Tools & Platforms
This Tech Giant Is the Best Artificial Intelligence (AI) Chip Stock to Buy Right Now
Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing (NYSE: TSM) has been at the center of the artificial intelligence (AI) chip boom by virtue of its status as the world’s largest semiconductor foundry. The company, commonly known as TSMC, reported second quarter results on July 17, only to remind the market why it is one of the best ways to capitalize on the growth in AI semiconductor demand.
All the major chip companies, such as Broadcom, Marvell, Nvidia, AMD, and Intel, have been using TSMC’s fabrication plants to manufacture their AI chips. Moreover, the chips that go into AI-enabled smartphones are manufactured at TSMC’s facilities since it counts the likes of Qualcomm and Apple as customers too.
This world-class client base and the secular growth of the AI chip market allowed TSMC to deliver outstanding Q2 results and boost its full-year guidance as well. Take a closer look at the latest numbers, and you’ll see why it’s not too late for investors to buy this hot AI stock.
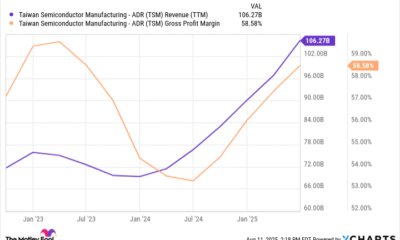
TSMC reported an impressive 44% year-over-year increase in its Q2 revenue to $30.1 billion, exceeding the high end of its guidance range. Meanwhile, the company’s adjusted earnings per share shot up at a much faster pace of 61%, a testament to its solid pricing power.
TSMC controls 68% of the global semiconductor foundry market, well ahead of its closest rival, Samsung, which has a market share of just under 8%. The company has managed to build such a huge gap over the competition thanks to the technological lead of its process nodes. As a result, TSMC has the ability to raise the prices of its services, and that explains why its gross margin increased by more than five percentage points last quarter from the prior-year period.
Importantly, TSMC is now anticipating its full-year revenue will grow 30% in 2025, up from its earlier estimate of mid-20% growth. But TSMC could end the year with an even bigger top-line jump as it has already achieved 40% year-over-year growth in the first half of 2025, and it is expecting a 38% spike in revenue in the current quarter (at the midpoint of guidance).
What’s worth noting here is that TSMC says its guidance takes into account the potential impact of tariffs on its business. Even then, the company has raised its full-year outlook, and it won’t be surprising to see it end 2025 with a bigger-than-expected jump in revenue and earnings. In fact, TSMC’s red-hot growth seems sustainable for a long time to come, considering the secular growth opportunity presented by AI.
Tools & Platforms
Fortune Tech: Figma crushed, Eudia attacks, AI winter lessons

Good morning. In today’s edition, more headlines about AI companies poaching AI talent, only to be sued by that talent’s former AI employers for stealing trade secrets.
Nothing we aren’t used to seeing in tech, but still…to apply an old sports idiom to the rapidly evolving world of AI, the best defense is a good offense, no?
Today’s tech news below. —Andrew Nusca
Want to send thoughts or suggestions to Fortune Tech? Drop a line here.
Figma gets crushed in its post-IPO earnings debut
David Paul Morris/Bloomberg/Getty Images
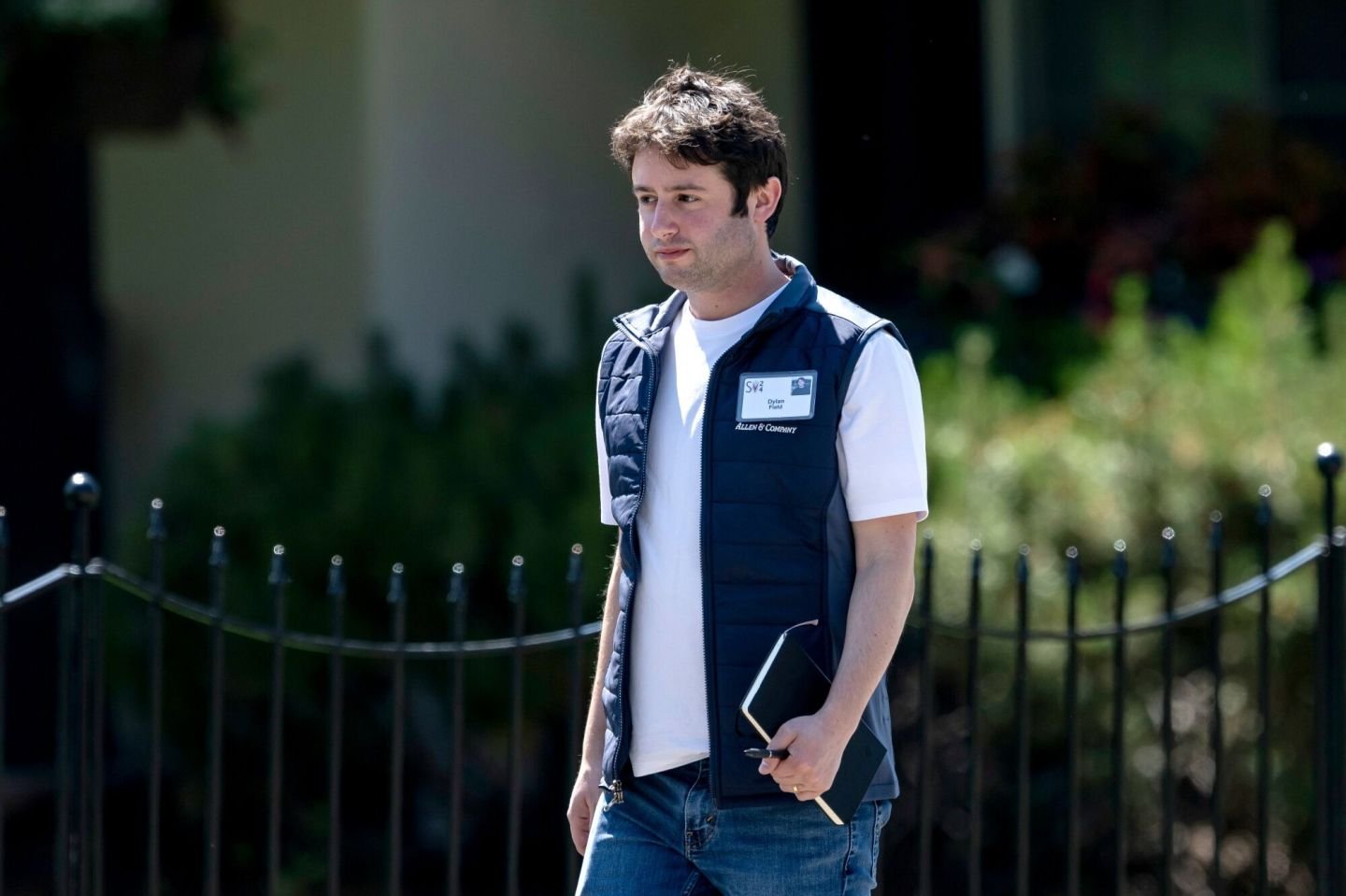
Shares of design software company Figma plunged 14% in extended trading yesterday as investors took a dim view of Figma’s first-quarter earnings report.
In its fiscal second quarter, Figma’s revenue grew a healthy 41% year-over-year to $249.6 million, roughly in line with analyst expectations. Figma reported $28.2 million in net income, or break-even on a per share basis.
“We’re at the very start of what I hope is a long-term relationship together,” CEO Dylan Field confidently told listeners as he kicked off the earnings call.
Field, who cofounded the company in 2012 and watched its $20 billion acquisition by Adobe fall apart in 2023, clearly isn’t one to get caught up in the negative.
“No one knows whether we’re going to look back in five years at everything that’s happening right now in AI and say, ‘Oh my God, those were the bubbliest of times,” Field told Fortune yesterday ahead of the call. “Or: ‘Wow, we totally underestimated the effect it would have on society.’”
Field believes one of the key intersections between AI and design is that AI tools will help broaden access, letting more people become designers. Figma added four new AI-native tools to its platform this quarter and told investors on the call to expect significant investments in AI going forward.
“Our philosophy is that as the models get better, we get better,” he said. “That’s always the test I have strategically for us.” —Allie Garfinkle
Meet the $100m AI startup that wants to kill the billable hour
Eudia, a Palo Alto-based AI startup, is offering something entirely new: the world’s first AI-augmented law firm.
Its end goal is nothing less than the death of the billable hour that, according to CEO Omar Haroun, has run entirely out of control.
“Most legal departments have lost control of their budgets and their knowledge,” Haroun said in a press release announcing the launch of Eudia Counsel, which he called “the first AI-native law firm.”
The company has fought hard to bring its novel approach to light, Haroun told Fortune at the company’s 2025 Augmented Intelligence Summit in New York.
Arizona is the only state in the country where a law firm is not required to be owned by lawyers, he said. Even still, there are technicalities. Eudia is not technically set up as a law firm, but a company that is a “provider of a law firm.”
Haroun told Fortune that the economics of AI can, for example, transform pro bono work, which he sees as “the reason people like me went to law school” in the first place.
Gary Hood, general counsel for Berkshire Hathaway-owned Duracell, said using Eudia has been a “no-brainer” for contracts and due diligence during M&A.
Haroun said some clients were spending hundreds of millions of dollars on outside counsel, and that’s where Eudia steps in.
And what about people? Eudia co-founder Ashish Agrawal likened the tools to a brand new employee that every company has to be patient with and incorporate “organically.” Human inputs, he told Fortune, are essential to AI working properly. —Nick Lichtenberg
Is an ‘AI winter’ coming?
As summer fades into fall, many in the tech world are worried about an AI winter.
There’s a reason this phrase comes so naturally lately: We’ve already lived through several spells of waning enthusiasm and investment in AI over its 70-year history.
The most recent talk has been triggered by growing concerns among investors that AI technology may not live up to the hype surrounding it—and that the valuations of many AI-related companies are far too high.
Is this chill in the air a passing breeze or the first hints of an impending Ice Age? A look at past AI winters may help.
For example, there are clear parallels between the hype generated by today’s prominent AI figures and the competing camps working on the technology in the early days of the Cold War.
There are also historical parallels for recent studies suggesting AI isn’t meeting expectations. In 1966, a committee commissioned by the National Research Council issued a damning report concluding that computer-based translation was more expensive, slower, and less accurate than human translation.
You can guess what happened to research funding after that.
There are some key differences between then and now. Most significantly, today’s AI boom is not dependent on public funding—though government entities are becoming important customers.
And unlike in the very first AI winter, when such systems were mostly just research experiments, today’s AI is being widely deployed in businesses and homes.
Three years after ChatGPT’s debut, there are certainly a few autumnal signs here and there. But only time will tell if it is the prelude to a deep freeze in AI investment or a momentary cold-snap before the sun appears again. —Jeremy Kahn
More tech
—Apple AI search tool in development. “World Knowledge Answers” reportedly arrives in the spring.
—Instagram for iPadOS arrives. It only took 15 years, Meta!
—xAI CFO Mike Liberatore departs. He joined Elon Musk’s AI startup in April and reportedly exited in late July.
—Scale AI sues former employee for allegedly stealing trade secrets and sharing them with Mercor.
—Tom Siebel steps down at C3 AI, to be replaced by Stephen Ehikian. The company reported a Q1 revenue drop of 19% from the same period a year ago.
—Streameast shuts down. The world’s largest illegal sports streaming platform is knocked out by Egyptian law enforcement and others.
—Mistral valued at €12B. The French AI firm (of Le Chat fame) is reportedly putting the finishing touches on a €2B investment.
Endstop triggered
Tools & Platforms
Navigating Geopolitical Risk and Technological Indispensability

The global AI chip market is a battleground of geopolitical strategy and technological innovation, with China’s demand for advanced semiconductors emerging as a critical focal point. For investors, the tension between U.S. export restrictions and China’s push for self-reliance creates a paradox: while geopolitical risks threaten to fragment markets, the indispensable nature of cutting-edge AI hardware ensures sustained demand. Nvidia, a leader in AI chip development, finds itself at the center of this dynamic, balancing compliance with its ambition to retain a foothold in China’s $50 billion AI opportunity [2].
Geopolitical Risk: The U.S. Export Control Conundrum
U.S. export restrictions have reshaped the AI chip landscape in China. In Q2 2025, Nvidia reported zero sales of its H20 AI chips to the region, a direct consequence of stringent export controls and the absence of finalized regulatory guidelines for its new licensing agreement [2]. This vacuum has allowed domestic competitors like Cambricon to surge, with the company’s revenue jumping 4,300% in the first half of 2025 [1]. The U.S. government’s 100% tariffs and revocation of VEU licenses have further fragmented global supply chains, compelling firms like AMD and Nvidia to develop lower-performance chips for China while TSMC shifts capital expenditures to the U.S. and Europe [1].
Yet, these restrictions have not eradicated demand for advanced AI hardware. China’s AI industry, supported by state-led investment funds and subsidized compute resources, is projected to grow into a $3–4 trillion infrastructure boom by 2030 [3]. The National Integrated Computing Network, a state-backed initiative, underscores Beijing’s commitment to building a self-sufficient ecosystem [4]. However, bottlenecks persist: limited access to EUV lithography and global supply chain integration remain significant hurdles [4].
Technological Indispensability: The Unmet Need for Performance
Despite China’s strides in self-reliance, the gap between domestic and U.S. semiconductor capabilities remains stark. Companies like Huawei and SMIC are closing this gap—Huawei’s CloudMatrix 384 and SMIC’s 7nm production expansion are notable advancements [1]. However, the performance of these chips still lags behind Nvidia’s Blackwell GPU, which offers unparalleled efficiency for large-scale AI training. This technological disparity has driven Chinese firms like Alibaba to invest in homegrown solutions, including a new AI chip, while still relying on U.S. technology for critical applications [2].
Nvidia’s recent development of the B30 chip—a China-compliant variant of the Blackwell GPU—exemplifies its strategy to navigate these challenges. By adhering to U.S. export restrictions while retaining performance, the B30 aims to secure market access in a landscape where even restricted chips are indispensable [3]. This approach mirrors the broader trend of “compliance-driven innovation,” where firms adapt to geopolitical constraints without sacrificing technological relevance.
Strategic Implications for Investors
For investors, the key lies in assessing how companies balance compliance with innovation. Nvidia’s ability to pivot to the B30 chip highlights its resilience, but the absence of H20 sales in Q2 2025 underscores the fragility of its China strategy [2]. Meanwhile, domestic players like Cambricon and SMIC offer high-growth potential but face long-term challenges in overcoming U.S. export controls and achieving parity with Western rivals [1].
The AI infrastructure boom, however, presents a universal opportunity. As global demand for advanced compute surges, firms that can navigate geopolitical risks—whether through compliance, localization, or hybrid strategies—will dominate. China’s push for self-reliance, while reducing its dependence on U.S. chips, also creates a fertile ground for innovation, with startups like DeepSeek optimizing FP8 formats for local hardware [1].
Conclusion
Nvidia’s experience in China encapsulates the dual forces shaping the AI chip sector: geopolitical risk and technological indispensability. While U.S. export controls have disrupted its access to the Chinese market, the company’s strategic adaptations—such as the B30 chip—demonstrate its commitment to maintaining relevance. For investors, the lesson is clear: the AI race is not just about hardware but about navigating a complex web of policy, innovation, and market dynamics. As China’s self-reliance drive accelerates, the winners will be those who can bridge the gap between compliance and cutting-edge performance.
Source:[1] China’s AI Chip Revolution: The Strategic Imperative and Investment Opportunities in Domestic Semiconductor Leaders [https://www.ainvest.com/news/china-ai-chip-revolution-strategic-imperative-investment-opportunities-domestic-semiconductor-leaders-2508/][2] Alibaba reportedly developing new AI chip as China’s Xi rejects AI’s ‘Cold War mentality’ [https://ca.news.yahoo.com/alibaba-reportedly-developing-ai-chip-123905455.html][3] Navigating Geopolitical Risk in the AI Chip Sector: Nvidia Remains a Strategic Buy Amid Chinese Restrictions [https://www.ainvest.com/news/navigating-geopolitical-risk-ai-chip-sector-nvidia-remains-strategic-buy-chinese-restrictions-2508/][4] Full Stack: China’s Evolving Industrial Policy for AI [https://www.rand.org/pubs/perspectives/PEA4012-1.html]
Tools & Platforms
How AI Can Strengthen Your Company’s Cybersecurity – New Technology

Key Takeaways:
- Using AI cybersecurity tools can help you detect threats
faster, reduce attacker dwell time, and improve your
organization’s overall risk posture.
- Generative AI supports cybersecurity compliance by accelerating
breach analysis, reporting, and regulatory disclosure
readiness.
- Automating cybersecurity tasks with AI helps your business
optimize resources, boost efficiency, and improve security program
ROI.
Cyber threats are evolving fast — and your organization
can’t afford to fall behind. Whether you’re in healthcare, manufacturing, entertainment, or another dynamic industry,
the need to protect sensitive data and maintain trust with
stakeholders is critical.
With attacks growing in volume and complexity, artificial
intelligence (AI) offers powerful support to help you detect
threats earlier, respond faster, and stay ahead of changing
compliance demands.
Why AI Is a Game-Changer in Cybersecurity
Your business is likely facing more alerts and threats than your
team can manually manage. Microsoft reports that companies face
over 600 million cyberattacks daily — far
beyond human capacity to monitor alone.
AI tools can help by automating key aspects of your cybersecurity strategy, including:
- Real-time threat detection: With
“zero-day attack detection”, machine learning identifies
anomalies outside of known attack signatures to flag new threats
instantly.
- Automated incident response: From triaging
alerts to launching containment measures without waiting on human
intervention.
- Security benchmarking: Measuring your defenses
against industry standards to highlight areas for improvement.
- Privacy compliance support: Tracking data
handling and reporting to meet regulatory requirements with less
manual oversight.
- Vulnerability prioritization and patch
management: AI can rank identified weaknesses by severity
and automatically push policies to keep systems up to date.
AI doesn’t replace your team — it amplifies their
ability to act with speed, precision, and foresight.
Practical AI Use Cases to Consider
Here are some ways AI is currently being used in cybersecurity
and where it’s headed next:
1. Summarize Incidents and Recommend Actions
Generative AI can instantly analyze a security event and draft
response recommendations. This saves time, supports disclosure
obligations, and helps your team update internal policies based on
real data.
2. Prioritize Security Alerts More Efficiently
AI triage tools analyze signals from across your environment to
highlight which threats require urgent human attention. This allows
your staff to focus where it matters most — reducing risk and
alert fatigue.
3. Automate Compliance and Reporting
From HIPAA to SEC rules to state-level privacy laws, the
regulatory landscape is more complex than ever. AI can help your
organization map internal controls to frameworks, generate
compliance reports, and summarize what needs to be disclosed
— quickly and accurately.
4. Monitor Behavior and Detect Threats
AI can track user behavior, spot anomalies, and escalate
suspicious actions (like phishing attempts or unauthorized access).
These tools reduce attacker dwell time and flag concerns in seconds
— not weeks or months.
5. The Next Frontier: Autonomous Security
The future of AI in cybersecurity includes agentic systems
— tools capable of acting independently when breaches occur.
For instance, if a user clicks a phishing link, AI could
automatically isolate the device or suspend access.
However, this level of automation must be used carefully. Human
oversight remains essential to prevent overreactions — such
as wiping a laptop unnecessarily. In short, AI doesn’t replace
your human cybersecurity team but augments it — automating
repetitive tasks, spotting hidden threats, and enabling faster,
smarter responses. As the technology matures, your governance
structures must evolve alongside it.
Building a Roadmap and Proving ROI
To unlock the benefits of AI, your business needs a strong data
and governance foundation. Move from defense to strategy by first
assessing whether your current systems can support AI —
identifying gaps in data structure, quality, and access.
Next, define clear goals and ROI metrics. For example:
- How much time does AI save in daily operations?
- How quickly are threats identified post-AI deployment?
- What are the cost savings from prevented incidents?
Begin with a pilot program using an off-the-shelf AI product. If
it shows value, scale into customized prompts or embedded tooling
that fits your specific business systems.
Prompt Engineering to Empower Your Team
Your teams can get better results from AI by using structured
prompts. A well-designed prompt ensures your AI tools deliver
clear, useful, business-ready outputs.
Example prompt:
“Summarize the Microsoft 365 event with ID
‘1234’ to brief executive leadership. Include the event
description, threat level, correlated alerts, and mitigation steps
— in plain language suitable for a 10-minute
presentation.”
This approach supports internal decision-making, board
reporting, and team communication — all essential for
managing cyber risks effectively.
Don’t Wait: Make AI Part of Your Cybersecurity
Strategy
AI is no longer a “nice to have”; it’s a core
component of resilient, responsive cybersecurity programs.
Organizations that act now and implement AI strategically will be
better equipped to manage both today’s threats and
tomorrow’s compliance demands.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general
guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought
about your specific circumstances.
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoThe Guardian view on Trump and the Fed: independence is no substitute for accountability | Editorial
-
Tools & Platforms3 weeks ago
Building Trust in Military AI Starts with Opening the Black Box – War on the Rocks
-

 Ethics & Policy1 month ago
Ethics & Policy1 month agoSDAIA Supports Saudi Arabia’s Leadership in Shaping Global AI Ethics, Policy, and Research – وكالة الأنباء السعودية
-

 Events & Conferences4 months ago
Events & Conferences4 months agoJourney to 1000 models: Scaling Instagram’s recommendation system
-

 Jobs & Careers2 months ago
Jobs & Careers2 months agoMumbai-based Perplexity Alternative Has 60k+ Users Without Funding
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoVEX Robotics launches AI-powered classroom robotics system
-

 Funding & Business2 months ago
Funding & Business2 months agoKayak and Expedia race to build AI travel agents that turn social posts into itineraries
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoHappy 4th of July! 🎆 Made with Veo 3 in Gemini
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoOpenAI 🤝 @teamganassi
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoMacron says UK and France have duty to tackle illegal migration ‘with humanity, solidarity and firmness’ – UK politics live | Politics