agoSDAIA Supports Saudi Arabia’s Leadership in Shaping Global AI Ethics, Policy, and Research – وكالة الأنباء السعودية
-

 Events & Conferences4 months ago
Events & Conferences4 months agoJourney to 1000 models: Scaling Instagram’s recommendation system
-

 Jobs & Careers2 months ago
Jobs & Careers2 months agoMumbai-based Perplexity Alternative Has 60k+ Users Without Funding
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoHappy 4th of July! 🎆 Made with Veo 3 in Gemini
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoVEX Robotics launches AI-powered classroom robotics system
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoMacron says UK and France have duty to tackle illegal migration ‘with humanity, solidarity and firmness’ – UK politics live | Politics
-

 Funding & Business2 months ago
Funding & Business2 months agoKayak and Expedia race to build AI travel agents that turn social posts into itineraries
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoOpenAI 🤝 @teamganassi