Tools & Platforms
5 Extraordinary Things AI Can Do Today
By Richard D. Harroch and Dominique A. Harroch
Artificial intelligence (AI), once confined to speculative science fiction, now permeates nearly every aspect of modern life, achieving feats previously unimaginable. From creating lifelike video impersonations and diagnosing complex diseases to crafting original artistic masterpieces, AI’s rapid advancement challenges conventional boundaries of technology and ethics. Each new development astonishes experts and laypeople alike, highlighting AI’s potential to redefine our collective future while raising critical concerns around accountability, privacy, and the fundamental nature of human creativity and interaction.
Yet, the astonishing capabilities of AI also carry profound ethical implications, prompting essential debates about the responsible use of such powerful technology. As AI increasingly integrates into sectors like healthcare, entertainment, military operations, and personal interactions, it continually forces us to question how much autonomy and trust we should delegate to intelligent machines. This article examines five of the most remarkable—and often controversial—capabilities of artificial intelligence today, exploring not only their impressive achievements but also their broader societal impacts.
Naturally, we have used AI for research assistance in preparing this article.
5 Surprising Capabilities of AI
1. Hyper-Realistic Deepfake Videos
One of AI’s most startling capabilities is creating hyper-realistic deepfake videos. These videos use advanced neural network algorithms to seamlessly alter or generate digital content, convincingly depicting individuals in scenarios that are fake. For instance, the viral deepfake videos of actor Tom Cruise on TikTok illustrate the chilling accuracy with which AI can fabricate reality, deceiving even the most attentive viewers.
While deepfakes have been used for entertainment purposes, such as resurrecting historical figures in movies or creating humorous internet content, they also carry serious risks. Deepfakes can manipulate public opinion, spread misinformation during elections, or facilitate fraud and blackmail, highlighting urgent ethical and regulatory challenges posed by this rapidly advancing technology.
Key Examples:
- Tom Cruise TikTok Deepfakes: The viral @deeptomcruise account created by Chris Umé and actor Miles Fisher featured hyperrealistic videos of “Tom Cruise” doing coin tricks, biting lollipops, and goofing around in clothing stores, accumulating tens of millions of views. Source: TikTok platform
- CNN’s Coverage: Detailed analysis of how these deepfakes led to the creation of Metaphysic company can be found in CNN’s comprehensive report.
- NPR Investigation: Public radio’s examination of deepfake technology and its implications is available at The 1A’s deepfakes segment.
2. Autonomous AI Surveillance Systems
AI-driven surveillance systems represent another remarkable yet controversial innovation, capable of analyzing vast amounts of real-time video footage to monitor public spaces autonomously. These intelligent systems, such as those deployed by Clearview AI, use facial recognition technology to identify individuals within seconds, significantly enhancing law enforcement capabilities and public safety measures.
However, these AI surveillance systems spark intense debate regarding privacy violations, potential misuse, and biases in facial recognition accuracy. Cities worldwide grapple with balancing the undeniable benefits of enhanced security against significant concerns about individual rights, especially in contexts involving mass surveillance and data misuse.
Key Examples:
3. Breakthroughs in Medical Diagnostics
The healthcare industry has benefited tremendously from AI, especially in diagnostics. Google’s DeepMind, IBM Watson Health, and PathAI have pioneered groundbreaking AI systems that can surpass human accuracy in detecting diseases such as cancers, Alzheimer’s disease, and cardiac conditions. For instance, Google’s DeepMind accurately predicts acute kidney injury up to two days earlier than traditional methods, significantly improving patient outcomes and healthcare efficiency.
Despite these promising advancements, AI-driven medical diagnostics raise crucial issues around data privacy, patient consent, and the evolving roles of medical professionals. Striking the right balance between technological innovation and ethical responsibility remains critical as AI continues to reshape healthcare.
Key Examples:
- DeepMind’s Official Research: Google’s detailed explanation of their kidney injury prediction breakthrough is available on their DeepMind blog.
- Nature Scientific Publication: The peer-reviewed research paper documenting the AI system’s 48-hour prediction accuracy is published in the journal Nature.
- Veterans Affairs Partnership: Coverage of the collaboration between Google DeepMind and the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs is detailed in Fierce Healthcare’s report.
4. Original Art, Music, and Literature
AI’s foray into creative arts has astonished the world, as generative models like Midjourney, DALL-E, and GPT-4 produce original paintings, music compositions, poetry, and even novels. For example, AI-generated artwork has been auctioned at major art houses, fetching prices previously reserved for human-created masterpieces. AI programs like AIVA (Artificial Intelligence Virtual Artist) can now compose symphonies that even seasoned musicians find impressive.
This unprecedented level of machine creativity raises significant philosophical and legal questions about authorship, originality, and intellectual property rights. As AI-generated content becomes more prevalent, society must redefine traditional artistic and legal frameworks to accommodate and regulate this emerging digital creativity.
Key Examples:
5. Conversational AI That Mimics Human Emotions
Conversational AI platforms such as Replika and Character.ai have evolved remarkably, and are now capable of simulating human emotions and providing empathetic, personalized responses. These AI companions serve as emotional support systems, assisting individuals coping with loneliness, anxiety, and depression. Their ability to understand and respond to nuanced emotional cues makes the interactions surprisingly realistic and meaningful.
While beneficial for mental health and emotional support, the authenticity of these interactions raises important ethical concerns about dependency, privacy, emotional manipulation, and data security. Ensuring users’ emotional well-being while protecting their privacy remains a complex but essential task.
Key Examples:
- Replika Platform: The leading AI companion app can be accessed at Replika.com, with detailed information about its capabilities available in their official guide and on the App Store.
- Academic Research: Scientific studies on user experiences with Replika’s emotional support capabilities have been published, including research examining how users receive social support from companion chatbots in everyday contexts. Source: PMC/National Center for Biotechnology Information
- Ethical Concerns Investigation: The Conversation’s in-depth analysis of emotional attachment to AI companions and the ethical questions they raise is available in their article “I tried the Replika AI companion and can see why users are falling hard”.
Conclusion on AI Breakthroughs
As AI technology continues to advance at an unprecedented pace, it is crucial for society to approach these innovations thoughtfully and responsibly. The remarkable capabilities of AI carry transformative potential, but they must be managed ethically and transparently to ensure that they enhance human life and foster trust rather than undermine societal values or individual freedoms.
Related Articles:
About the Authors
Dominique A. Harroch is the Chief of Staff at AllBusiness.com. She has been the Chief of Staff or Operations Leader for multiple companies where she leveraged her extensive experience in operations management, strategic planning, and team leadership to drive organizational success. With a background that spans over two decades in operations leadership, event planning at her own start-up and marketing at various financial and retail companies. Dominique is known for her ability to optimize processes, manage complex projects and lead high-performing teams. She holds a BA in English and Psychology from U.C. Berkeley and an MBA from the University of San Francisco. She can be reached via LinkedIn.
Richard D. Harroch is a Senior Advisor to CEOs, management teams, and Boards of Directors. He is an expert on M&A, venture capital, startups, and business contracts. He was the Managing Director and Global Head of M&A at VantagePoint Capital Partners, a venture capital fund in the San Francisco area. His focus is on internet, digital media, AI and technology companies. He was the founder of several Internet companies. His articles have appeared online in Forbes, Fortune, TIME, MSN, Yahoo, Fox Business and AllBusiness.com. Richard is the author of several books on startups and entrepreneurship as well as the co-author of Poker for Dummies and a Wall Street Journal-bestselling book on small business. He is the co-author of a 1,500-page book published by Bloomberg on mergers and acquisitions of privately held companies. He was also a corporate and M&A partner at the international law firm of Orrick, Herrington & Sutcliffe. He has been involved in over 200 M&A transactions and 250 startup financings. He can be reached through LinkedIn.
Copyright (c) by Richard D. Harroch. All rights reserved.
Tools & Platforms
AI stethoscope could detect heart conditions in seconds
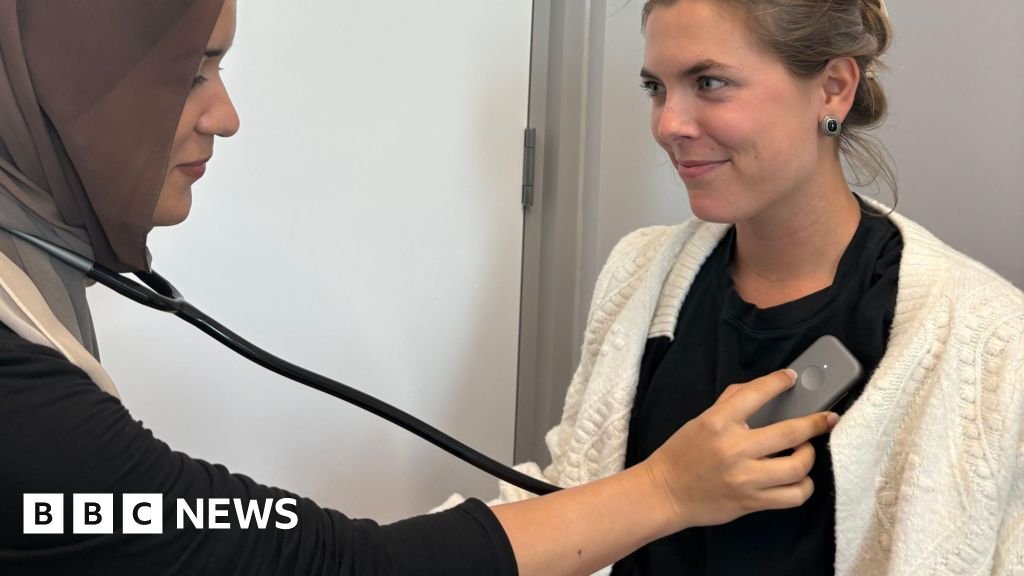
Stethoscopes powered by artificial intelligence (AI) could help detect three different heart conditions in seconds, researchers say.
The original stethoscope, invented in 1816, allows doctors to listen to the internal sounds of a patient’s body.
But now a British team have designed one that can spot heart failure, heart valve disease and abnormal heart rhythms almost instantly.
The breakthrough AI-powered tool could be a “real game-changer” resulting in patients being treated sooner, the researchers say, with plans to roll the device out across the country.
The new device replaces the traditional chest piece with a device around the size of a playing card. It uses a microphone to analyse subtle differences in heartbeat and blood flow that the human ear cannot detect.
The study by Imperial College London and Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust involved more than 200 GP surgeries in London.
More than 12,000 patients from 96 surgeries were examined with the AI stethoscope and were then compared to patients from 109 GP surgeries where the technology was not used.
Those examined with the device were 2.33 times more likely to be diagnosed with heart failure in the next 12 months, researchers said.
Abnormal heartbeat patterns, which have no symptoms but can increase stroke risk, were 3.5 times more detectable with the AI stethoscopes, while heart valve disease was 1.9 times more detectable.
Dr Sonya Babu-Narayan, clinical director at the British Heart Foundation (BHF) and consultant cardiologist, said: “This is an elegant example of how the humble stethoscope, invented more than 200 years ago, can be upgraded for the 21st century”.
Such innovations are vital “because so often this condition is only diagnosed at an advanced stage when patients attend hospital as an emergency”, she said.
“Given an earlier diagnosis, people can access the treatment they need to help them live well for longer.”
The findings have been presented to thousands of doctors at the European Society of Cardiology annual congress in Madrid, the world’s largest heart conference.
There are plans to roll out the new stethoscopes to GP practices in Wales, south London and Sussex.
Tools & Platforms
Taco Bell is having second thoughts about relying on AI at the drive-through

Taco Bell’s chief digital officer says the company is having an “active conversation” about when to use and not to use AI.
The company has apparently rolled out voice AI-powered ordering at more than 500 drive-throughs, leading to unflattering viral moments like someone ordering 18,000 water cups in order to “bypass” the AI and get connected to a human server.
Chief Digital and Technology Officer Dane Matthews told The Wall Street Journal that even he has mixed experiences with technology: “Sometimes it lets me down, but sometimes it really surprises me.”
Overall, it sounds like Taco Bell is still deciding how broadly to deploy AI at the drive-through, with leeway for different franchisees to do things their own way. For example, rather than relying on AI exclusively, Matthews said it might make sense to have a human handle drive-through orders at busy restaurants with long lines.
“For our teams, we’ll help coach them: at your restaurant, at these times, we recommend you use voice AI or recommend that you actually really monitor voice AI and jump in as necessary,” he said.
Tools & Platforms
Why Alibaba AI chip launch rattles Wall Street tech giants
Chinese tech giant’s semiconductor move triggers selloff in American AI leaders
Wall Street woke up from its Labor Day weekend to an uncomfortable reality check. While American traders were enjoying their extended holiday, Chinese tech giant Alibaba dropped a bombshell that sent shockwaves through the AI sector — the launch of its own advanced artificial intelligence chip designed to compete directly with American semiconductor leaders.
The market’s reaction was swift and telling. Stock futures tumbled as investors suddenly faced the prospect that America’s dominance in the AI chip space might not be as unshakeable as they’d assumed. Nvidia, the poster child of the AI boom whose stock has soared over the past two years, saw its shares decline in premarket trading as reality set in.
The end of the AI monopoly
For months, Wall Street has operated under the assumption that American companies like Nvidia, AMD and Intel would continue to dominate the AI chip landscape without serious competition. That comfortable narrative just got a lot more complicated. Alibaba’s new chip, specifically designed for cloud computing and generative AI applications, represents more than just another product launch — it signals China’s determination to break free from dependence on U.S. technology.
This isn’t happening in isolation. Huawei and other Chinese firms are also pushing hard into semiconductor development, creating a competitive environment that American companies haven’t had to navigate before. The cozy dominance that allowed for premium pricing and massive profit margins is beginning to face real challenges.
Geopolitics meets market reality
The timing of Alibaba’s announcement couldn’t be more pointed. Washington’s restrictions on advanced semiconductor exports to China, implemented citing national security concerns, have essentially forced Chinese companies to develop their own alternatives. What was intended as a protective measure for American interests may have accelerated the very competition it sought to prevent.
Chinese firms now have powerful incentives to create homegrown solutions, and they’re backed by significant government resources and a massive domestic market to test and refine their products. Alibaba’s chip gives the company a potential competitive edge within China’s huge market while positioning it to challenge American dominance globally.
Market expectations vs reality
The selloff reflects more than just concern about a single competitor. It reveals how stretched valuations in the AI sector had become, built on assumptions of continued American dominance that may not hold up. One market strategist captured the sentiment perfectly, noting that the market had been priced for near-perfect execution from U.S. chipmakers, making any credible competition a significant threat to those expectations.
Futures for major indices all moved lower as investors reassessed growth projections that suddenly seemed overly optimistic. The Dow Jones, S&P 500 and Nasdaq all reflected this cautious sentiment as traders returned from the holiday weekend.
Beyond the immediate panic
While the market reaction was dramatic, some analysts argue the fears may be overblown. American companies still maintain significant advantages in chip design, global adoption and established relationships with major technology companies. The infrastructure supporting AI development — from data centers to software platforms — continues growing rapidly, suggesting sustained demand for semiconductor solutions.
However, the market’s response indicates that investors are beginning to brace for a more competitive landscape where growth comes harder and profit margins face pressure from international rivals.
The broader implications
This development marks a potential inflection point for the AI sector that has driven much of the stock market’s gains over the past year. As the technology matures and competition intensifies, the days of explosive, unchallenged growth may be ending.
The question now becomes whether American semiconductor companies can maintain their momentum while facing legitimate competition from well-funded Chinese rivals. Much depends on how U.S.-China tensions evolve and whether domestic demand can offset lost opportunities in international markets.
Alibaba’s chip launch forces investors to confront an uncomfortable truth: the AI revolution won’t remain an American monopoly forever. The market is finally pricing in that reality, and the adjustment process is just beginning.
-
Tools & Platforms3 weeks ago
Building Trust in Military AI Starts with Opening the Black Box – War on the Rocks
-

 Ethics & Policy1 month ago
Ethics & Policy1 month agoSDAIA Supports Saudi Arabia’s Leadership in Shaping Global AI Ethics, Policy, and Research – وكالة الأنباء السعودية
-

 Events & Conferences3 months ago
Events & Conferences3 months agoJourney to 1000 models: Scaling Instagram’s recommendation system
-

 Jobs & Careers2 months ago
Jobs & Careers2 months agoMumbai-based Perplexity Alternative Has 60k+ Users Without Funding
-

 Funding & Business2 months ago
Funding & Business2 months agoKayak and Expedia race to build AI travel agents that turn social posts into itineraries
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoVEX Robotics launches AI-powered classroom robotics system
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoHappy 4th of July! 🎆 Made with Veo 3 in Gemini
-

 Podcasts & Talks2 months ago
Podcasts & Talks2 months agoOpenAI 🤝 @teamganassi
-

 Jobs & Careers2 months ago
Jobs & Careers2 months agoAstrophel Aerospace Raises ₹6.84 Crore to Build Reusable Launch Vehicle
-

 Mergers & Acquisitions2 months ago
Mergers & Acquisitions2 months agoDonald Trump suggests US government review subsidies to Elon Musk’s companies